SAM-Chlorobi RNA motif
| SAM-Chlorobi RNA | |
|---|---|
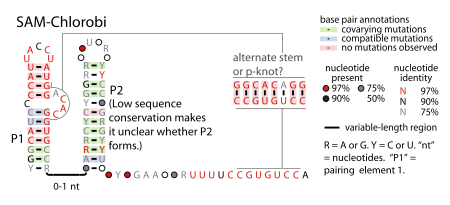 | |
| Consensus secondary structure of SAM-Chlorobi RNAs | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | SAM-Chlorobi RNA |
| Rfam | RF01724 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Cis-regulatory element |
| Domain(s) | Chlorobi |
The SAM-Chlorobi RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was identified by bioinformatics.[1] The RNAs are found only in bacteria classified as within the phylum Chlorobi. These RNAs are always in the 5' untranslated regions of operons that contain metK and ahcY genes. metK genes encode methionine adenosyltransferase, which synthesizes S-adenosyl methionine (SAM), and ahcY genes encode S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase, which degrade the related metabolite S-Adenosyl-L-homocysteine (SAH). In fact all predicted metK and ahcY genes within Chlorobi bacteria as of 2010 are preceded by predicted SAM-Chlorobi RNAs.[1] Predicted promoter sequences are consistently found upstream of SAM-Chlorobi RNAs,[1] and these promoter sequences imply that SAM-Chlorobi RNAs are indeed transcribed as RNAs. The promoter sequences are commonly associated with strong transcription in the phyla Chlorobi and Bacteroidetes, but are not used by most lineages of bacteria. The placement of SAM-Chlorobi RNAs suggests that they are involved in the regulation of the metK/ahcY operon through an unknown mechanism.
References
- 1 2 3 Weinberg Z, Wang JX, Bogue J, et al. (March 2010). "Comparative genomics reveals 104 candidate structured RNAs from bacteria, archaea and their metagenomes". Genome Biol. 11 (3): R31. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-3-r31. PMC 2864571
 . PMID 20230605.
. PMID 20230605.