Siphonia
| Siphonia Temporal range: Cretaceous | |
|---|---|
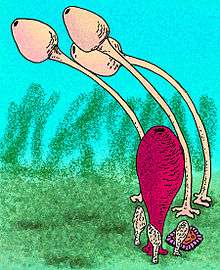 | |
| S. pyriformis & S. tulipa | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Porifera |
| Class: | Demospongiae |
| Order: | Heteroscleromorpha |
| Family: | Hallirhoidae |
| Genus: | Siphonia Goldfuss, 1826 |
| Species | |
| |
Siphonia ("Siphon") is a genus of extinct hallirhoid demosponges of the Upper Cretaceous, from about 125 to 66 million years ago. [1] They lived in the Western Tethys Ocean, in what is now Europe.
Description
They all had distinctive pear-shaped bodies that were attached to the seafloor via a long stem. Their common name, "tulip sponges," refers to their suggestive shape, while the genus name refers to how the spongocoel (the main tube of the sponge body) runs almost the entire length of the sponge, as though it were almost a drinking straw.
Gallery
- Siphonia lycoperdites , on display at the Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Milano
 Siphonia pyriformis - Muséum de Toulouse (fr)
Siphonia pyriformis - Muséum de Toulouse (fr)
References
- Parker, Steve. Dinosaurus: the complete guide to dinosaurs. Firefly Books Inc, 2003. Pg. 34
External links
Reconstruction of S. pyriformis
Reconstruction of S. tulipa, S. pyriformis, and the related Hallirhoa costata
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/10/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.