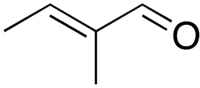
trans-2-Methyl-2-butenal
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
trans-2-methyl-2-butenal | |
| Other names
trans-2,3-dimethylacrolein, tiglic aldehyde, tiglinaldehyde, tiglaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
| 497-03-0 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL53493 |
| ChemSpider | 4479558 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.122 |
| PubChem | 5321950 |
| UNII | 27ZVE2K81C |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H8O | |
| Molar mass | 84.12 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.871 |
| Melting point | −78 °C (−108 °F; 195 K) |
| Boiling point | 116 to 119 °C (241 to 246 °F; 389 to 392 K) (752 mm Hg) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 65 °C (149 °F; 338 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkenals |
Citral |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
trans-2-Methyl-2-butenal is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH=C(CH3)CHO. This colorless liquid is a building block in organic synthesis. It is an α,β-unsaturated aldehyde related to the better known crotonaldehyde. The European rabbit, Oryctolagus cuniculus, utilizes 2-methyl-2-butenal as a pheromone.[1] The rabbit pheromone, trans-2-methyl-2-butenal, was reported to be involved in the communication between species, defined under the class of Interomone by John J McGlone, Texas Tech University, USA. [2]
References
- ↑ Schaal, B., Coureaud, G., Langlois, D., Ginles, C., Semon, E., and Perrier, G. 2003. Chemical and behavioural characterization of the rabbit mammary pheromone. Nature. 424:68-72.
- ↑ "The Pheromone Site | Research | Animal Welfare | TTU". www.depts.ttu.edu. Retrieved 2016-05-09.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/9/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.