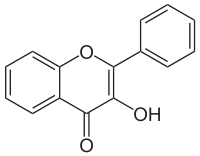
3-Hydroxyflavone
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-hydroxy-2-phenylchromen-4-one | |
| Other names
3-Hydroxyflavone Flavon-3-ol 3-HF 3-Hydroxy-2-phenylchromone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 577-85-5 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:5078 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL294009 |
| ChemSpider | 10871 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.562 |
| KEGG | C01495 |
| PubChem | 11349 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 238.23 g/mol |
| Density | 1.367 g/mL |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
3-Hydroxyflavone is a chemical compound. It is the backbone of all flavonols, a type of flavonoid. It is a synthetic compound, which is not found naturally in plants. It serves as a model molecule as it possesses an excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) effect[1] to serve as a fluorescent probe to study membranes for example[2] or intermembrane proteins.[3] The green tautomer emission (λmax ≈ 524 nm) and blue-violet normal emission (λmax ≈ 400 nm) originate from two different ground state populations of 3HF molecules.[4] The phenomenon also exists in natural flavonols. Although 3-hydroxyflavone is almost insoluble in water, its aqueous solubility (hence bio-availability) can be increased by encapsulation in cyclodextrin cavitiies [5]
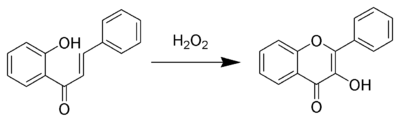
Synthesis
The Algar-Flynn-Oyamada reaction is a chemical reaction whereby a chalcone undergoes an oxidative cyclization to form a flavonol.
References
- ↑ All-optical switchings of 3-hydroxyflavone in different solvents. Wu Feng, Lin Lie, Li Xiang-Ping, Yu Ya-Xin, Zhang Gui-Lan and Chen Wen-Ju, Chinese Phys. B 17 1461-1466.
- ↑ Excited state proton transfer fluorescence of 3-hydroxyflavone in model membranes. Jayanti Guharay , Rupali Chaudhuri , Abhijit Chakrabarti and Pradeep K. Sengupta, Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, Volume 53, Issue 3, March 1997, Pages 457-462
- ↑ Interaction of flavonoids with red blood cell membrane lipids and proteins: Antioxidant and antihemolytic effects. Sudip Chaudhuri, Anwesha Banerjee, Kaushik Basu, Bidisha Sengupta, and Pradeep K. Sengupta, International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, Volume 41, Issue 1, 1 June 2007, Pages 42-48
- ↑ Effect of reverse micelles on the intramolecular excited state proton transfer (ESPT) and dual luminescence behaviour of 3-hydroxyflavone. Munna Sarkar, Jayanti Guha Ray and Pradeep K. Sengupta, Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, Volume 52, Issue 2, February 1996, Pages 275-278
- ↑ Encapsulation of 3-hydroxyflavone in γ-cyclodextrin nanocavities: Excited state proton transfer fluorescence and molecular docking studies. Biswapathik Pahari, Sandipan Chakraborty, Pradeep K. Sengupta.Journal of Molecular Structure, Volume 1006, Issues 1–3, 14 December 2011, Pages 483–488