Moiety (chemistry)
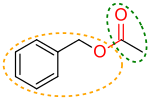
Benzyl acetate has an ester functional group (in red), an acetyl moiety (circled with dark green) and a benzyloxy moiety (circled with light orange). Other divisions can be made.
In organic chemistry moiety (/ˈmɔɪəti/) is a term used for part of a molecule.[1] Larger moieties are often functional groups.[2]
A functional group is a moiety that participates in similar chemical reactions in most molecules that contain it.[3] In turn the parts of the group are termed moieties. For example, methyl p-hydroxybenzoate contains a phenol functional group within the acyl moiety, which in turn is part of the paraben moiety.
Moieties that are branches extending from the backbone of a hydrocarbon molecule, which can often be broken off and substituted with others, are called substituents or side chains.
See also
References
- ↑ "moiety". IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology (the "Gold Book") (2 ed.). Blackwell Scientific Publications. 2014-02-24. doi:10.1351/goldbook.M03968. ISBN 0-9678550-9-8.
- ↑ Mezey, P. G. (October 1996). "Functional Groups in Quantum Chemistry". Advances in Quantum Chemistry. 27: 165. ISBN 978-0-08-058252-8.
- ↑ "functional group". IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology (the "Gold Book") (2 ed.). Blackwell Scientific Publications. 2014-02-24. doi:10.1351/goldbook.F02555. ISBN 0-9678550-9-8.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/20/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.