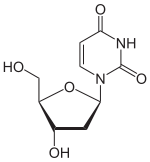
Deoxyuridine
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| 951-78-0 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:16450 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL353955 |
| ChemSpider | 13118 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.232 |
| MeSH | Deoxyuridine |
| PubChem | 640 |
| UNII | W78I7AY22C |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H12N2O5 | |
| Molar mass | 228.202 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Deoxyuridine (dU) is a compound and a nucleoside. It is similar in chemical structure to uridine, but without the 2'-hydroxyl group.
Idoxuridine and Trifluridine are variants of deoxyuridine used as antiviral drugs. They are similar enough to be incorporated as part of DNA replication, but they possess side groups on the uracil component (an iodine and a CF3 group, respectively), that prevent base pairing.
A known use of dU is as a precursor in the synthesis of Edoxudine.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/22/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.