Typhoon Son-Tinh (2012)
| Typhoon (JMA scale) | |
|---|---|
| Category 3 (Saffir–Simpson scale) | |
 Typhoon Son-Tinh at peak intensity on October 27 | |
| Formed | October 21, 2012 |
| Dissipated | October 29, 2012 |
| Highest winds |
10-minute sustained: 155 km/h (100 mph) 1-minute sustained: 205 km/h (125 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 945 hPa (mbar); 27.91 inHg |
| Fatalities | 42 total, 9 missing |
| Damage | $513 million (2012 USD) |
| Areas affected | Philippines, Vietnam, China |
| Part of the 2012 Pacific typhoon season | |
Typhoon Son-Tinh, known in the Philippines as Tropical Storm Ofel, was a powerful, late-forming typhoon that devastated the Philippines with tropical storm strength, and battered Northern Vietnam with hurricane-force winds at landfall on October 28, 2012. Originating from a broad area of low pressure over Palau on October 20, the system strengthened into a tropical depression by October 21, and on October 22, it became the 23rd named storm of the season.
Twenty-seven people were killed in the Philippines due to the heavy rain from Son-Tinh. Six fishermen were reported missing, and more than 13,000 passengers were stranded at ferry terminals and ports. Widespread flooding was reported as rivers burst their banks, in some instances rising as much as 12.8 meters in 24 hours. A cargo ship, called the ML Lady RP II, sank with around 1,200 sacks of copra near Zamboanga City at the height of the storm. Strong winds derailed a train in Quezon.[1]
Meteorological history
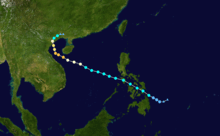
On October 19, a tropical disturbance formed southeast of Yap, and the JMA mentioned the system as a tropical depression on October 21.[2] On October 22, the PAGASA started to monitor the tropical depression and named it Ofel. On October 23, as the system started to increase in size, strong thunderstorms which were fragmented in a band that was wrapping loosely around the center of circulation, reaching high into the troposphere with cloud top temperatures are as cold as −63 Fahrenheit (−52 Celsius). On October 24, the storm made landfall over Leyte, as a tropical storm, with convection stretching over the entire republic, and the strongest convection remained to the east of the storm, over the Philippine Sea. On October 25, as Son-Tinh strengthened into a severe tropical storm, the western half of the storm, associated with the low level circulation center, had already moved into the South China Sea, while powerful thunderstorms in the eastern half were still dropping heavy rainfall the Philippines.[3] Son-Tinh reached typhoon strength on 27 October. Late on October 27, the system rapidly strengthened into a category 3 typhoon in just 6 hours, as it developed a ragged eye, but soon developed into a well defined eye.[4][5] After affecting Vietnam and Hainan Island, it weakened rapidly, first to a severe tropical storm and then to a tropical depression, due to land interaction and strong wind shear from the north west. Late on October 29, the remnant low of Son-Tinh was pushed to the south by a cold front from the north, reentered the Gulf of Tonkin, and soon made landfall over the western half of Hainan Island on 07:00 (UTC). On October 31, the remnant low of Son-Tinh moved south, into the South China Sea, before dissipating completely off the coast of Vietnam.[6][7][8]
Preparations and impact
Philippines

Son-Tinh was forecast to hit Central Philippines. However, it impacted the entire islands with almost every provinces of the country receiving storm signals. The PAGASA issued Storm Signals as the storm approached. Storm Signal No. 1 was hoisted over Surigao del Norte, Surigao del Sur, Agusan del Norte, Leyte provinces, Western and Eastern Samar. As the tropical depression neared the country, it intensified into a tropical storm. Signal No. 2 was hoisted over Cebu, Leyte provinces, Samar provinces and Surigao provinces. As a precaution, All classes in Cebu City were suspended because gale-force winds and moderate to heavy rains were battering the area.
On October 24, the storm capsized 6 boats in Tacloban City.[9] The storm caused heavy rains and strong winds over the Visayas. At the night of October 24, the storm hardly hit Cebu with rain and winds. Classes in Cebu City were suspended the next day.[10]
Throughout the Philippines, 27 people were killed by the storm and damage amounted to PHP155 million (US$3.8 million).[11]
China
As Son-Tinh neared the Gulf of Tonkin, 82,326 people in South China's Hainan Province have been relocated into temporary shelters, where water, food and medicine was provided as the arrival of Typhoon Son-Tinh, on October 27, which also brought down numerous trees across the province, with waves of five to eight meters has been reported. Son-Tinh brought heavy rains to the cities of Beihai, Qinzhou, Fangchenggang, Chongzuo, Yulin and Nanning on Sunday, with water levels on rivers in the worst-hit cities of Beihai, Qinzhou and Fangchenggang rose significantly.[12]
The center warned ships and people in affected areas to be careful urging authorities to take full precautions. It was forecast up to 80 cm of precipitation that day along the coast of eastern and southern Hainan province and eastern coast of Leizhou peninsula.
Vietnam
In Vietnam, the typhoon moved along the Tonkin Gulf, ravaging the coastal provinces of Nghệ An, Thanh Hóa, Ninh Bình and Thái Bình before making landfall 20 kilometers west of Halong Bay on October 29. A 180 m (590 ft) tall mast tower at the Nam Định collapsed during the storm.[13] A total of eight people were killed in the country while three others were listed as missing. Another 90 people were injured in various accidents related to the typhoon. In all, 429 homes collapsed and 55,251 were damaged while about 95,000 hectares (235,000 acres) of crops were flooded. The storm caused ₫3.9 – 7 trillion (US$184 – 331 million) in damage.[14][15]
See also
References
- ↑ "Tropical Storm 'Ofel' slices across Visayas; 4 dead". News Inquirer. October 21, 2012. Retrieved October 21, 2012.
- ↑ "JMA WWJP25 Warning and Summary October 21, 2012 12z". Japan Meteorological Agency. October 21, 2012. Retrieved October 21, 2012.
- ↑ http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hurricanes/archives/2012/h2012_Son-tinh.html
- ↑ http://www.webcitation.org/6BimlItl9
- ↑ "Typhoon Son-Tinh Tropical Cyclone Advisory 0600z". Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on October 27, 2012. Retrieved October 27, 2012.
- ↑ "Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 23W (Son-Tinh) Warning NR 21". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. United States Navy. August 27, 2012. Archived from the original on October 29, 2012. Retrieved September 5, 2012.
- ↑ http://www.hko.gov.hk/contente.htm
- ↑ http://www.weather.gov.hk/wxinfo/currwx/tc_gis_e.htm
- ↑ "16 missing, 6 boats capsize in Tacloban". News Inquirer. October 21, 2012. Retrieved October 21, 2012.
- ↑ "Cebu City classes suspended, Signal No. 2 for Typhoon Ofel". News Inquirer. October 21, 2012. Retrieved October 21, 2012.
- ↑ "SitRep No. 17 re Effects of Tropical Storm "Ofel" (Son-Tinh)" (PDF). National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council. November 1, 2012. Retrieved November 15, 2012.
- ↑ http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/china/2012-10/28/content_15852067.htm
- ↑ "3 người chết, tháp truyền hình đổ sập vì bão Sơn Tinh" (in Vietnamese). VnExpress.net. Retrieved 2012-10-29.
- ↑ "Vietnam – Typhoon Son-Tinh (No. 8) Situation Report No. 2" (PDF). United Nations Department of Humanitarian Affairs. ReliefWeb. November 1, 2012. Retrieved November 15, 2012.
- ↑ "Recent storm causes losses over VND7,000 billion". Government of Vietnam. ReliefWeb. November 5, 2012. Retrieved November 15, 2012.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Typhoon Son-Tinh (2012). |
- JMA General Information of Typhoon Son-Tinh (1223) from Digital Typhoon
- JMA Best Track Data of Typhoon Son-Tinh (1223) (Japanese)
- JTWC Best Track Data of Typhoon 24W (Son-Tinh)
- 24W.SON-TINH from the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory