Thermal ellipsoid
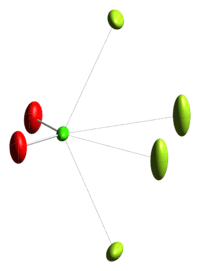
2 (chloryl), formula [ClO2][SbF6]. The chlorine atom (Cl) is in the +5 oxidation state, and is at the center in bright green; the two oxygens (O) are in red, and four fluoride anions from a hexafluoroantimonate (SbF6) anion that coordinate to the electropositive chlorine atom are shown in yellowish-green at the periphery, at right (with light lines indicating the coordinating F-Cl interactions. This reactive compound is prepared by treatment of FClO2 with the perfluoro-Lewis acid, SBF5.[2] The origin of the data for the image (the crystal structure publication) is unknown.
Thermal ellipsoids, more formally termed atomic displacement parameters, are ellipsoids used in crystallography to indicate the magnitudes and directions of the thermal vibration of atoms in crystal structures. Since the vibrations are usually anisotropic (different magnitudes in different directions in space), an ellipsoid is a convenient way of visualising the vibration and therefore the symmetry and time averaged position of an atom in a crystal.
Thermal ellipsoids can be defined by a tensor, a mathematical object which allows the definition of magnitude and orientation of vibration with respect to three mutually perpendicular axes. The three principal axes of the thermal vibration of an atom are denoted , , and , and the corresponding thermal ellipsoid is based on these axes. The size of the ellipsoid is scaled so that it occupies the space in which there is a particular probability of finding the electron density of the atom. The particular probability is usually 50%.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Angshuman R. Choudhury, Kabirul Islam, Michael T. Kirchner, Goverdhan Mehta & Tayur N. Guru Row, 2004, "In situ cryocrystallization of diphenyl ether: C−H···π mediated polymorphic forms," J. Am. Chem. Soc., 126(39), pp 12274–12275, DOI: 10.1021/ja046134k, see accessed 23 June 2105.
- ↑ K. O. Christe; C. J. Schack (1976). Harry Julius Emeléus, A. G. Sharpe, ed. Chlorine Oxyfluorides. Advances in Inorganic Chemistry and Radiochemistry, Volume 18. Academic Press. pp. 319–399, esp. p. 357f. ISBN 0-12-023618-4. Retrieved 23 June 2015.
- ↑ Massa, Werner (2004). Crystal Structure Determination (2nd ed.). Springer-Verlag. pp. 35–37. ISBN 978-3540206446.