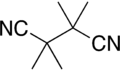Tetramethylsuccinonitrile
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Tetramethylsuccinonitrile [2] | |||
| Other names
Butanedinitrile, 2,2,3,3-tetramethyl [2] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 3333-52-6 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| Abbreviations | TMSN[3] | ||
| ChemSpider | 17700 | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.129.378 | ||
| MeSH | tetramethylsuccinonitrile | ||
| PubChem | 18745 | ||
| UNII | 116XMU2GHK | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H12N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 136.20 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless crystals | ||
| Odor | odorless[4] | ||
| Density | 1.07 g mL−1 | ||
| Melting point | 169.1 °C; 336.3 °F; 442.2 K | ||
| Boiling point | sublimes[4] | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
13.6–16.2 kJ mol−1 | ||
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH |
−4.8767–−4.8793 MJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
| LD50 (median dose) |
38.9 mg/kg (rat, oral)[5] | ||
| LCLo (lowest published) |
28 ppm (mouse, 3 hr) 6 ppm (rat, 30 hr)[5] | ||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
| PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 3 mg/m3 (0.5 ppm) [skin][4] | ||
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 3 mg/m3 (0.5 ppm) [skin][4] | ||
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
5 ppm[4] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related alkanenitriles |
|||
| Related compounds |
DBNPA | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tetramethylsuccinonitrile or TMSN is an organic compound with the formula (C(CH3)2CN)2. Classified as a dinitrile, it is a colorless and odorless solid. TMSN is the by-product from the use of some radical initiators used in polymer manufacture.[6]
TMSN is derived from 2,2'-azobis-isobutyronitrile:
- (NC(CH3)2CN)2 → (C(CH3)2CN)2 + N2
AIBN is a common radical initiator in the manufacture of polyvinyl chloride polymers.
Safety considerations
Because PVC is pervasive and can contain TMSN, the safety aspects of this dinitrile has generated interest.[7]
Symptoms of large or short exposure to this substance include convulsions, dizziness, headache, nausea, vomiting or even unconsciousness, hence affects central nervous system.
In regards to occupational exposures, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health have set limits for dermal exposure at 3 mg/m3 over an eight-hour time-weighted average.[3]
References
- ↑ "TETRAMETHYL SUCCINONITRILE". International Chemistry Safety Cards. Vermont Safety Information Resources Inc. Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- 1 2 "Tetramethyl succinonitrile". Royal Society of Chemistry. Retrieved 21 October 2015.
- 1 2 "Tetramethyl succinonitrile". NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 15 November 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0604". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- 1 2 "Tetramethyl succinonitrile". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Polymeric Materials Encyclopedia, Joseph C. Salamone, 1996, CRC Press, ISBN 0-8493-2470-X
- ↑ Ishiwata, H; Inoue T; Yoshihira K. (July 1987). "Tetramethylsuccinonitrile in polyvinyl chloride products for food and its release into food-simulating solvents". Z Lebensm Unters Forsch. 185 (1): 39–42. PMID 3617937.