Ammonium phosphate
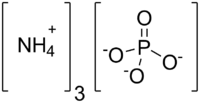 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
ammonium phosphate | |
| Other names
triammonium phosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 10361-65-6 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 140090 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.709 |
| UNII | 2ZJF06M0I9 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H12N3O4P | |
| Molar mass | 149.09 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White, tetrahedral crystals |
| 58.0 g/100 mL (25 °C) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
−1671.9 kJ/mol |
| Related compounds | |
| Other cations |
Trisodium phosphate Tripotassium phosphate |
| Related compounds |
Diammonium phosphate Monoammonium phosphate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Ammonium phosphate is the salt of ammonium and phosphate. It is a highly unstable compound with the formula (NH4)3PO4. Because of its instability, it is elusive and of no commercial value (except for scientific research). In addition to (NH4)3PO4, a related double salt (NH4)2HPO4 is also recognized. It too is unstable. The instability of these salts results in their facile decomposition with evolution of ammonia:[2]
- (NH4)3PO4 → H(NH4)2PO4 + NH3
In contrast to the fragile nature of the triammonium salts, diammonium phosphate (H(NH4)2PO4) is a valuable material, mainly used as a fertilizer.
See also
References
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. pp. 4–42, 5–19. ISBN 0-8493-0594-2.
- ↑ Klaus Schrödter, Gerhard Bettermann, Thomas Staffel, Friedrich Wahl, Thomas Klein, Thomas Hofmann "Phosphoric Acid and Phosphates" in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2008, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_465.pub3
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/13/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
