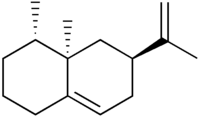
Aristolochene
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(4S,4aR,6S)-6-Isopropenyl-4,4a-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-1H-naphthalene | |
| Other names
(+)-Aristolochene | |
| Identifiers | |
| 123408-96-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:43445 |
| ChemSpider | 570881 |
| PubChem | 656496 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H24 | |
| Molar mass | 204.36 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.894 g/ml |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Aristolochene is a bicyclic sesquiterpene produced by certain fungi including the cheese mold Penicillium roqueforti. It is biosynthesized from farnesyl pyrophosphate by aristolochene synthase and is the parent hydrocarbon of a large variety of fungal toxins.[1]
The substance was first isolated from Penicillium roqueforti, a fungus used to make blue cheeses like Roquefort, Danish Blue, Stilton cheese and Gorgonzola.
Aristolochene is a precursor to the toxin known as PR toxin, made in large amounts by Penicillium roqueforti.[2] PR-toxin has been implicated in incidents of mycotoxicoses resulting from eating contaminated grains.[3]
Related Compounds
References
- ↑ Terpene Biosynthesis Archived February 25, 2007, at the Wayback Machine., Chem 549, College of Pharmacy, University of Arizona
- ↑ Proctor RH, Hohn TM (February 1993). "Aristolochene synthase. Isolation, characterization, and bacterial expression of a sesquiterpenoid biosynthetic gene (Ari1) from Penicillium roqueforti". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (6): 4543–8. PMID 8440737. Retrieved 2008-12-03.
- ↑ Chen FC, Chen CF, Wei RD (1982). "Acute toxicity of PR toxin, a mycotoxin from Penicillium roqueforti". Toxicon. 20 (2): 433–41. doi:10.1016/0041-0101(82)90006-X. PMID 7080052. Retrieved 2008-12-03.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/15/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.