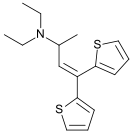
Diethylthiambutene
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
86-14-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 6833 |
| DrugBank |
DB01533 |
| ChemSpider |
6572 |
| UNII |
2Z91X9052O |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL2106573 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H21NS2 |
| Molar mass | 291.477 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Melting point | 152 to 153 °C (306 to 307 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Diethylthiambutene (Thiambutene, Themalon, Diethibutin, N,N-Diethyl-1-methyl-3,3-di-2-thienylallylamine) is an opioid analgesic drug developed in the 1950s[1] which was mainly used as an anesthetic in veterinary medicine and continues, along with the other two thiambutenes dimethylthiambutene and ethylmethylthiambutene to be used for this purpose, particularly in Japan.[2][3] It is now under international control under Schedule I of the UN Single Convention On Narcotic Drugs 1961, presumably due to high abuse potential, although little more information is available. It is listed under Schedule I of the US Controlled Substances Act as a Narcotic and has an ACSCN of 9616 with zero annual manufacturing quota as of 2013.
References
- ↑ BECKETT AH, CASY AF, HARPER NJ, PHILLIPS PM. Analgesics and their antagonists: some steric and chemical considerations. II. The influence of the basic group on physico-chemical properties and the activity of methadone and thiambutene-type compounds. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 1956 Nov;8(11):860-73.
- ↑ Hayes MJ. The use of thiambutene hydrochloride. The Veterinary Record. 1968 Nov 16;83(20):528.
- ↑ Harbison WD, Slocombe RF, Watts SJ, Stewart GA. Thiambutene and acepromazine as analgesic and preanaesthetic agents in horses and sheep. Australian Veterinary Journal. 1974 Dec;50(12):543-6.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/24/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.