Postage stamps and postal history of the Confederate States

The postage stamps and postal system of the Confederate States of America carried the mail of the Confederacy for a brief period in American history. Early in 1861 when South Carolina no longer considered itself part of the Union and demanded that the U.S. Army abandon Fort Sumter, plans for a Confederate postal system were already underway. Indeed, the Confederate Post office was established on February 21, 1861; and it was not until April 12 that the American Civil War officially began, when the Confederate Army fired upon US soldiers who had refused to abandon the fort. However, the United States Post Office Department continued to handle the mail of the seceded states as usual during the first weeks of the war. It was not until June 1 that the Confederate Post office took over collection and delivery, now faced with the task of providing postage stamps and mail services for its citizens.
The CSA Constitution had provided for a national postal service to be established, then required it to be self-financing beginning March 1, 1863 (Section 8. Powers of Congress, Item 7). President Jefferson Davis had appointed John Henninger Reagan on March 6, 1861, to head the new Confederate States of America Post-office Department. The Confederate Post Office proved to be very efficient and remained in operation for the entire duration of the Civil War.[1][2][3]
Beginnings
During the first seven weeks of the Civil War, the US Post Office still delivered mail from the seceded states. Mail that was postmarked after the date of a state’s admission into the Confederacy through May 31, 1861, and bearing U.S. (Union) postage is deemed to represent 'Confederate State Usage of U.S. Stamps'. i.e., Confederate covers franked with Union stamps.[4] After this time, private express companies still managed to carry the mail across enemy lines. The three major express companies in operation throughout the south were Adams Express, American Letter Express, and Whiteside's Express. They had been operating freely for approximately two months when the U.S. Post Office ordered an end to such traffic, effective August 26, 1861. Mail destined to states that were not among their own unions now had to be sent by Flag of Truce, although some express companies still continued to run their mail operations illegally; Adams continued its Southern operations under a nominally-separate Southern Express Company, in actuality a subsidiary. Mail was also smuggled in and out by blockade-running ships—which, however, were often captured or destroyed by Union ships on blockade patrol. Because Confederate post offices existed for only a few years and official and informal records of them are lacking, relatively little is known about their operations in many regions of the South. Existing data has been studied by several experts in the field, who have reconstructed an account of their existence and operation largely from surviving Confederate covers (stamped-addressed envelopes), and by researchers specializing in advanced studies of Confederate philately, notably Colonel Harvey E. Sheppard, United States Army, Fort Hood, Texas; the late Van Dyk MacBride, Newark, New Jersey; George N. Malpass, St. Petersburg, Florida; Earl Antrim, Nampa, Idaho; David Kohn, Washington, D. C., and a few others, each contributing material in the concerted effort to create an overall account of Confederate postal history.[3][5]
Confederate Post Office

One of the first undertakings in establishing the Confederate Post Office was the appointment of John H. Reagan (1818–1905) to Postmaster General, by Jefferson Davis in 1861, making him the first Postmaster General of the newly formed Confederate post office. Reagan was a Democratic congressman from Texas (many years after the Civil War, Texas would elect him to a Senate seat). Upon appointment Reagan became a close friend of Davis and was Postmaster General for the duration of the war, making him the only PMG of the short-lived Confederacy.[6] In preparation for wartime mail delivery Reagan proved to be very resourceful. He sent an agent to Washington with letters asking the various heads of the U.S. Post Office Department to come work for the new Confederate Post Office. Amazingly nearly all of them did, bringing copies of records, and account books along with them. "Reagan in effect had stolen the U.S. Post Office," notable historian William C. Davis wrote. Reagan was obviously an able administrator, presiding over the only CSA cabinet department that functioned well during the war. It established new rates rather higher than those in the Union: 5¢ (equal to $1.32 today) per half-ounce under 500 miles (800 km), 10¢ per half-ounce over 500 miles (800 km), 2¢ for drop letters and circulars. Later the under-500 miles (800 km) rate was raised to 10¢ also. There was a 50¢ rate for express mail, and after 1863 a 40¢ rate for Trans-Mississippi mail to cover the costs of smuggling the mail through a Federal blockade that operated along the entire length of the lower Mississippi River. At the beginning of the war, Union blockades prevented supplies from reaching their destinations in the South, which from time to time resulted in the shortage of postage stamps, paper and other basic supplies that were much needed throughout the Confederate states.

Although the Confederate government had contracted for the printing of its own stamps, they were not yet available on June 1, forcing postmasters all over the South to improvise.[7] Most of the time they simply went back to the old practice of accepting payment in cash and applying a "PAID" hand-stamp to the envelope. However, a number of postmasters, particularly those in the larger cities, could not afford to be handling long lines of cash customers, and developed a variety of Postmaster's provisionals. These took a variety of forms, from envelopes prestamped with a postmark modified to say "paid" or an amount, to regular stamps produced by local printers. Some are today among the great rarities of philately.[7]
Confederate postage

Within a month after his appointment as Postmaster General, Reagan ordered that ads be placed in both Southern and Northern newspapers seeking sealed proposals from printing companies for producing Confederate postage stamps. Bids arrived from companies in New York, Baltimore, Philadelphia, Newark, New Orleans and Richmond. After the war started, however, it became evident that the contract to print Confederate stamps should go to a Confederate firm. The Confederate Post Office Department therefore awarded the contract to lithographers Hoyer & Ludwig, a small firm in Richmond. The stamps they produced were inferior in image quality to the line engraved stamps printed by the U.S. Post Office, but with what resources they had, they produced some handsome images by many accounts. The first Confederate postage issues were placed in circulation in October 1861, five months after postal service between the North and South had ended. Jefferson Davis is depicted on the first issue of 1861. The appearance of a living person on a postage stamp marked a break from the tradition adhered to by the US Post Office, that a person may be depicted on U.S. postage or currency only after death.
Provisional stamps

During the five months between the US Post office's withdrawal of services from the seceded states and the first issue of Confederate postage stamps, postmasters throughout the Confederacy used temporary substitutes for postal payment. Postmasters had to improvise and used various methods to apply confirmation of postage to mailed covers, ranging from the creation of their own adhesive postage stamps to the marking of letters with either rate-altered hand-stamps or the manuscript indication “Paid.” The improvised stamps and pre-paid covers are known to collectors as 'Postmaster Provisionals', so-called because they were used 'provisionally' until the first Confederate general postage stamp issues appeared. Some Confederate post offices would subsequently experience shortages in postage stamps and would revert to the use of Provisional stamps and hand-stamps. There are many dozens of types of Provisional stamps and hand-stamps from different towns and cities about the Confederacy. In some circles, Postmaster Provisionals are referred to as 'locals' since they were intended only for use from the town in which they were issued.[8]
Postage stamps
As the Confederate States of America existed for only four years, it was able to issue only a modest number of postage stamps, nine basic types in all. During this brief span, the Confederate Post Office contracted with five different printing companies to produce postage stamps: Archer & Daly of Richmond, Virginia; Hoyer & Ludwig of Richmond, Virginia; J. T. Paterson & Co. of Augusta, Georgia; Thomas de la Rue & Co., Ltd., of London, England; and Keatinge & Ball of Columbia, South Carolina. Among them, these firms employed all three methods of printing commonly in use at that time: lithography, typography and line-engraving. The first Confederate Postage stamps were issued and placed in circulation on October 16, 1861, five months after postal service between the North and South had been suspended.[9]
 |
 |
 |
 |
- The first postage stamp issued by the Confederate States (1861) was a 5¢ green depicting Jefferson Davis. It was printed by the lithograph process by Hoyer and Ludwig of Richmond, Virginia. Like almost all Confederate issues, these stamps were imperforate, and single stamps had to be cut from the sheet with razors or scissors. This stamp was reprinted in blue in 1862.
- A 10¢ blue with Thomas Jefferson also appeared in 1861, designed by Charles Ludwig of Hoyer & Ludwig, Richmond, Virginia. This issue was printed by two different companies: Hoyer & Ludwig and, later, J. T. Paterson & Co. of Augusta, Georgia. The image of Thomas Jefferson used on both printings lithographically reproduced the same image that had been engraved on the U.S. 5-cent issue of 1856. Secret marks were added by the Paterson firm to the transfer stones to distinguish its version from the Hoyer & Ludwig prints of the same design. The most typical use was for the ten-cent rate after July 1, 1862. This stamp, like the 5¢ Davis, was reprinted in 1862, in a rose-colored version that is considerably rarer than the blue original.[10]
- In 1862, a 2¢ stamp of Andrew Jackson appeared, in green, and was issued imperforate. This issue was again lithographed by Hoyer & Ludwig of Richmond, Virginia. Only one transfer stone used in this printing. The earliest known usage of this stamp was March 21, 1862. Sheets of this issue consisted of two panes of 100 stamps each arranged in two blocks of fifty (10X5) taken from the 50-subject transfer stone with a wide vertical gutter between panes.[11] This was the last lithographed stamp produced by the Confederate Post Office.
- Also in 1862, a new 5¢ stamp of Davis, this time utilizing typography, was issued in large quantities. Produced by the De La Rue firm in London (which had been supplying postage stamps for England since 1855), it employed an engraving of Davis by Ferdinand Joubert (1810–1884). De La Rue shipped 12,000,000 copies of this issue to the Confederacy, accompanied by a set of printing plates and a supply of English paper so that additional copies could be produced locally. More than 36,000,000 of the 5¢ Davis stamps were subsequently printed from the De La Rue plates by Archer and Daly in Richmond. Archer and Daly eventually ran out of the English paper, and their later printings on Confederate paper tended to become increasingly coarse, with individual examples exhibiting blank areas in the design from plate damage or filled in areas due to plate wear. (Today they can be purchased for approximately US$10 depending on condition.)
- De La Rue also printed and shipped a typographed 1¢ orange stamp depicting John C. Calhoun. The Confederate Post office had planned to reduce the drop-letter rate to one cent, but this proved impractical and, as a result, the 1¢ stamp was never put into use. Joubert De La Ferte again engraved the central image of Calhoun, placing it in the same framework design used for the Jefferson Davis 5-cent issue, a clear attempt to show that the two stamps were part of the same series. (Later, De La Rue sent altered plates of both typographed stamps to the Confederacy with revised denominations, intended for 2-cent Calhoun and 10-cent Davis issues, but neither stamp was put into production. The printed versions of these that are sometimes seen all date from the 20th century, and cannot be considered true Confederate stamps.)
 |
 |
 |
- In 1863, a new 2¢ Jackson design appeared, engraved in steel by Frederick Halpin and printed by Archer & Daly in pale red. A second printing appeared in brown red. Line-engraving would be employed in all subsequent Confederate stamps.
- Also in 1863, a 10-cent stamp was released bearing the profile of Jefferson Davis in blue. This issue was designed and engraved on steel by John Archer and transferred to either copper plates or steel plates. Many shades of exist for these stamps, ranging from light milky blue and darker blue to shades that tend toward greenish blue and green. There are four similar designs of engraved ten cent stamps.
 |
 |
 |
 |
- The easiest to distinguish from the other three has the value expressed as "TEN". The portrait of Jefferson Davis was designed and line engraved by John Archer, and then transferred to a copper plate. This issue was imperforate and was printed on soft, porous paper of varying thickness and with colorless gum. The earliest recorded usage is April 23, 1863. Color variations occur from dark-blue to gray-blue.[12]

- The next easiest to distinguish (on which the value is expressed as "10") has straight lines enclosing the design in a rectangle. Several distinct shades of blue occur in this printing. The earliest recorded usage is April 23, 1863. All of these were printed by Archer and Daly of Richmond. This "frame-line" variety is by far the rarest of the stamps issued by the Confederate Post Office. Even poor copies shorn of most of the framing can command prices upwards of US$1000.
- Type I, initially printed by Archer & Daly, Bank Note Engravers, Richmond, Virginia, employs the same engraving as the “Frame Line” issue but without the frame lines. There were approximately 23,800,000 stamps printed from two plates, each with two panes of one hundred. The earliest recorded usage is April 21, 1863.
- Type II, also at first printed by Archer & Daly, is very similar to type I. Frederick Halpin designed and engraved the image of Davis. The corner ornaments are filled, and a faint line follows the outside of the design and encloses it. The Archer & Daly plates for both Type I and Type II were moved from Richmond to Columbia, South Carolina, when the fall of Richmond became imminent in late 1864. The company of Keatinge & Ball then printed the two stamps. A small number of Types I and II in Archer & Daly printings were perforated and released for use by the Confederate Post Office Department in 1864.[13] The perforations (gauge 12 1⁄2) on these were often of notably poor quality, and forgeries abound, many of which betray themselves by perforations that either employ the wrong gauge or are cut too crisply.
- A 20¢ stamp with George Washington also appeared in 1863, again employing a design engraved in steel by Halpin and printed by Archer & Daly. This issue saw only limited use, with the result that genuine used copies are today worth 10 times more than mint examples.[14]
Covers

A considerable number of Confederate covers (i.e. stamped - addressed envelope) survived the Civil War and through the many years since they were mailed and have been avidly sought after and preserved by historians and collectors alike. The war had divided family members and friends across the country, and letter writing naturally increased dramatically, especially to and from the men who were away serving in an army. Letters written by soldiers reveal how they would frequently ask parents, wives and family members to write often and to also ask others to write letters back to them. As mail sent to and from the soldiers became more commonplace in the mail streams of the divided states, various Christian charity groups provided pens, paper and envelopes for the soldiers in response to their constant need for these items, since soldiers on active duty during wartime rarely had the opportunity to buy these things. The variety of mail from this time period provides the student of Civil War history with an excellent cross-reference of the history involved then.[15] Special categories of interest include covers to and from soldiers, patriotic covers, prisoner-of-war covers, Flag of Truce and through-the-lines mail, mail carried by blockade runners to and from Europe, and a variety of other types. All of these specialties have been intensively studied. Although contemporary official records are often fragmentary or missing, and many details remain unclear, the covers with their addresses, dated postmarks, special markings and the letters themselves have provided much insight for historians and collectors in their studies of Civil War postal history. Some forging of material went on in the late 19th century, and authentication is a challenge for experts. As a rule of thumb a collector should be wary of fancy cancels on Confederate mail, as the CSA Post Office never used fancy cancels. Other common types of forgeries include added stamps to a cover and forged postmarks. Another common oversight of the forger is postmarking stamps with dates before the stamp was issued.[16] Many collectors over the years have marked or destroyed fakes and forgeries upon identification in an effort to keep the collecting pool safe from such material. This is a practice common to most of philately.[17]
Prisoner of war mail

During the American Civil War the number of Union and Confederate soldiers in prisoner of war prisons and camps would reach an astonishing one and a half million men. The prison population at the Andersonville Confederate POW camp alone reached 45,000 men by the war's end. At the onset of the war the United States did not recognize the legitimacy of the Confederate States and refused to establish a system that allowed for a formal prisoner and mail exchange. By the summer of 1862, more than a year into the war, prison populations in the north were at alarming proportions and the US government began to see the necessity of a prisoner and mail exchange system. On July 2, 1862 it signed what was referred to as a Prisoner exchange cartel, and by September of that year prison populations were almost emptied. However, as the war dragged on the US government had increasing distrust for the Confederate government and stopped the prisoner and mail exchanges in June 1863, less than a year after it had signed the exchange agreement.

Flag of Truce mail exchanges resumed a month later and were used until the end of the war. Prisoner mail that was carried by Flag-of-Truce had to be put in an unsealed envelope with address and postage for delivery on the other side, then placed in an outer cover for delivery to the exchange point where the outer envelope would be destroyed and the inner envelope containing the prisoner's letter was inspected. The letter would then be placed in and sealed in the stamped addressed envelope and hand-stamped indicating that the item had been inspected.
Often correspondents did not observe the two-envelope regulation, so there are examples of covers where instead of an inner and outer envelope arrangement both US and Confederate postage was applied to the prisoner's letter and where both US and Confederate markings were applied. These covers are often referred to as dual-use postage covers Mail exchange between the divided states was only allowed to cross the lines at specified exchange points. Mail which was going from the North destined to points in the South passed primarily at City Point, Virginia, while most of the mail going from the South to the North passed through at Fortress Monroe, Virginia, and usually bear an Old Point Comfort postmark.
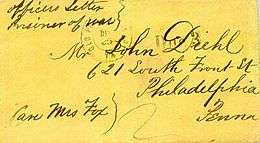
A prisoner's cover was usually docketed with the prisoner's name, rank, and company. The marking, "Examined", on the face of the cover, usually in manuscript, indicated that the cover had been opened and examined by prison officials. Once at the exchange point, the outer envelope was removed and discarded while the inner cover containing the prisoner's letter was examined by military officials and delivered. There also exist covers that were carried to transfer points by exchanged prisoners and consequently bear no confederate examiner's markings.
Mail to and from the various military prisons and prison camps is one of the most intriguing and challenging areas in Civil War postal history. Letters addressed to the various prisoner of war prisons are in most cases much scarcer than letters sent from these facilities. The south had its paper shortages, and because Confederate prisons limited the amount of correspondence mail from Confederate prisons is much rarer than mail from Union prisons.[18][19][20]
 North-to-South POW Cover, 1864. From Lt Col Wharton Jackson Green, wounded, captured at Gettysburg |
 Prisoner letter from Fort Delaware, October 26, 1864 |
 Prisoner letter from Johnson's Island, prison for Confederate Officers, May 12, 1863 |
Prisoner of war prisons and camps

When the Civil War got underway, both sides were ill prepared to deal with the very large numbers of captured troops. For a time a prisoner and mail exchange program was in use that lasted until June 1863, when the U.S. Government terminated any further cooperation due to mounting war tensions and increased mistrust.[20] The postmarks and stampings found on wartime mail from military prisons and camps during the war are sought after by historians and collectors, not only for their souvenir value but also as confirmation that various people, events and places existed at the time of mailing indicated by the name, address, postmark and other official markings. The mailed covers often bear the postmark of the nearest town or city from where the prison or camp was located. The study of Civil War military postal history and postmarks is an area of philately that involves a great volume of material covering town names, history, rarity, postmarks and other official markings found on mail to and from POW facilities. In the Nav-boxes below are two partial lists of some of the larger prison facilities, Union and Confederate, in operation during some or all of the war. Numbers for inmate totals are included to provide insight into knowing the amount of any surviving mail that is or may be in existence. There were also prison facilities that contained much smaller numbers of prisoners (a couple listed here) also. Records for some prison facilities are completely lacking, the total numbers of prisoners held, peak prison population amounts, escapes and deaths remaining unknown at the present time. Surviving prisoner of war mail to or from some of these places is exceedingly rare, and in some cases no covers are known to exist.[21]
- Alton Military Prison - Alton, Illinois - 12,000
- Camp Butler - Springfield, Illinois - 3,000
- Camp Chase – Columbus, Ohio - 10,000
- Camp Douglas – Chicago, Illinois - 18,000
- Camp Morton - Indianapolis, Indiana - 3,000
- Castle Williams - Governors Island, New York City - 1,500
- Davids' Island – New York City - 2,500
- Elmira Prison – Elmira, New York - 12,000
- Fort Delaware – Delaware City, Delaware - 12,500
- Fort Lafayette - New York City - 163
- Fort McHenry - Baltimore, Maryland - 6,900
- Fort Warren – Boston, Massachusetts - 1,000
- Gratiot Street Prison – St. Louis, Missouri - 2,000
- Hart Island New York City - 3,400
- Johnson's Island – Lake Erie, Sandusky, Ohio - 10,000
- Ohio Penitentiary – Columbus, Ohio - 360
- Old Capitol Prison – Washington, D.C. - 300
- Point Lookout – Saint Mary's County, Maryland - 52,000
- Rock Island Prison – Rock Island, Illinois - 12,000
- Andersonville – Andersonville, Georgia - 45,000 - 50,000
- Belle Isle – Richmond, Virginia - 18,000
- Blackshear Prison – Blackshear, Georgia - 5,000
- Cahaba Prison (Castle Morgan) – Selma, Alabama - 600
- Camp Ford – near Tyler, Texas - 5,300
- Camp Groce - Hempstead, Texas - 600 - 1,100
- Camp Oglethorpe - Macon, Georgia 1,200
- Castle Pinckney – Charleston, South Carolina - 300
- Castle Sorghum – Columbia, South Carolina - 1,400
- Castle Thunder – Richmond, Virginia - 1,400
- Danville Prison – Danville, Virginia - 4,000
- Florence Stockade – Florence, South Carolina - 18,000
- Fort Pulaski – Savannah, Georgia - 600
- Libby Prison – Richmond, Virginia - 50,000
- Salisbury Prison – Salisbury, North Carolina - 1,700
Blockade mail

'New Orleans' postmarks.
At the onset of the American Civil War it was imperative for the Confederacy to get crucial correspondence to suppliers and other mail into and out of the country. On April 19, 1861, President Lincoln proclaimed a blockade along the entire coastline of the Confederacy to prevent it from obtaining supplies and to prevent it from communicating with the rest of the world by means of mail. Twelve major ports and approximately 3,500 miles (5,600 km) of coastline along the Confederate States were patrolled by some 500 ships[23] that were commissioned by the US Navy; however, some accounts vary considerably and place the number of commissioned ships for blockade patrol at about 200, taking into account the high numbers of Union ships that were withdrawn from blockade duty for repairs.[24] The blockade played a major role in the Union's victory over the Confederate states. By the end of the Civil War, the Union Navy had captured more than 1,100 blockade runners and had destroyed or run aground another 355 vessels. The Union blockade reduced a vital source of revenue for the south, cotton exports, to a fraction of what they were prior to the war, as well as preventing much of its mail from being sent or received. (See also: Anaconda Plan) In response to the blockade various specially-built steamers were built and put to use by British investors who were heavily invested in the cotton and tobacco trade. These vessels were typically smaller and lighter in weight, often giving them an advantage of maneuverability and record speeds of up to 17 knots, which enabled them to evade or outrun Union ships on patrol. Their cargoes were usually small, light-weight and often included mail.[24]
Blockade runners

During the beginning of the Civil War, getting Confederate mail in and out of the Confederacy to and from foreign suppliers and other interested parties overseas posed a problem. At first, getting a ship through the Union blockade was easier, but as the war transpired the number of Union ships on blockade patrol increased while veteran crews were becoming more experienced and growing wiser to the evasive tactics employed by blockade-runners. To escape detection, blockade-runners would often try to get the mail and cargo through by making night runs, especially when the moon was new. Many of the vessels were also painted a dark gray color to help them blend in with the backdrop of the night sea, a practice that earned these vessels the nickname of Greyhounds. Some of the steamers also burned a smokeless anthracite coal which greatly reduced their profile against the horizon. However, as the war went on, the prospect of getting a ship through diminished greatly, and many of these ships faced capture or destruction, their cargoes and mail never reaching their ports of destination. As many of the vessels used as blockade-runners were built in England for British investors, the captured crews and passengers were usually British also. The cargo aboard was rewarded to the captain and crew of the capturing vessel, it is assumed as an added incentive for captains and crews on blockade patrolling ships to be extra vigilant. Mail was also confiscated and sometimes used as evidence against the parties involved with the ship and its cargo. (figure 2) Consequently, inbound covers that were prepared by forwarding agents for transfer to and delivery within the Confederacy never received various postmarks or other markings from the Confederate post office.[23][25]
Among the most notable blockade runners were steamers like the SS Syren, a 169-foot (52 m) steel-hulled sidewheel steamer that made a record 33 successful runs through the Union blockade. Another steamer called the Alice, a 177-foot (54 m) steel-hulled vessel, made 24 successful runs, while the Kate, a wooden-hulled steamer, made 20 successful runs before being run aground in November 1862. It is likely that most of the blockade runners brought mail into the Confederate mail stream, as the Confederate states were in dire need of basic supplies, the procurement of which was conducted through mailed correspondence. The various cargoes would likely have mail attached to them to notify various parties that their shipment has arrived at port. Today, Confederate blockade covers are highly sought after by collectors and historians who often regard these mailings as figurative time-stamps and historical confirmation that various people, ships and post offices existed in and among these times and places.[23][25]
The principal transfer points for mail arriving from or destined to Europe and other locations were Nassau in the Bahamas, Bermuda, and Cuba. Ships carrying letters that were addressed to points in the Confederacy would deposit their cargo of mail at one of these transfer points. Here the inbound mail was handled by a forwarding agent who would remove the mail or inner cover and prepare it for transfer on a blockade runner. Often the forwarding agents would apply their own markings to the cover of mail. Mail placed aboard a blockade runner would then, perhaps with some luck, make its way to the ports of New Orleans, Charleston or Wilmington, where it was received by Confederate postal operators who would then include it in with the regular Confederate mail for delivery.

The captain of the blockade runner would typically get two cents for every letter he delivered to port, which was a nominal sum, as his main source of revenue was from delivering his cargo. The average number of successful runs by a blockade runner was only about four, many of them meeting a fateful ending on their first run. Various ports along the coastline of the Confederacy saw the most traffic from blockade runners. Charleston in South Carolina was particularly well situated as a port for blockade runners with their shallow drafts, as was the Port in Wilmington in North Carolina which saw the most traffic. Because the lower Mississippi River was being blockaded effectively dividing the Western Confederate states from those east, New Orleans became one of the busiest of ports. Consequently, many blockade covers have postmarks from these locations.[23][25]
Patriotic covers
The years during the American Civil War were a period marked with strong sentiments and loyalties towards both sides involved, and this sentiment is clearly displayed on various Civil War correspondence known to collectors and historian as Patriotic Covers. Citizens, many of whom had family members and friends off fighting in the war, or who had died in battle, often expressed their loyalties with envelopes illustrated with flags, portraits, slogans and allegorical figures such as that of Liberty, which clearly captured the sentiments of that time. This practice was most evident in the North where there were many printers, especially in the larger cities, who produced an assortment of envelopes that proudly displayed these designs and which quickly became popular among the citizenry. The situation in the south was quite different. The demand for printers in the agrarian South was much less, and consequently established and qualified printers were generally nonexistent throughout most of the Confederacy. The South also lacked the North's industrialized advantages and supplies, and so the various Confederate patriotic covers that have survived the years are scarce and rare and usually have considerable value.[26][27]
 with Confederate seven star flag |
 Allegory of Standing Liberty and Flag mailed from West Chester, PA. (Black area is color of background) |
Adversity covers
Due to the Union blockade, the South was unable to get many needed basic supplies including paper, and as such envelopes and writing paper were scarce throughout most of the South. People would reuse old paper and envelopes, bags, and old forms and sometimes would use wallpaper to construct envelopes with. These covers are usually referred to by collectors as adversity covers.
Mourning covers
 Mourning cover with characteristic black border
Mourning cover with characteristic black border
Mourning covers are also widely collected. These are covers which bear signs of sympathy or recognition of an adverse event. The most common type of adversity cover that occurs in Civil War postal history, Confederate or Union, are what is referred to by collectors as Mourning covers. Many families shared in the loss of loved ones and friends who died in battle during the four-year war. Letters of sympathy were often sent between family members and friends. The covers often bear various markings, usually pen inscribed by the sender. One of the most common markings found on these covers is the symbolic black border put about the outer face of the envelope. As many thousands of men died during the war, the black border became commonplace in the Union and Confederate mail streams and in Civil War philately.[28][29]
Manuscript covers

May 29, 1864 arrived Wilmington with manuscript 12-cent ship rate due
- Manuscript covers are addressed envelopes that were designated as Paid or where the amount of postage due was hand-written with pen and ink. Manuscript markings can also be found along with various hand-stamp markings, or in combination with postage stamps, which were sometimes applied prior to or after the manuscript marking(s). If the manuscript cover was mail carried by a blockade runner, the cover is usually referred to then as a blockade cover, and so forth with patriotic and other covers.[23]
Postal history exhibits
 Adams Express Company postmark, with 'Paid 10' handstamp, 1861 |
 CSA Stamp on cover from Richmond, Va. Various departments of the Confederate government used envelopes which were printed with the names of their department. Examples where the words 'Official Business' are used are common, but these envelopes were not official in any way, and required payment of postage, unlike official envelopes of the US government whose postage is free, referred to as the free franking privilege. |
 Confederate handstamp 'Paid 10', 1861 |
 |
 Old Point Comfort, Fortress Monroe, Virginia, 1864 |
 1862 Washington, D.C. cover with 3c Washington 1861 Issue to Enfield Center, N.H. Red Patriotic Eleventh New Hampshire Regiment. |
 Blockade cover, 1863, carried on CSA cruiser Florida |
 Confederate blockade cover, with Pendleton S.C. 'Jul 22' postmark, carried aboard the blockade runner Nuestra Senora de Regla, by Emilio Puiz, when ship was seized on November 29, 1861. Cover used as evidence in court. Hand-stamped,'Paid 5', court docket of 'HHE' |
 CSA Provisional overprint on US postal stationery The CSA ended franking privileges on March 15, 1861, but the CSA Post Office made provision that allowed the postmaster general and other officials in the CSA Post Office to send official mail free of charge when endorsed “Official Business” over their signatures. |
 Confederate POW cover mailed from Washington, D.C. on May 22, 1865, (after Lee's surrender), Class B. Addressed to Thomas C. Trombs, Point Lookout, MD. Examined and manuscript marking by censor at Fredericksburg, Virginia, May 19, 1865. |
 Mail from Virginia bearing a manuscript Virginia town, "Gravelton, Va" with postmaster’s signature.“H. A. Camp PM” ties the CSA stamp to cover, dated "Feb 27, 1865". Manuscript “Gen Ould Commissioner Exchange Richmond, Va” at upper left. Cover sent via Fortress Monroe Va with Old Point Comfort, Va double-ring Postmark, Mar 25, 1865, and the US stamp tied with cork cancel. |
 CSA POW inner letter, North to South, 1864 |
 Prisoner letter from Fort Delaware, October 26, 1864 |
 Cover is postmarked Delaware City, Delaware, August 9, 1864, bears a Federal prison mark, confirming examination of the prisoner's letter. Cancel for stamp is a concentric circle killer. |
 North-to-South Civil War POW cover, with dual postage, Fort Delaware, 1864 |
 Blockade cover, New Orleans, March 18, 1863 |
 Cover mailed after the new uniform postage rate of ten cents had gone into effect, July 1, 1862. |
 Fort Delaware, postmarked Delaware City, Delaware, August 9, 1864, with Federal prison mark, indicating prisoner's letter was examined. |
 Johnson's Island POW camp for Confederate Officers, 1865 |
 South-to-North POW cover, Richland to Mass' 1864 |
 North-to-South Civil War POW cover, with dual postage, 1863, via Flag of Truce |
 Civilian Flag-of-Truce, 1863 |
 Flag of Truce cover, Old Point Comfort (Fortress Monroe transfer point), 1863 |
 Flag of Truce, 1864 |
 The 1861 3-cent Washington issue is the most frequently found on Civil War era mail. |
 Flag of Truce, 1864 |
 Flag of Truce, 1864 |
 Unmailed Civil War Confederate patriotic cover, 1865 |
 T.Jefferson, 1861 Confederate 10-cent Thomas Jefferson. Postmark, Richmond, Virginia, November 11, 1861, circular date stamp on eleven-star flag patriotic envelope to Oxford, Georgia. |
 CSA provisional handstamp patriotic cover, 1861 |
 CSA Paid 5 manuscript, patriotic cover |
 Point Look Out, MD, 1864 |
 Unmailed patriotic cover from the American Civil War. The Union government/army presented metaphorically as a pharmacist's shop, 1860 |
 Unmailed Civil War Union patriotic cover, 1865 |
 Unmailed Civil War Union patriotic cover, 1863 |
See also
- August Dietz, publisher of Confederate States of America postal history
- Confederate States of America
- Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps
- Frank Crown
- Lawrence L. Shenfield, author of Confederate States of America: The Special Postal Routes (1961)
- Postage stamps and postal history of the United States
- Presidents of the United States on U.S. postage stamps, Civil War era
- U.S. Postage stamp locator
- Confederate Stamp Alliance
References
- ↑ "Confederate States Post Office". Smithsonian National Postal Museum. Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- ↑ "History of the Confederate States Post Office Service". New York Times; about.com . Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- 1 2 Boyd B. Stutler, 1962. "The Confederate Postal Service in West Virginia". West Virginia Archives and History . Retrieved 19 November 2010.
- ↑ "U.S. Postal Issue Used in the Confederacy (1893)". Smithsonian National Postal Museum. Retrieved 29 January 2011.
- ↑ "Express Covers". S.N.P.M.. Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- ↑ "JOHN H. REAGAN - The Old Roman". John H. Reagan Camp #2156; Sons of Confederate Veterans. Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- 1 2 "Shortage of Postal Supplies". S.N.P.M.
. Retrieved 17 November 2010. - ↑ Postmaster Provisionals, National Postal Museum
- ↑ "Confederate Postage stamps". S.N.P.M.. Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- ↑ "Thomas Jefferson, 10-cent Blue". Smithsonian National Postal Museum. Retrieved 4 January 2011.
- ↑ "2-cent Green Andrew Jackson". Smithsonian National Postal Museum. Retrieved 6 February 2011.
- ↑ "10-cent Jefferson Davis "T-E-N"". Smithsonian National Postal Museum. Retrieved 6 February 2011.
- ↑ "10-cent Jefferson Davis, Type II". Smithsonian National Postal Museum. Retrieved 6 February 2011.
- ↑ 1-cent John C. Calhoun, National Postal Museum
- ↑ American Civil War Soldier Letters Home; AmericanCivilWar.com
- ↑ "Contrived Confederate Covers". John L. Kimbrough MD Colonel USAF MC (Ret). Retrieved 31 January 2011.
- ↑ "Declaring a stamp a forgery ". Stamp Community Family (APS Chapter). Retrieved 29 November 2010.
- ↑ "American Civil War: POW camp at Andersonville ". New York Times, about-com. Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- ↑ "Civilian Flag-of-Truce Covers ". S.N.P.M. Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- 1 2 "Prisoner mail exchange ". Prisoner of War mail, Smithsonian National Postal Museum. Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- ↑ "Prisoner of War Camps". Family History 101,. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- 1 2 Sources for prison numbers:
National Park Service, U.S. Dept. of the Interior Historical Publications Inc., Civil War News
Gratiot Street Prison, Civil War St. Louis
Illinois State Historical Library
Ohio State Penitentiary
The "Old Capitol" Prison, By Colonel N. T. Colby
Shotgun's Home of the American Civil War
University of Texas
The American Civil War - 1 2 3 4 5 "Tales from the Blockade, essay". Richard Frajola, philatelist and historian. . Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- 1 2 "Blockade essays" (PDF). Retrieved June 8, 2010.
- 1 2 3 "Blockade-Run Covers". National Postal Museum, Blockade-Run Covers . Retrieved 17 November 2010.
- ↑ Patriotic Covers from Smithsonian National Postal Museum
- ↑ Frajola, Patriotic Covers
- ↑ Mourning covers, Frajola exhibit
- ↑ Adversity Covers, Smithsonian National Postal Museum
Further reading
- Anderson, John Nathan. (2013) "Money or Nothing: Confederate Postal System Collapse during the Civil War," American Journalism, 30 (Winter 2013), 65–86.
- Bennett, Michael, (1998) United States and Confederate Postal History: The 206th Public Auction, November 15, 1998, Michael Bennett, Incorporated, 214 pages, Book
- Boyd, Steven R. (2010). Patriotic Envelopes of the Civil War: The Iconography of Union and Confederate Covers, LSU Press, 169 pages, Book
- Clemens, William Montgomery (1884). Confederate Postage-Stamps, Book
- Confederate Stamp Alliance, (2012).Confederate States of America Catalog and Handbook of Stamps and Postal History, Confederate Stamp Alliance, 528 pages, Book
- Deaton, Charles W. (2012). The Great Texas Stamp Collection, University of Texas Press, 118 pages, Book
- Leavy, Joseph B. (1916). The Philatelic Gazette, Volume 6, Nassau Stamp Co., 396 pages, E'book
- MacBride, Van Dyk (1950). Fort Delaware and Its Prisoner-of-war Covers, American philatelic, 11 pages, Book
- Seward, Henry; MacBride, Van Dyk (1952). Season's Greetings from a Philatelic Confederate, 2 pages, Book
- Smith, R.M. (1864). The statutes at large of the provisional government of the Confederate States of America,
from the institution of the government, February 8, 1861, to its termination, February 18, 1862, inclusive,
R. M. Smith, printed to Congress, 411 pages, E'book - Todd, Richard Cecil (2009). Confederate Finance, University of Georgia Press, 270 pages, ISBN 9780820334547, Book
Other sources
- August Dietz, Postal Service of the Confederate States of America (1929) - the standard work on Confederate philately
- Dietz Confederate States Catalog and Hand-Book (1931–1986)
- AskPhil – Glossary of Stamp Collecting Terms
- Encyclopaedia of Postal History
- Stuart Rossiter & John Flower: The Stamp Atlas
- Stanley Gibbons Ltd: various catalogues
- Civil War Prisons and Their Covers, by Earl Antrim
- Prisoners' Mail from the American Civil War, by Galen D. Harrison. Union and Confederate Civil War covers from prisoners of war in 83 Union and 58 Confederate Prisons, compiled from a total over 2,700 covers.
- The Handbook of Civil War Patriotic Envelopes and Postal History, Grant, 1977
External links
- Smithsonian National Postal Museum, Confederate hand-stamp cover collection
- Confederate Stamp Alliance homepage
- Civil War Prisons
- Prisoner of War Camps, the American Civil War
- Postal History of Vicksburg
- Sons of Confederate Veterans
- The Confederate Philatelist
- Civil War Postal History Articles and Resources, by Patricia A. Kaufmann
- Confederate Stamp Alliance, John L. Kimbrough, MD, Conrad L Bush
- Adam's Express Company
- Boston Athenæum: Postage Stamps from the Confederate States of America, Digital Collection.