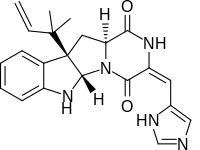
Roquefortine C
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| 58735-64-1 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 10246629 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H23N5O2 | |
| Molar mass | 389.5 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid |
| Soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF or DMSO | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Roquefortine C is a mycotoxin that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines[1] produced by various fungi, particularly species from the Penicillium genus.[2] It was first isolated from a strain of Penicillium roqueforti, a species commercially used as a source of proteolytic and lipolytic enzymes during maturation of the blue-veined cheeses, Roquefort, Danish Blue, Stilton and Gorgonzola.
Roquefortine C is a cyclodipeptide mycotoxin derived from the diketopiperazine cyclo(Trp-dehydro-His) and is a relatively common fungal metabolite produced by a number of Penicillium species. It is also considered as one of the most important fungal contaminants of carbonated beverages, beer, wine, meats, cheese and bread.[3] At high doses roquefortine C is classified as a toxic compound.[4] Although it is a potent neurotoxin [5][6] at high doses, at low concentrations of 0.05 to 1.47 mg/kg that occur in domestic cheeses, it was found to be "safe for the consumer".[7] The mechanisms underlying its toxicity and metabolism have been investigated by studying its interaction with mammalian Cytochrome P450.[4] In addition to these toxic properties, roquefortine C reportedly possesses bacteriostatic activity against gram-positive bacteria,[8] but only in those organisms containing haemoproteins.[4][9]
Roquefortine C contains the unusual E-dehydrohistidine moiety, a system that typically undergoes facile isomerization under acidic, basic, or photochemical conditions to isoroquefortine C, the 3,12 double-bond Z-isomer of roquefortine C.[10]
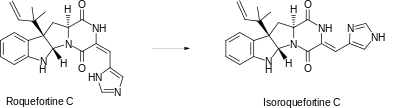
However isoroquefortine C is not a natural product and in contrast to roquefortine C does not bind iron. Both have been synthesised.[10]
Related compounds
References
- ↑ Borthwick AD (2012). "2,5-Diketopiperazines: Synthesis, Reactions, Medicinal Chemistry, and Bioactive Natural Products". Chemical Reviews. 112 (7): 3641–3716. doi:10.1021/cr200398y. PMID 22575049.
- ↑ Kokkonen M, Jestoi M, Rizzo A (2005). "The effect of substrate on mycotoxin production of selected Penicillium strains". International Journal of Food Microbiology. 99 (2): 207–14. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.08.014. PMID 15734568.
- ↑ Borthwick AD, Da Costa NC (January 2015). "2,5-Diketopiperazines in Food and Beverages: Taste and Bioactivity". Critical reviews in food science and nutrition. doi:10.1080/10408398.2014.911142. PMID 25629623.
- 1 2 3 Aninat C, Hayashi Y, André F, Delaforge M (July 2001). "Molecular requirements for inhibition of cytochromes P450 activities by roquefortine". Chemical research in toxicology. 14 (9): 1259–1265. doi:10.1021/tx015512l. PMID 11559041.
- ↑ SCBT. "Roquefortine - A potent neurotoxin produced most notably by Penicillium species".
- ↑ EPA. "Penicillium roqueforti Final Risk Assessment".
- ↑ Finoli C, Vecchio A, Galli A, Dragoni I. "Roquefortine C occurrence in blue cheese.". PMID 11271775.
- ↑ Kopp-Holtwiesche B, Rehm HJ (December 1989). "Antimicrobial action of roquefortine". Journal of environmental pathology, toxicology and oncology: official organ of the International Society for Environmental Toxicology and Cancer. 10 (1-2): 41–44. PMID 2231314.
- ↑ Aninat C, Andre F, Delaforge M (April 2005). "Oxidative metabolism by P450 and function coupling to efflux systems: modulation of mycotoxin toxicity". Food additives and contaminants. 22 (4): 361–368. doi:10.1080/02652030500073287. PMID 16019806.
- 1 2 Shangguan N, Hehre WJ, Ohlinger WS, Beavers MP, Joullie MM (April 2008). "The total synthesis of roquefortine C and a rationale for the thermodynamic stability of isoroquefortine C over roquefortine C". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 130 (19): 6281–6287. doi:10.1021/ja800067q. PMID 18412344.