Polyglutamic acid
 Gamma PGA | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Poly[imino[1-carboxy-4-oxo-1,4-butanediyl]] | |
| Identifiers | |
| 25736-27-0 | |
| Properties | |
| (C5H7NO3)n | |
| Molar mass | variable |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
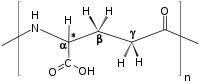
Polyglutamic acid (PGA) is a polymer of the amino acid glutamic acid (GA). Gamma PGA (Poly-γ-glutamic acid, γ-PGA) - the form where the peptide bonds are between the amino group of GA and the carboxyl group at the end of the GA side chain) - is a major constituent of the Japanese food natto. Gamma PGA is formed by bacterial fermentation.
Gamma PGA has a wide number of potential uses ranging from food and medicine to water treatment. It is widely being used as a drug delivery system in cancer treatment[1] and research is underway for its application in a treatment of type I diabetes and its potential use in the production of an AIDS vaccine.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/5/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.