Shenzhen Metro
|
| |||
  | |||
| Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Locale | Shenzhen | ||
| Transit type | Rapid transit | ||
| Number of lines | 8: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 11 | ||
| Number of stations | 199[1] | ||
| Daily ridership |
3.9 million (2016) | ||
| Annual ridership | 1.122 billion (2015)[3] | ||
| Website |
SZMC (Shenzhen Metro Group) official website (English)(English)
MTR Corporation (Shenzhen) official website (Chinese)(Chinese) | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | 28 December 2004 | ||
| Operator(s) |
| ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 286.2 km (177.8 mi)[4] | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) (Standard Gauge) | ||
| |||
| Shenzhen Metro | |||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 深圳地鐵 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 深圳地铁 | ||||||||||||
| Cantonese Yale | Sàmján Dèihtít | ||||||||||||
| Cantonese Jyutping | Sam1zan3 Dei6tit3 | ||||||||||||
| Hanyu Pinyin | Shēnzhèn Dìtiě | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
The Shenzhen Metro (simplified Chinese: 深圳地铁; traditional Chinese: 深圳地鐵; pinyin: Shēnzhèn Dìtiě; Jyutping: Sam1 Zan3 Dei6 Tit3) is the subway or underground system for the city of Shenzhen in Guangdong province, China. The system opened on 28 December 2004, making Shenzhen the sixth city in mainland China to have a subway after Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Wuhan. The Shenzhen Metro currently has eight lines, 166 stations, and 286 kilometres (178 miles)[4][1] of total trackage in operation. The network underwent rapid expansion prior to the 2011 Summer Universiade, opening 110 km (68 mi) of tracks in June 2011.[5] The system underwent another major expansion with the opening of Line 11 in June 2016 and both Lines 7 and 9 in October 2016 making the system the third longest in China.[6] Two new lines and extension of several existing lines are underway.
Current system
The current system has eight lines and provides a relatively fast and economical way of travelling in Shenzhen compared to buses and taxis. Line 1 and Line 4 run to the border crossings between the Shenzhen Special Economic Zone and the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region at Luohu/Lo Wu and Futian Checkpoint/Lok Ma Chau, where riders can transfer to Hong Kong's MTR East Rail Line for travel onward to Hong Kong.
Map of Shenzhen Metro
|
| Line | Terminals (District) |
Opened | Latest Extension |
Length /km |
Stations | Operator | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Luohu (Luohu) |
Airport East (Bao'an) |
2004 | 2011 | 41.04 | 30 | |
| 2 | Chiwan (Nanshan) |
Xinxiu (Luohu) |
2010 | 2011 | 35.78 | 29 | |
| 3 | Yitian (Futian) |
Shuanglong (Longgang) |
2010 | 2011 | 41.66 | 30 | |
| 4 | Futian Checkpoint (Futian) |
Qinghu (Longhua) |
2004 | 2011 | 19.96 | 15 | |
| 5 | Qianhaiwan (Nanshan) |
Huangbeiling (Luohu) |
2011 | — | 40.00 | 27 | |
| Xili Lake (Nanshan) |
Tai'an (Luohu) |
2016 | — | 30.3 | 28 | ||
| Hongshuwan South (Nanshan) |
Wenjin (Luohu) |
2016 | — | 25.33 | 22 | ||
| Futian (Futian) |
Bitou (Bao'an) |
2016 | — | 51.94 | 18 | ||
| Total | 286.2 | 199 | |||||
Line 1
Line 1 formerly known as the Luobao Line runs westward from Luohu to Airport East. Trains operate every 2 minutes during peak hours and every 4 minutes at other times. The line is operated by SZMC (Shenzhen Metro Group).
- 28 December 2004: Luohu – Window of the World
- 28 September 2009: Window of the World – Shenzhen University
- 15 June 2011: Shenzhen University – Airport East[7]
Line 2
Line 2 formerly known as the Shekou Line runs from Chiwan to Xinxiu. It connects with Line 1 at Window of the World, with Line 4 at Civic Center, with Line 3 at Futian and with Line 1 again at Grand Theater. The line is operated by SZMC (Shenzhen Metro Group).
- 28 December 2010: Chiwan – Window of the World[8]
- 28 June 2011: Window of the World – Xinxiu
Line 3
Line 3 formerly known as the Longgang Line runs from Yitian to Shuanlong in Longgang, in the north-east part of the city. Construction began on 26 December 2005.[9] The line is operated by Shenzhen Metro Line 3 Operations, which has been a subsidiary of SZMC (Shenzhen Metro Group) since 11 April 2011 when an 80% stake was transferred to SZMC.
- 28 December 2010: Caopu – Shuanglong
- 28 June 2011: Yitian – Caopu[10]
Line 4
Line 4 formerly known as the Longhua Line runs northward from Futian Checkpoint to Qinghu. Trains operate every 2.5 minutes at peak hours and every 6 minutes during off-peak hours. Stations from Futian Checkpoint to Lianhua North are underground. The line has been operated by MTR Corporation (Shenzhen), a subsidiary of MTR Corporation, since 1 July 2010.
- 28 December 2004: Fumin – Children's Palace
- 28 June 2007: Futian Checkpoint – Fumin
- 16 June 2011: Children's Palace – Qinghu
Line 5
Line 5 formerly known as the Huanzhong Line runs from Qianhaiwan in the west to Huangbeiling in the east. Construction began in May 2009 and the line opened on 22 June 2011.[11] Line 5 required a total investment of 20.6 billion RMB. The line is operated by SZMC (Shenzhen Metro Group).
- 22 June 2011: Qianhaiwan – Huangbeiling
Line 7
Line 7 of the Shenzhen Metro opened on 28 October 2016, with a length of 30.3 km and a total of 28 stations. It connects the Xili Lake to Tai'an. The line travels East–West across Shenzhen in a "V" shape. The line is operated by SZMC (Shenzhen Metro Group).
- 28 October 2016: Xili Lake – Tai'an
Line 9
Line 9 of the Shenzhen Metro opened on 28 October 2016. The line runs eastward from Hongshuwan South to Wenjin. It has 10 transfer stations. The line is 25.33 km long, running through the districts of Nanshan, Futian and Luohu. The line is operated by SZMC (Shenzhen Metro Group).
- 28 October 2016: Hongshuwan South – Wenjin
Line 11
Line 11, also known as the Airport Express, runs from Bitou in the north-east to Futian in the city centre via Shenzhen Bao'an International Airport. Construction began in April 2012 and the line opened on 28 June 2016. Line 11 runs at a higher speed of 120 km/h. The line is operated by SZMC (Shenzhen Metro Group).
- 28 June 2016: Bitou – Futian
Ridership
| Annual Ridership | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | million riders | ±% p.a. |
| 2005[12] | 58 | — |
| 2006[13] | 90 | +55.17% |
| 2007[14] | 118 | +31.11% |
| 2008[15] | 136 | +15.25% |
| 2009[16] | 138 | +1.47% |
| 2010[17] | 163 | +18.12% |
| 2011[18] | 460 | +182.21% |
| 2012[19] | 781 | +69.78% |
| 2013[20] | 914 | +17.03% |
| 2014[21] | 1,037 | +13.46% |
| 2015[3] | 1,122 | +8.20% |
Since the opening of the first phase in 2004, there has been a steady growth in passenger traffic. In 2009 and 2010, passenger traffic soared with major openings of new phase 2 lines, with a three-fold increase in passenger traffic in 2010.[22] The maximum daily passenger record was 4.17 million passengers.
July is the busiest month of the year for the Shenzhen Metro, accounting for 9.3% of annual passenger traffic, while January is the least busy month, accounting for only 6.7%. This is caused by Shenzhen's large migrant worker population.[23]
History
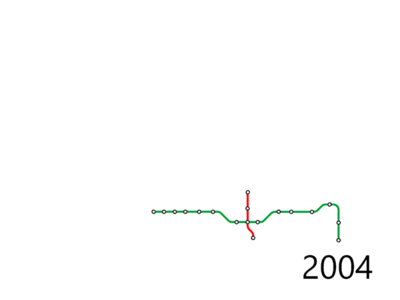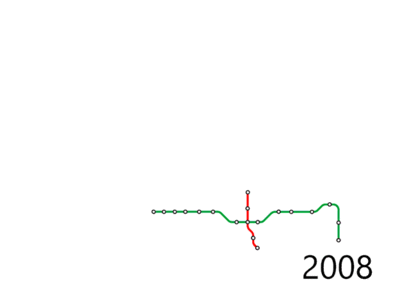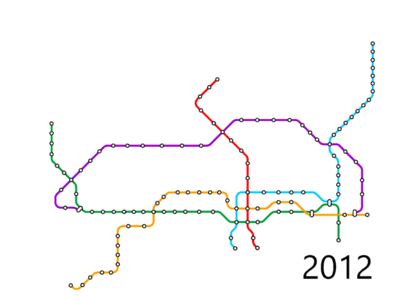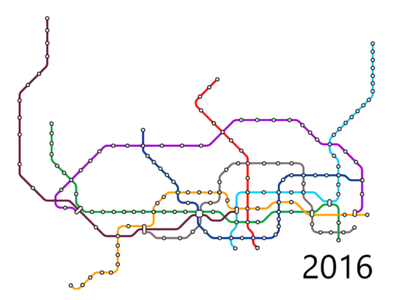
Early planning
In late 1983, Party Secretary of Shenzhen Mayor Liang Xiang led a team to Singapore to study its mass transit system. Upon returning it was decided that 30 meters on each side of Shennan Avenue should be protected as a green belt, and to set aside a 16-meter wide median reserved for a light rail or light metro line.[24] In 1984, the "Shenzhen Special Economic Zone Master Plan (1985–2000)" pointed out that, with the growing population and traffic in Shenzhen, a light metro system would not have sufficient capacity to meet future demand. Instead the report proposed a heavy rail subway line to be built along Shennan Avenue.[25] The project was finally approved by the Central Planning Department in 1992.[26]
In August 1992, during and re-feasibility and rail network planning, The Shenzhen Municipal Government decided to move from building a light metro line to a heavy rail subway line. The rapid growth of Shenzhen City made a lower capacity light metro line impractical.[27] In 1994, Shenzhen organized the preparation of the "Shenzhen urban rail network master plan" to be incorporated into the "Shenzhen City Master Plan (1996–2010)".[28] The city's vision for an urban rail network would consists of nine lines. Of the nine transit lines, three of them would be commuter rail lines upgraded from existing national mainline railways. The total length of the proposed network would be about 270 km. The three upgraded commuter rail lines would overlap the Guangzhou–Shenzhen Railway, Pinghu–Nanshan Railway and Pingyan railway.[28] This plan established the basic framework for the Shenzhen Metro network.[29]
Construction suspended and restarted
In December 1995, the State Council issued the "moratorium on approval of urban rapid transit projects" to suspend approval of rail transit projects in all Chinese cities except Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangzhou. The Shenzhen Metro project was postponed.[30] In 1996, prior to the handover of Hong Kong, authorities attempted to restart construction by renaming the project "The Luohu, Huanggang / Lok Ma Chau border crossing passenger rail connection project", stressing that the project is designed to meet the potential growing demand for cross-border passenger traffic after the handover.[28]
In 1997, Shenzhen reapplied its Subway plans to the State Planning Commission, and received approval in May 1998.[27] The project was renamed the "Shenzhen Metro first phase".[31] On July 1998, SZMC (Shenzhen Metro Group). was formally established.[31] By April 1999, the subway project feasibility study report has been approved by the state.
Phase I (1998-2004)
Construction of the first sections of Line 1 and Line 4 began in 1999. The grand opening of the Shenzhen Metro system occurred at 5:00pm on Tuesday, December 28, 2004. Initially the trains operated at 15-minute frequencies and consisted of Line 1 services between Luohu and Shijie Zhi Chuang (now Window of the World) and the Line 4 services between Fumin and Shaonian Gong (now Children's Palace). Initially the English names of the stations were rendered in Hanyu Pinyin, but some of the names were changed to English translation with American spelling in mid-2011.
The Futian Checkpoint station opened on 28 June 2007 using the name Huanggang.[32]
Name changes
On April 23, 2008, Shenzhen Municipal Planning Bureau announced that it would change the nomenclature of Shenzhen's subway lines. Instead of using numbers as the lines official designation, as typically used in other mainland Chinese metro systems, lines would be given Chinese names more akin to the Hong Kong MTR.[33] On 23 October 2013, SZMC (Shenzhen Metro Group) combined both the number with the name for the current operational lines and the future lines will be in number only.[34] Since 2016, only numerical names have been used.
| Original name | 2008–2013 name | 2013–2016 name | Current name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Line 1 | Luobao Line | Line 1 (Luobao Line) | Line 1 |
| Line 2 | Shekou Line | Line 2 (Shekou Line) | Line 2 |
| Line 3 | Longgang Line | Line 3 (Longgang Line) | Line 3 |
| Line 4 | Longhua Line | Line 4 (Longhua Line) | Line 4 |
| Line 5 | Huanzhong Line | Line 5 (Huanzhong Line) | Line 5 |
| Line 6 | Guangming Line | Line 6 (Guangming Line) | Line 6 |
| Line 7 | Xili Line | Line 7 (Xili Line) | Line 7 |
| Line 8 | Yantian Line | Line 8 (Yantian Line) | Line 8 |
| Line 9 | Meilin Line | Line 9 (Meilin Line) | Line 9 |
| Line 11 | Airport Line | Line 11 (Airport Line) | Line 11 |
Phase II (2007-2011)
From 2004 to 2007, there was a lack of official government interest and attention to expanding the subway after completion of Phase 1 with little or no active projects.[35] Subway construction speed was ridiculed as "earthworm speed".[36] In January 17, 2007 Shenzhen won the right to host the 2011 Universiade. In the bid Shenzhen committed to complete 155 km of subway lines before the games.[35] The mayor of Shenzhen at the time, Xu Zongheng, sharply criticized the speed and efficiency of Shenzhen's subway construction procedures and calls for reform.[37] Subsequently, the Shenzhen municipal government and various departments signed a liability form, requiring Phase II subway expansion to be completed in time for the Universiade.[38] Shenzhen Metro increased to over a hundred operating metro stations in June 2011, just before the Shenzhen Universiade games. In the span of two weeks, the network expanded from 64 km to 177 km. This expansion increased rail transit's share of total public transit trips from 6% to 29% in 2014.[21]
| |
|
|
in km |
| |
| 28 September 2009 | - section 2 (trial) | Window of the World | Shenzhen University | 3.39 | 3 |
| 28 December 2010 | - phase 1 | Chiwan | Window of the World | 15.1 | 12 |
| - phase 1 section 1 | Shuanglong | Caopu | 25.6 | 16 | |
| 15 June 2011 | - section 2 | Shenzhen University | Airport East | 23.6 | 12 |
| 16 June 2011 | - phase 2 | Children's Palace | Qinghu | 15.9 | 10 |
| 22 June 2011 | Qianhaiwan | Huangbeiling | 40.0 | 27 | |
| 28 June 2011 | - east extension | Window of the World | Xinxiu | 20.65 | 17 |
| - phase 1 section 2 | Caopu | Hongling | 7.72 | 6 | |
| - west extension | Hongling | Yitian | 8.8 | 8 | |
Phase III (2012-2020)
In 2010, the Shenzhen Urban Planning and Land Resources Committee proposed a building program (Phase III) between 2011 and 2020. In 2011 this plan was approved by the NDRC. Phase III formally commenced in May 2011 with an expected cost of 125.6 billion yuan. It will cover Lines 6, 7, 8, 9, and 11 and will extend the length of the Shenzhen Metro to 348 kilometres and 10 lines.[39][40] In June 2011, the Shenzhen Urban Planning and Land Resources Commission started gather public input on Phase III station names.[41] On June 30, 2016 Line 11 opened being the first subway line in Shenzhen with 8 car trains and 120 km/h maximum service speed and the first in China with a First Class service. Lines 7 and 9 followed on October 28, 2016 bringing the length of the Shenzhen Metro to 285 km and the third longest in China.
Expansion plans
Phase III Revised Expansion
Anticipated development and growth in Longgang has prompted officials to fast track the planning and construction of Line 10 (formerly Line 16), from Futian Free Trade Zone to Pinghu via Meilin, to start in 2015 instead of after 2020.[42][43][44] Although Line 10 is not part of the original three projects (Lines 7, 9 and 11) approved by the National Development and Reform Commission, the project was fast tracked in order to ease the pressure on Line 4 and accommodate further growth of the Longgang area.[45][46] According to the original plan, the northern section of Line 10 runs through Fenggang town of the neighboring Dongguan City. Due to legal and government coordination problems, Line 10 will temporarily terminate in Pinghu, with capability to extend further north into Dongguan.[47] In addition, extension projects of Line 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 9, a total of 83.9 km of new subway, were added to the revised plan.
| |
|
|
in km |
|
| |
| 2017 (structural works only, actual opening time TBC) | south extension | Qianhaiwan | Chiwan | 8.6 | 7 | Under construction[48] |
| 2019 | Shenzhen North | Songgang | 37.9 | 20 | Under construction[49][50][51][52] | |
| Futian Checkpoint | Pinghu Center | 29.9 | 23 | Under construction[50][53][54] | ||
| 2020 | east extension 2 | Xinxiu | Liantang | 3.82 | 3 | Under construction[55][56][57] |
| south extension | Yitian | Baoshuiqu | 1.5 | 1 | Under construction[56][58] | |
| east extension | Shuanglong | Liulian | 9.4 | 6 | Under construction[56][57][59] | |
| west extension | Hongshuwan | Hanghai Road | 10.8 | 8 | Under construction[56][57][60][61] | |
| north extension | Qinghu | Niuhu | 10.6 | 8 | Under construction[56][57][62] | |
| south extension | Shenzhen North | Science Museum | 11.5 | 6 | Under construction[56][57] | |
| Yantian Road | Kuichong Cultural Plaza | 24 | 12 | Under study, monorail preferred, construction may start in 2016[63] | ||
Network Phase 4 expansion
With the shortening of the Phase III implementation period,[64] a number of lines (Lines 16 and 12) planned in 2007's Phase III moved into the next phase which could possibly be completed by 2020.[65] By 2016, it was determined that Phase 4 will have an implementation period between 2017 and 2022 and consist of 274 km of new subway.[66]
| |
|
|
in km |
|
| |
| Before 2022 | Branch | Lilin | Sun Yat-sen University | TBC | TBC | Planned |
| Phase 2 | Xiaomeisha | Dapeng | TBC | TBC | Planned | |
| East Extension | Futian Checkpoint | Futian Free Trade Zone | TBC | TBC | Planned | |
| East Extension | Futian | Huangbeiling Station | TBC | TBC | Planned | |
| Line 12 |
Taiziwan | New Exhibition Center North | 20.7 | TBC | Construction starting in 2017[67] | |
| Line 13 |
Shenzhen Bay Checkpoint | Gongming Square | 38.6 | TBC | Planned | |
| Line 14 |
Huangmugang | Pingdi / Kengzi | 67.5 | TBC | Construction starting in 2017[68] | |
| Line 15 |
Dachan Bay | Mawan | TBC | TBC | Planned | |
| Line 16 |
Universiade | Xinqiao Industrial Zone | 27.8 | TBC | Planned | |
| Line 17 |
Luohu | Pinghu | 28.7 | 24 | Construction starting in 2017[69] | |
| Airport North | Great Airport New Town | 11.5 | 4 | Under Construction opening in 2018.[70] | ||

Long-term plan
In the Shenzhen Metro 2007 masterplan has a further 4 lines (
) which have a planned completion target of 2030.[71] In 2012, 4 further lines Qiannan (Line 17), Pinghu (Line 18), Pingshan (Line 19) and Fuyong (Line 20) where unveiled. This brings the total planned length of the Shenzhen Metro to 720 km spread out over 20 lines. In addition to metro lines, 5 Pearl River Delta Rapid Transit lines connecting neighboring urban centers in the Pearl River Delta such as Dongguan, Huizhou, Foshan and Guangzhou, totaling 146 km, have also been revealed.[72]
| |
|
|
in km |
|
| |
| After 2022 | Bao'an-Longgang Line | Shiyan | Buji East | TBC | TBC | Planned |
| 107 Line | Hongshuwan South | Xitou | TBC | TBC | Planned | |
| Sungang Line | Laojie | Mawan | TBC | TBC | Planned | |
| Central Axe Line | Shangsha | Guanlan North | TBC | TBC | Planned | |
| Nanshan - Longgang(Longhua) Line | TBC | TBC | TBC | TBC | Planned | |

Extended intercity proposal
Aside from the set masterplan, at the 12th Guangdong Provincial People's Congress in January 2014,[73] it was proposed to extend Line 4 beyond the planned Phase III terminus at the Songyuan Bus Terminal in Guanlan. The proposal wanted to further extend this line to reach the future planned Dongguan Metro Line 4 at Tangxia station. This proposal aims to shorten the distance between the two cities in residents' minds, boost tourism industries in both cities and expand housing options. It would also allow for direct connection between Hong Kong and Dongguan. As the area in the proposed area is less developed, the cost in building the line is expected to be reasonable, with a feasibility study yet to be conducted.
Fares and tickets
Metro rides are priced according to distance travelled, and fares vary from 2 RMB to 14 RMB.[74] Since December 2010 fares are based on a usage fee (2 RMB) + a distance fee. The distance fee is 1 RMB for each 4 km from 4 km to 12 km; after that 1 RMB for each 6 km from 12 km to 24 km and finally 1 RMB for every 8 km over 24 km distance.[75] For passengers who wish to ride on business coach in line 11, they have to pay 3 times the amount of price that calculated by the regulations above.
| Distance
(km) |
Fares
(RMB) |
Fares(RMB)
(For business coach only) |
|---|---|---|
| 0~4 | 2 | 6 |
| 4~12 | 2+1/per 4 km | 6+3/per 4 km |
| 12~24 | 5+1/per 6 km | 15+3/per 6 km |
| over 24 | 7+1/per 8 km | 21+3/per 8 km |
Children under the height of 120 cm or aged below 6 may ride for free when accompanied by an adult.[76] The metro also offers free rides to senior citizens over the age of 65, the physically disabled and military personnel. Tickets for children between 120 cm and 150 cm, or aged between 6 and 14 years, or middle school students, are half priced.
Metro fares can be paid for with single-ride tokens, multiple-ride Shenzhen Tong cards or 1- day passes.[77]
Tokens
When using cash, a RFID token (NXP Mifare Classic) is purchased and used for a single, non-returnable journey. There are two different types of tokens that showing in yellow or green color. Yellow RFID tokens is used for business coach of line 11 only. All ticket vending machines offer both English and Chinese interface. The purchaser touches a station name to calculate the fare. After payment, a green token is dispensed, which must be scanned at the entrance station and deposited at the exit station. A penalty fare applies should a token be lost. Also, people who purchased Green tokens will NOT ALLOWED to take the business coach in line 11 directly. Instead, they must get off at any transfer stations with line 11 and purchase a separate yellow token in order to ride the business coach.
Note that as of 2015 many machines accept only 5 or 10 RMB notes. The token(s) are only valid at the station where issued. Passengers are unable to buy an extra token for return journey prior to departure. Baggage X-Ray machines are located at each station, and may be manned during peak hours.
Shenzhen Tong cards
Shenzhen Tong is similar to the Octopus card system used on the MTR rail lines in Hong Kong. The multiple fare card stores credit purchased at stations. The card can be used by waving it in front of the card reader located at all entrances and exits to the subway system. Riders who pay for metro fare with a card receive a 5% discount. Since March 1, 2008, riders who pay for a bus fare with a card and then a subway fare within 90 minutes receive an additional 0.4 RMB discount on the subway fare. Card users pay a distance based fare.
Since June 30, 2011, cards containing both a Shenzhen Tong and Hong Kong Octopus chip have been available in both Shenzhen and Hong Kong. There are plans to further integrate the two systems, and for a new card which will be accepted all over Guangdong province and China's two SARs.[78][79]
Unlike Hong Kong Octopus Cards, Shenzhen Tong cards cannot be sold back to the stations or have faults dealt with by SZMC. Instead, the customer must go to the offices of Shenzhen Tong. Students studying in Shenzhen can use the Shenzhen Tong to receive a 50% discount.
Note that all sorts of discounts will not applicable for people who wish to ride business coach in line 11.
Metro 1-day passes
Metro 1-day pass is a smart card that allowed the card holder have unlimited access of the metro system in 24 continuous hours. Passengers can purchase an 1-day pass for RMB 20 in the service center in any metro station. The pass will be activated and the passenger will have 24 continuous hour for unlimited access after the first entrance. When the pass expired, the pass is no longer available for entering a station but able to exiting a station and finish a journey in 27.5 hours. The 1-day passes are not applicable for business coach in line 11.
Station facilities, amenities and services
Some stations have toilets (free of charge), and public telephones. SZMC also operates luggage storage facilities in the concourse above Luohu Station. Mobile phone service is available throughout the system provided by China Mobile, China Telecom, and China Unicom.[80]
Like the Hong Kong MTR, Guangzhou, and Foshan metros, station announcements are in Mandarin, Cantonese and English. Some announcements, such as train arrival, are in Mandarin and English only. Cantonese, an important local language, is chosen for the local Cantonese population as well as Cantonese speakers in the Canton (Guangdong) province, Hong Kong and Macau.
Equipment
Rolling Stock

Line 1
- 22 Bombardier Transportation Movia 456 6-car sets (101–122)
- 4 Changchun Railway Vehicles Type A 6-car sets, traction units by Bombardier Transportation (123–126)
- 26 Zhuzhou Electric Locomotive Works Type A 6-car sets, traction units by Siemens (127–152)
- 33 Zhuzhou Electric Locomotive Works Type A 6-car sets, traction units by CSR Times Electric. (153-185)
Line 2
- 35 Changchun Railway Vehicles Type A 6-car sets, traction units by Bombardier Transportation (201–235)
- 17 Changchun Railway Vehicles Type A 6-car sets, traction units by Bombardier Transportation (236-252)
Line 3
- 43 Changchun Railway Vehicles Type B 6-car sets, traction units by Hyundai Rotem (301-343)
- 33 Nanjing Puzhen Rolling Stock Works Type B 6-car sets (344-376)
Line 4
- 28 Nanjing Puzhen Rolling Stock Works Type A 6-car sets (401-428)
Line 5
- 22 Zhuzhou Electric Locomotive Works Type A 6-car sets, traction units by Siemens (501–522)
- 8 Zhuzhou Electric Locomotive Works Type A 6-car sets, traction units by CSR Times Electric (523–530)
- 21 Changchun Railway Vehicles Type A 6-car sets (531-551)
Line 7
- 41 Changchun Railway Vehicles Type A 6-car sets (701-741)
Line 9
- 29 Changchun Railway Vehicles Type A 6-car sets (901-929)
Line 11
- 33 Zhuzhou Electric Locomotive Works Type A 8-car sets (1101-1133)
Signalling system
On Line 1 and Line 4, Siemens Transportation Systems supplied 7 (Phase 1) and 6 (Phase 2) LZB 700 M continuous automatic control systems; 7 (Phase 1) and 6 (Phase 2) electronic Sicas ESTT interlockings; the Vicos OC 501 operations control system with 2 operations control centers, fall-back level with Vicos OC 101 and RTU (FEP), 230 (Phase 1) and 240 (Phase 2) FTG S track vacancy detection units.[81]
Line 2 and Line 5 use Casco CBTC system with 2.4 GHz frequencies, and so the system has suffered frequent problems with interference from consumer Wi-Fi equipment.[82] By the end of November 2012, CASCO solved the problem on Lines 2 and 5 by switching to their standard solution with frequency diversity on 2 different channels.
See also
- List of Shenzhen Metro stations
- List of rapid transit systems
- Dongguan Rail Transit
- FMetro
- Guangzhou Metro
- Hong Kong MTR
References
- 1 2 "Shenzhen Metro". exploremetro. Retrieved May 27, 2014.
- ↑ "深圳地铁机场线试运营"满月"迎"月考"". 深圳大件事. 2016-10-29.
- 1 2 深圳市交通运输委员会 (2016-01-19). "2015年12月交通运输运营指标统计月报".
- 1 2 深圳市统计局 (December 2, 2008). "深圳市2011年国民经济和社会发展统计公报".
- ↑ ""【深圳】2011年地铁达177公里 长过香港地铁" 星岛网讯" (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 2013-09-23.
- ↑ UK, DVV Media. "Shenzhen metro adds two lines". Railway Gazette. Retrieved 2016-10-30.
- ↑ Shenzhen Metro Line 1, from Luohu to Airport East was put into a trial operation
- ↑ photo of ongoing construction in Shekou
- ↑ (Chinese) Wang, Xiaoqing and Qiu, Gang, "深圳地铁3号线动工 2009年建成通车" southcn.com December 27, 2005
- ↑ (Chinese) 深圳地铁3号线规划线路图 August 21, 2008
- ↑ (Chinese) Xiaoqing, Wang, "深圳地铁5号线全面开工" Xinhua September 19, 2008
- ↑ 深圳市统计局. "2005年度12月份深圳统计月报:运输邮电:地铁客流量1-12月累计" (in Chinese). Archived from the original on January 25, 2013.
- ↑ 深圳市统计局 (December 2, 2008). "深圳市2006年国民经济和社会发展统计公报" (in Chinese).
- ↑ 深圳市统计局 (December 2, 2008). "深圳市2007年国民经济和社会发展统计公报" (in Chinese).
- ↑ 深圳市统计局 (March 24, 2009). "深圳市2008年国民经济和社会发展统计公报" (in Chinese).
- ↑ 深圳市统计局 (April 27, 2010). "深圳市2009年国民经济和社会发展统计公报" (in Chinese).
- ↑ 深圳市统计局 (April 28, 2011). "深圳市2010年国民经济和社会发展统计公报" (in Chinese).
- ↑ 深圳市统计局. "2011年度12月份深圳统计月报:运输邮电:地铁客流量1-12月累计" (in Chinese). Archived from the original on December 4, 2012.
- ↑ "深圳地铁客流量 去年猛增近七成" (in Chinese). 深圳商报. January 10, 2013.
- ↑ "深圳市2013年国民经济和社会发展统计公报" (in Chinese). 深圳市统计局. April 8, 2014.
- 1 2 "2014年度全市交通运输运营主要概况及分析" (in Chinese). Retrieved January 16, 2015.
- ↑ 杨丽,杨德明 (2012). "深圳市城市轨道交通网络化客流变化研究". 现代城市轨道交通 (in Chinese). 6.
- ↑ 陈煜 (2011). "深圳地铁运营对轨道交通客流预测的启示". 铁道工程学报 (in Chinese). 8.
- ↑ 彭森 (August 21, 2005). "从7米到140米——深南大道的宽度之谜" (in Chinese). 深圳晚报.
- ↑ 深圳经济特区总体规划简介[J]. 城市规划,1986,06:9–14.
- ↑ 深圳市地铁有限公司 (2007). 深圳地铁一期工程建设与管理实践.上册 (in Chinese). 北京: 人民交通出版社. ISBN 978-7-114-06262-9.
- 1 2 "深圳地铁十年始获"出生证"" (in Chinese). 深圳新闻网. June 22, 2011.
- 1 2 3 张家识 (1999). "深圳地铁一期工程建设前期工作回顾". In 陈锡贤. 地下铁道文集:中国土木工程学会隧道及地下工程分会地下铁道专业委员会第十三届学术交流会论文选 (in Chinese). 深圳: 海天出版社. ISBN 7-80615-959-2.
- ↑ "深圳地铁网络框架15年前基本敲定" (in Chinese). 深圳特区报. June 25, 2011.
- ↑ "深圳地铁"十年怀胎"终圆梦". 深圳特区报. 2010-04-10.
- 1 2 "深圳地鐵一期工程主要里程碑時間" (in Chinese). 深圳新闻网. Archived from the original on 2012-12-02.
- ↑ "深圳地铁皇岗站正式开通" (in Chinese). Archived from the original on 2007-09-30. Retrieved 2007-07-01.
- ↑ "關於我市近期建設地鐵線路及站點命名的通告" (in Chinese). Retrieved 2012-11-22.
- ↑ "New Line Naming Scheme". Shenzhen Metro Group Official Weibo. Shenzhen Metro Group. Retrieved October 23, 2013.
- 1 2 "地铁不如期完工,我主动请求处分". 南方日报. 2007-02-01.
- ↑ "网友声讨"进度慢",市长强调"拖不起",地铁建设"蚯蚓速度"". 南方日报. 2007-01-19.
- ↑ ""地铁不如期完工,我主动请求处分"_新闻中心_新浪网". news.sina.com.cn. Retrieved 2016-10-30.
- ↑ "2011年5地铁贯通深圳-搜狐新闻". news.sohu.com. Retrieved 2016-10-30.
- ↑ "City to spend 48b yuan on 3 Metro lines". Shenzhen Daily. Retrieved 2012-07-28.
- ↑ "The Shenzhen urban rail transportation recent construction plan approval (2011–2016)". National Development and Reform Commission. Retrieved 2012-08-27.
- ↑ "Public notice (draft)". Shenzhen Urban Planning and Land Resources Committee. Retrieved 2012-08-27.
- ↑ "龙岗加快地铁16号线建设准备". 深圳商报. Retrieved 2012-08-27.
- ↑ "地铁16号线 2014年初开工". 深圳商报. Retrieved 2012-08-27.
- ↑ SZ to advance Metro Line 16 work-szdaily多媒体数字报刊平台
- ↑ "深圳交委称早7点以前或实行地铁票价优惠". 南方网. December 5, 2012.
- ↑ "我市召开轨道交通建设指挥部会议,地铁16号线有望提前开工". 深圳市交通运输委员会. January 7, 2013.
- ↑ "市地铁集团首席规划师刘卡丁:16号线力争提前建设,暂时不到龙岗中心城". 南方日报. December 5, 2012.
- ↑ 深圳地鐵-地鐵5號線南延段破土動工
- ↑ "深圳地铁6号线拟年底开建 11号线预计后年通车". 搜房网. June 10, 2014.
- 1 2 地铁6号线10号线预计2019年通车-深圳晚报
- ↑ "地铁6号线10号线预计2019年通车".
- ↑ 刘世雄,陈福贵 (2013). "深圳地铁6号线运营成本测算研究". 现代城市轨道交通. 1.
- ↑ 地铁10号线预计本月开工|10号线|地铁|轨道_新浪新闻
- ↑ 深圳地铁10号线拟年底开工 2019年12月开通
- ↑ http://jt.sz.bendibao.com/news/2016617/772214.htm
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "深圳地铁7,9,11号线明年开通 今年将增加铁路始发列车". 本地宝. 2015-03-31. Retrieved 2015-04-07.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "8号线用磁悬浮相对经济 现有线路除1号线外都要延长". 深圳晚报. February 19, 2014. Retrieved 2014-02-19.
- ↑ http://jt.sz.bendibao.com/news/2016617/772214_2.htm
- ↑ "深圳地铁3号线东延工程正式开工 计划2020年底开通- 新华网". www.gd.xinhuanet.com. Retrieved 2016-08-25.
- ↑ http://jt.sz.bendibao.com/news/2016818/778763.htm
- ↑ 深圳地铁9号线西延线前海段动工 - 中国轨道交通协会官网
- ↑ "深圳地铁4号线北延线正式施工 各大站点示意图曝光 - 深圳本地宝". jt.sz.bendibao.com. Retrieved 2016-09-18.
- ↑ 深圳地铁6条延长线线路图!看看哪些经过你家 - 深圳本地宝
- ↑ "未来五年深圳再建五条地铁". 南方都市报. Retrieved 2012-08-27.
- ↑ "轨道交通近期建设规划方案". Shenzhen Urban Planning and Land Resources Committee. Retrieved 2012-08-27.
- ↑ http://www.sutpc.com/ad.asp
- ↑ "深圳地铁12号线最快明年开工建设 工期5年 - 深圳本地宝". jt.sz.bendibao.com. Retrieved 2016-10-28.
- ↑ "深圳地铁14号线提前至明年开建 深惠两段同步动工 - 深圳本地宝". jt.sz.bendibao.com. Retrieved 2016-09-18.
- ↑ "深圳地铁17号线什么时候开工? - 深圳本地宝". jt.sz.bendibao.com. Retrieved 2016-09-18.
- ↑ 网易. "深圳地铁20号线开工建设 将接驳穗莞深城际和东莞地铁_金羊网新闻_网易新闻". news.163.com. Retrieved 2016-11-28.
- ↑ "轨道线网规划方案". Shenzhen Urban Planning and Land Resources Committee. Retrieved 2012-11-21.
- ↑ "Four more Metro lines planned". Shenzhen Daily. Retrieved 2012-11-21.
- ↑ "Dongguan Metro connection called for". Shenzhen Daily. Retrieved 2014-01-22.
- ↑ (Chinese) fare information
- ↑ New Metro fares announced
- ↑ (Chinese) SZMC fare policy
- ↑ types of tickets
- ↑ One smartcard to rule them all: Guangdong, HK team up to offer unified travel card | The Nanfang
- ↑ Guangdong and Hong Kong Linked by One Transportation Card _Life of Guangzhou
- ↑ "features". southcn.com. Retrieved 2012-08-27.
- ↑ "Metro Lines 1 and 4, Shenzhen, China". Archived from the original on 2009-02-04. Retrieved 2008-07-06.
- ↑ "Pocket Wi-Fi hotspots paralyse Chinese metro lines."
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
- SZMC (Shenzhen Metro Group) official website (English)
- MTR Corporation (Shenzhen) official website (English)
