Absaroka (proposed state)
| State of Absaroka (proposed) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| Nickname(s): None | |||||
 | |||||
| Capital | Sheridan, Wyoming (proposed 1939) | ||||
| Largest city | Rapid City, South Dakota | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • Total |
62,800 sq mi (162,700 km2) | ||||
| • Width | 210 miles (340 km) | ||||
| • Length | 460 miles (740 km) | ||||
| • % water | unknown | ||||
| • Latitude | 43° N to 45° 56′ N | ||||
| • Longitude | 102°W to 111°3'W | ||||
| Population | |||||
| • Total | 367,019 | ||||
| • Density |
5.84/sq mi (5.84/km2) Ranked 50th of 51 (hypothetical) | ||||
| Elevation | |||||
| • Highest point |
Grand Teton 13,775 ft (4,199 m) | ||||
| • Mean | unknown ft (unknown m) | ||||
| • Lowest point | unknown ft (unknown m) | ||||
| Admission to Union | (Not admitted) | ||||
| Legislature | |||||
| U.S. House delegation | List | ||||
| Time zone | Mountain: UTC-7/-6 | ||||
| Abbreviations | |||||
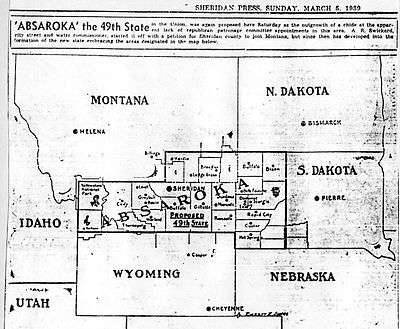
Absaroka, (pronounced ab-SOR-o-ka), from the Crow word meaning “children of the large-beaked bird", named after the Absaroka Range, was an area in the United States, comprising parts of the states of Montana, South Dakota, and Wyoming, that contemplated secession and statehood in 1939. The region's complaints came from ranchers and independent farmers in remote parts of the three states, who resented the New Deal and Democratic control of state governments, especially the government of Wyoming.[1] One of the leaders of the secessionist movement was A. R. Swickard, the street commissioner of Sheridan, Wyoming, who appointed himself "governor" and started hearing grievances in the "capital" of Sheridan.[2]
In a craze for state secession felt by the public, state automobile license plates bearing the name were distributed, as well as pictures of "Miss Absaroka 1939".[3]
The movement was unsuccessful and fairly short-lived. The chief record of its existence comes from the Federal Writers' Project, which included a story about the plan as an example of Western eccentricity.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Johnson, Kirk. "A State That Never Was in Wyoming". New York Times. July 24, 2008.
- ↑ Florence, Mason, Marisa Gierlich, and Andrew Dean Nystrom. 2001. Lonely Planet Rocky Mountains: Colorado, Wyoming, Montana and Idaho. p413.
- ↑ License plate for “State of Absaroka.” Inventory of the H.H. Horton papers, 1897–1960. Series III, Box 4: Artifacts, circa 1917–circa 1939. University of Wyoming. American Heritage Center.
- ↑ Writers' Program of the Work Projects Administration in the State of Wyoming. Wyoming: A Guide to Its History, Highways, and People. Oxford University Press. 1941.
External links
- Eight rebellious U.S. regions and secessionist efforts
- Look At the State You’re In: Absaroka, Strange Maps, July 25, 2008
- The State of Absaroka, South Dakota Magazine
Bibliography
- Roberts, Phil. "The Great Depression and the New Deal in Wyoming". Accessed July 24, 2008.
- Parker, Watson. Deadwood: The Golden Years. 1981. p220. University of Nebraska Press.

