WAVE regulatory complex
The WAVE regulatory complex (WRC) is a five-subunit protein complex in the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) family involved in the formation of the actin cytoskeleton through interaction with the Arp2/3 complex. The holocomplex comprises WAVE1 (also known as WASF1), CYFIP1, Abi2, Nap1 and HSPC300 in its canonical form, or orthologues of these.[1]
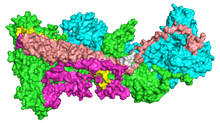
Composition
The proteins within the WRC form a CYFIP1-Nap1 heterodimer and a WAVE1-Abi2-HSPC300 heterotrimer,[1][2] and following interaction with Rac1, the holocomplex has been observed in a CYFIP1-Nap1-Abi2 heterotrimer subcomplex and an active WAVE1-HSPC300 heterodimer subcomplex.[3]
Function
The WRC is activated by interaction with the Rac1 (via the CYFIP1 component of the complex) and Arf small GTPases,[1][2] which causes dissociation of the CYFIP1-Nap1-Abi2 heterotrimer at the membrane periphery.[3] This allows the V domain of the WAVE1 component to interact with the actin monomers while its CA domain interacts with the Arp2/3 complex, allowing the Arp2/3 complex to act as a nucleation core for the branching and extension of actin filaments.
References
- 1 2 3 Chen, Zhucheng; Borek, Dominika; Padrick, Shae B.; Gomez, Timothy S.; Metlagel, Zoltan; Ismail, Ayman M.; Umetani, Junko; Billadeau, Daniel D.; Otwinowski, Zbyszek; Rosen, Michael K. (25 November 2010). "Structure and control of the actin regulatory WAVE complex". Nature. 468 (7323): 533–538. doi:10.1038/nature09623. PMID 21107423.
- 1 2 Koronakis, V.; Hume, P. J.; Humphreys, D.; Liu, T.; Horning, O.; Jensen, O. N.; McGhie, E. J. (15 August 2011). "WAVE regulatory complex activation by cooperating GTPases Arf and Rac1". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 108 (35): 14449–14454. doi:10.1073/pnas.1107666108.
- 1 2 Abekhoukh, Sabiha; Bardoni, Barbara (27 March 2014). "CYFIP family proteins between autism and intellectual disability: links with Fragile X syndrome". Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 8. doi:10.3389/fncel.2014.00081.