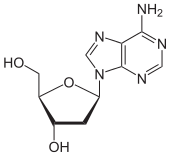
Deoxyadenosine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-(6-Aminopurin-9-yl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-ol | |
| Other names
2'-Deoxyadenosine; α-Deoxyadenosine; dA | |
| Identifiers | |
| 958-09-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:17256 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL416340 |
| ChemSpider | 13135 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.262 |
| 5109 | |
| MeSH | 2'-deoxyadenosine |
| PubChem | 636 |
| UNII | P582C98ULC |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H13N5O3 | |
| Molar mass | 251.24192 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Deoxyadenosine (symbol dA or dAdo) is a deoxyribonucleoside. It is a derivative of the nucleoside adenosine, differing from the latter by the replacement of a hydroxyl group (-OH) by hydrogen (-H) at the 2' position of its ribose sugar moiety. Deoxyadenosine is the DNA nucleoside A, which pairs with deoxythymidine (T) in double-stranded DNA.
In absence of adenosine deaminase (ADA) it accumulates in T lymphocytes and kills these cells resulting in a genetic disorder known as adenosine deaminase severe combined immunodeficiency disease (ADA-SCID).[1]
See also
- Deoxyribonucleotide
- Cordycepin (3'-deoxyadenosine)
- Severe combined immunodeficiency
References
- ↑ Griffiths, Anthony J. F.; Wessler, Susan R.; Carroll, Sean B.; Doebly, John (2012). Introduction to Genetic Analysis (10th ed.). New York: W . H. Freeman and Company. ISBN 1-4641-0661-4.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/1/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.