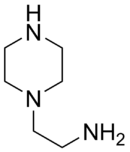
Aminoethylpiperazine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Piperazin-1-ylethanamine | |
| Other names
2-(1-Piperazinyl)ethylamine, AEP, N-AEP, N-(2-Aminoethyl)piperazine, 2-Piperazinoethylamine, 1-(2-Aminoethyl)piperazine, 1-Piperazine ethanamine, 1-Aminoethylpiperazine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 140-31-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL209790 |
| ChemSpider | 8465 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.920 |
| EC Number | 205-411-0 |
| PubChem | 8795 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H15N3 | |
| Molar mass | 129.21 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless to yellowish liquid |
| Density | 0.984 g/cm3 at 20 °C |
| Melting point | −19 °C (−2 °F; 254 K) |
| Boiling point | 222 °C (432 °F; 495 K) |
| Fully miscible | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.076 mmHg @ 20 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | harmful, corrosive, sensitizing |
| R-phrases | R21 R22 R43 R52 R53 |
| S-phrases | S26 S36 S37 S39 S45 S61 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 93 °C (199 °F; 366 K) |
| 315 °C (599 °F; 588 K) | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Aminoethylpiperazine is a derivative of piperazine. This ethyleneamine contains one primary, secondary and tertiary nitrogen atom. It is a corrosive liquid and can cause second or third degree burns. Aminoethylpiperazine can also cause pulmonary edema as a result of inhalation. Uses include inhibition of corrosion, epoxy curing, surface activation, and as an asphalt additive.
See also
External links
- Catalytic method for the conjoint manufacture of N-aminoethylpiperazine
- Safety MSDS Data
- Safety data sheet
- Data sheet
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/11/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
