Vogtland
| County of Vogtland, County of Greiz | |||||
| Vögte von Weida, Gera und Plauen → terra advocatorum (lat) → Voigtland (de) Královský Rychtář (cs) | |||||
| State of the Holy Roman Empire | |||||
| |||||
|
| |||||
 The location of the Vogtland, against modern German Land boundaries | |||||
| Capital | Weida (Osterburg), Gera, Plauen | ||||
| Languages | "Vogtländisch" (East Franconian German, North Bavarian) | ||||
| Government | Principality | ||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||
| • | Established | 11th century | |||
| • | Bohemian protectorate | 1327 | |||
| • | Land exchange with Margraviate of Meissen |
1357 | |||
| • | Power struggles with Electorate of Saxony |
fourteenth–sixteenth centuries | |||
| • | Restored to Vögte after Battle of Mühlberg |
1547 | |||
| • | Annexed to Saxony | 1563 | |||
Vogtland (German pronunciation: [ˈfoːktlant],[1][2] Czech: Fojtsko) is a region reaching across the German free states of Bavaria, Saxony and Thuringia and into the Czech Republic (north-western Bohemia). It overlaps with and is largely contained within Euregio Egrensis. The name alludes to the former leadership by the Vögte (approximately "advocates" or "lords protector") of Weida, Gera and Plauen.
Nowadays Vogtland also serves as a common colloquial abbreviation for Vogtlandkreis.
Geography
Natural geography
The landscape of the Vogtland is sometimes referred to as idyllic, bearing in mind its fields, meadows and wooded hilltops. In the south and southeast, Vogtland rises to a low or mid-height mountain range also called Oberes Vogtland, or Upper Vogtland. Here, monocultural coniferous forest is the predominant form of vegetation. The Vogtland's highest mountain is Schneehübel, reaching 974 metres, another remarkable landmark is the Schneckenstein, 883m above sea level, which gained some renown for its (falsely alleged) unique abundance of topaz crystals. Its mountains spread from Erzgebirge in the south-east to Fichtelgebirge in the south-west, some peaks also belonging to Elstergebirge.
Neighboring regions are Frankenwald, Erzgebirge, Thüringer Schiefergebirge (Thuringian Slate Mountains) and Fichtelgebirge. The south-eastern part of the Vogtland belongs to Naturpark Erzgebirge/Vogtland, a protected area comparable to a national park.
In its northern part, which averages around 250m above sea level, the landscape is marked by several river valleys, as the Weiße Elster, the Zwickauer Mulde and the Göltzsch have their spring in the Vogtland, while the Saale flows through Bavaria and Thuringia in the west of Vogtland.
Cultural geography

The river valley geography in Vogtland's north made it necessary to build comparatively big bridges to channel railroad and automobile traffic streams. Especially famous is the Göltzsch Viaduct for being the world's largest bridge built of bricks and her "little sister", the Elster Viaduct. Both of them are in use as railroad bridges closing the gap between Dresden and Nuremberg.
As road bridges are concerned, the major bridges forming part of the A 72 near Hof, Pirk and Weißensand are the most important ones, while one urban bridge poses as a rarity: The Syratalviaduct is Europe's biggest mono-arch bridge made of chunked natural stone - to be found in Plauen, commonly called Friedensbrücke.
Integral part of the Vogtland landscape are its reservoirs, the shores of which mostly are popular holiday and camping destinations.
Plauen, the largest town, is known as the "capital of the Vogtland" or, with a proud note, as "Vogtlandmetropolis". Other towns of regional significance are:
In Saxony:
In Thuringia:
In Bavaria:
In the Czech Republic:
History

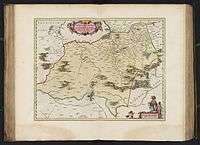
The larger settlemental region surrounding Gera has been recorded in documents as early as the year 1000. It is thought to have been inhabited since late 7th or early 8th century by Slavic Settlers who tribally belonged to the Sorbs. Large portions of the Vogtland, however, were still covered with pristine forests and were not settled before the High Middle Ages, especially until the period called Deutsche Ostsiedlung. Those settlers arrived mainly in eleventh and twelfth centuries, ethnically being Slavic or German, coming from areas of traditionally older settlement like Franconia, Thuringia and Saxony. Even today this can be traced along lines dividing dialectal areas, providing linguistic differences at close distances of settlement while demonstrating peculiar commonalities with varieties spoken in more distant regions of Germany. For instance, in a number of villages of the upper Vogtland even nowadays a dialect is spoken similar to that in Oberpfalz (/ou/ sounds instead of /u:/ as in Kou (en. cow) etc.).
The place name Vogtland (formerly also known as Voigtland, terra advocatorum) originates in the rule of the Vogts in this region from the eleventh to the sixteenth century A.D., specifically in reference to the Vogts of Weida, Gera and Plauen. In the 12th century, Kaiser Barbarossa appointed the first Vogts as administrators of his imperial forest areas in the East to facilitate his rule. Their headquarters was the Osterburg at Weida, thus giving it the reputation as the cradle of the Vogtland. Among the privileges of the Vogts were the endowment over minerals still unextracted from the ground (Bergregal) and the entitlement to regulating mint and coinage affairs (Münzregal), which were both handed down to them by Kaiser Frederick II in 1232.
As in the 14th century claims to power by the Margraves of Meißen emerged, Heinrich von Plauen submitted to the tenure-based regnancy of the Bohemian Crown, excepting only the dominion of Voigtsberg, that stayed tenured to the Reich. In 1349, his equinomic son Heinrich also handed Voigtsberg over to Bohemian tenure; thus the whole Vogtland had become a Reichsafterlehn (a specific status of tenure). In 1357 an exchange of territories was agreed with by the Margraviate of Meißen, effectually making Wiedersberg, Liebau, Adorf, Pausa, Neuenkirchen and Hirschberg (among others) Meißenian while Borna, Geithein and Kohren were handed to the Vogt. The exchange was heavily disputed by branch line cousins of Heinrichs. The Lords of Plauen, as they called themselves, retrieved Auerbach, Pausa and Liebau as Meißenian tenure in 1379. Since 1426 the Lords of Plauen were Burggrafs of Meißen and found themselves in constant power struggles with the Saxonian Kurfürsts.
King George of Podiebrad took the burning of the royal castle of Graslitz due to fights between Heinrich II of Plauen and his enemies to be an occasion to withdraw his tenure and have the Vogtland occupied by Ernest in 1466. Heinrich II von Plauen had fallen into disgrace with him for his open opposition against nobility. Thus, Ernest received tenure over the Vogtland which, at the occasion of the Leipziger Teilung in 1485, was transferred to the House of Ernest while keeping the Bergregal under joint control. In 1547, after the Battle of Mühlberg, the Ernestines forfeited the tenure over the Vogtland and Kaiser Ferdinand I handed it down to his Chancellor Heinrich IV von Plauen, making Maurice, Elector of Saxony co-tenant to the Vogtland tenure. Heinrich V and Heinrich VI could not settle up their debts towards Augustus, Elector of Saxony. Due to arrears in Tithe and other liabilities the Brothers impawned the Vogtland to Kursachsen in 1559.
With Heinrich VI the rule of the Vogts of Plauen over the Vogtland ended, as he could not redeem the pawn any more. In 1566, Augustus acquired the office and towns of Voigtsberg, Oelsnitz, Plauen and Pausa. Matters were furtherly resettled in 1657, among other transactions assigning office over Plauen, Voigtsberg and Pausa to the Duchy of Saxe-Zeitz while schriftsässige Rittergüter and the town of Schöneck remained in Kursaxon possession. In 1718, after the Duchy of Saxe-Zeitz line had vanquished, the areas in concern reverted to Kursachsen. Asides from the Kursaxonian share, the forests around Auerbach and Schöneck remained an exceptional area being both Kursaxonian and ducal at the same time.
Transportation and infrastructure
Two major motorways (A 72 and A 9) serve the Vogtland with connection to the surrounding regions and cities. Providing connections locally within the region and beyond state and national borders, Vogtlandbahn is a private railway company which operates the Vogtland Express. Vogtlandbahn services includes direct connections to Leipzig, Regensburg and Berlin independently from Deutsche Bahn and cooperates with Bohemian (Czech) railway company Viamont as well as with Bavaria-based Alex train services to provide further connections to Munich, Prague and further destinations of note in Euregio Egrensis and beyond. There is a bus service that runs from Vogtland to Berlin.
While the European Union develops into a Europe of Regions, Vogtland could experience an increase of significance for transiting traffic and tourism for the region of Euregio Egrensis, independently from the political meaning of Vogtlandkreis.
See also
- Vogtlandkreis (a district in Saxony covering a part of the Vogtland)
- Euregio Egrensis (the EU-based structure of a regions-based Europe as rough equivalent of the Vogtland beyond current nationality-based structuring)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Vogtland. |
 "Vogtland". Encyclopædia Britannica. 28 (11th ed.). 1911.
"Vogtland". Encyclopædia Britannica. 28 (11th ed.). 1911.- (German) (Czech) Official Website of Vogtlandkreis providing insights into anything relevant in this part of the region
- (German) (Czech) Euregio Egrensis, a site concerned with developing Euregio Egrensis
References
- ↑ Krech, Eva-Maria; Stock, Eberhard; Hirschfeld, Ursula; Anders, Lutz Christian (2009). Deutsches Aussprachewörterbuch (in German). Berlin: Walter de Gruyter. p. 1038. ISBN 978-3-11-018202-6.
- ↑ Mangold, Max (2005). Das Aussprachewörterbuch (in German) (6th ed.). Mannheim: Dudenverlag. p. 824. ISBN 9783411040667.
Coordinates: 50°24′49″N 12°10′42″E / 50.41361°N 12.17833°E

