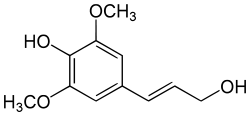
Sinapyl alcohol
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-(3-hydroxyprop-1-enyl)-2,6-dimethoxyphenol | |
| Other names
sinapoyl alcohol, 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxycinnamyl alcohol | |
| Identifiers | |
| 537-33-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:64557 |
| ChemSpider | 4444145 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.190.507 |
| KEGG | C02325 |
| PubChem | 5280507 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H14O4 | |
| Molar mass | 210.226 |
| Appearance | colourless solid |
| Melting point | 61 to 65 °C (142 to 149 °F; 334 to 338 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Sinapyl alcohol is an organic compound structurally related to cinnamic acid. It is biosynthetized via the phenylpropanoid biochemical pathway, its immediate precursor being sinapaldehyde. This phytochemical is one of the monolignols, which are precursor to lignin or lignans.[1] It is also a biosynthetic precursor to various stilbenoids and coumarins.
See also
References
- ↑ Wout Boerjan, John Ralph, Marie Baucher "Lignin Biosynthesis" Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, vol. 54, pp. 519–46. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.54.031902.134938
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/8/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.