Bursaphelenchus xylophilus
| Bursaphelenchus xylophilus | |
|---|---|
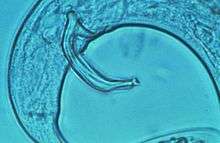 | |
| male with spicule visible | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Nematoda |
| Class: | Secernentea |
| Subclass: | Tylenchia |
| Order: | Aphelenchida |
| Superfamily: | Aphelenchoidoidea |
| Family: | Parasitaphelenchidae |
| Subfamily: | Bursaphelenchinae |
| Genus: | Bursaphelenchus |
| Species: | B. xylophilus |
| Binomial name | |
| Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner & Buhrer) Nickle | |
Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, commonly known as pine wood nematode or pine wilt nematode (PWN), is a species of nematode that infects pine trees and causes the disease pine wilt.[1][2] It occurs in much of the United States, Canada, and Mexico. It also occurs in Japan, China, Taiwan, Korea, and Portugal.[2]
History
Pine mortality in Japan was first reported Munemoto Yano (矢野宗幹) in Nagasaki prefecture in 1905.[3]
The nematode was first discovered in the timber of longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) in Louisiana, United States. Steiner and Burhrer reported that the nematode was a new species, and they named it Aphelenchoides xylophilus in 1934.[4] In 1969, Japanese plant pathologists Tomoya Kiyohara (清原友也) and Yozan Tokushige (徳重陽山) discovered many unfamiliar nematodes on dead pine trees around the Kyushu islands in Japan.[5] Then, they experimentally inoculated the nematode to healthy pine and other conifer trees and observed them. The healthy pine trees were killed—especially Japanese red and Japanese Black pine. However, Jack and Loblloly pine, Sugi cedar, and Hinoki cypress trees were able to survive.[6] The researchers concluded that the nematode was the pathogen behind the increase of mortality in Japanese pine trees.
In 1972, the year after the ground-breaking paper of Kiyohara and Tokushige was published, Yasuharu Mamiya (真宮靖治) and T. Kiyohara posited that the nematode was the pathogen behind pine mortality, and that it was a new species. They named it Bursaphelenchus lignicolous .[7] Bursaphelenchus lingnicolous, the Japanese nematode, was re-classified as the American species B. xylopilus in 1981.[8]
Pine wilt nematode epidemics have occurred in Japan, particularly during warm, dry summers.[9][10][11][12]
Morphology
Species of the genus Bursaphelenchus are difficult to distinguish because they are similar in morphology. A positive identification can be made with molecular analyses such as restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP).[9][13]
B. xylophilus is distinguished by three characteristics: the spicule is flattened into a disc-shaped cucullus at the tip, the front vulval lip is flap-like, and the tail of the female is rounded.[2]
Life cycle
The pine wilt nematode has a typical nematode life cycle, with four juvenile stages and an adult stage with both male and female individuals that reproduce sexually. The mycophagous phase of the life cycle takes place in dead or dying wood, where the nematodes live and feed upon fungi, rather than the wood itself. The nematode cannot travel outside of the wood independently; it must be transported by an insect vector.
B. xylophilus has the shortest life cycle of any known parasitic nematode. In laboratory studies in which it is cultured on fungal media, its life cycle is completed in four days. In nature it reproduces most rapidly in the summer, producing large numbers of individuals that spread throughout the resin canal system of susceptible pines, into the trunk, the branches, and the roots. If living tree cells are no longer available the parasite feeds and reproduces on the fungal hyphae growing in the resin canals. In the fall and winter the parasite becomes inactive.[9][13][14]
Vectors
As soon as the pathogen of nematode was known, Monochamus alternatus, sawyer beetle, it had been one of the noticed insects because this sawyer found frequently dead pine trees, prove the important vector of the nematode and know that the nematode infected healthy pine trees.[15] The nematodes drop off the sawyer, and infect healthy pine tree when the adult sawyers eat the young pine branches.[15]
The pine wilt nematode is vectored by a number of bark beetles and wood borers, and is most often associated with beetles in the genus Monochamus, the pine sawyers. Pine sawyers lay their eggs in the bark of dead timber. The growing larva feeds on the wood and pupates in the resulting cavity. Nematodes of the third juvenile stage congregate in the cavity around the pupa, molt into the fourth juvenile stage, and invade the trachea of the adult beetle. During this dispersive stage the beetle transports the nematode to other trees.[9][13]
-

Monochamus alternatus main vector in Japan.
-

M. saltuarius, secondary vector in Japan.
-
M. galloprovincialis, main vector in Europe
Mechanism of wilt and spread
The mechanism from nematode infection to finally pine death is partially unknown now, but the outline has been recognized. The cause of pine death is stopping moving water in the timber. The phenomenon is caused by small bubbles, then air embolism of xylem tissue stops water movement.[16] The embolism doesn’t make tylose or clog the nematode or pine cell. Why the several cavitation and non-reversible embolism occur, is unknown. In primary transmission, when the beetle feeds on a susceptible host pine, the pine wilt nematode enters the tree and feeds on the epithelial cells which line the resin ducts. This is referred to as the phytophagous phase of the nematode, and it results in pine wilt disease. Water transport in the tissues of the infested tree is disrupted, and the disease can manifest within a few weeks. Signs include browning of the needles or yellowing of the leaves, and the tree may die within two to three months.
Grade of resistance
Furuno(1982)[17] observed standing pine trees in Japanese forest, and ranked their resistance to pine wood nematode.The "High resistance" pines are rarely killed by the nematode , but young saplings or trees in weakened condition may succumb.[9][17]
- High resistance
- Pinus taeda, P. elliottii, P. palustris, P. rigida, P. taiwanensis
- Low resistance
- P. strobus, P. massoniana, P. resinosa, P. tabulaeformis, P. banksiana, P. contorta, P. thumb×P. masso
- Low susceptible
- P. bungeana, P. monticola, P. parviflora, P. strobiformis, P. densiflora
, P. pinaster, P. sylvestris, P. ponderosa, P. rudis, P. pseudostrobus, P. oocarpa, P. radiata, P. greggii
- Highly susceptible
- P. koraiensis, P. leiophylla, P. luchuensis, P. thunbergii, P. nigra, P. mugo, P. khasya, P. muricata
Management
In Japan, scientists and officers think that the mainstream of prevent this disease is removing sawyers, the vector of the nematode. The sawyers like to spawn at dying or dead pine trees, so they advise to cut down these trees until next spring. Then the timber chipped, burned or sprayed insecticide to kill the sawyer larva and pupa in them.The adult sawyers go out from the timber in late spring or early summer. They start eating young pine branch, and the nematode dropping from the sawyer. Among the two event has a few time lag.[15] So, it is profitable to kill the adult sawyers at this time to prevent the nematode infection to other trees. In Japan, the insecticide to the sawyers use organophosphorus compound or neonicotinoid. For example fenitrothion, malathion, acetamiprid, and thiacloprid. Some environmentalist warn and oppose to use these insecticide.
Bioinsecticides to remove the sawyers are studying. Entomopathogenic fungus, woodpeckers and some parasitoid or prey insects are noticed and continue studying.
Embargoes have been placed on untreated lumber from the United States and Canada. Management practices have concentrated on preventing the spread of the nematode. Infected trees are cut and either burned or chipped, soft wood timber is stripped of its bark to prevent oviposition by vectors, and all lumber shipped overseas is either fumigated or kiln-dried. Despite these preventative measures the nematode has been confirmed in Portugal, and may spread in Europe.[9][10][11][12][13]
-
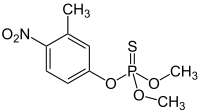
fenitrotion (organophosphorus compound)
-
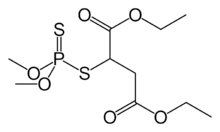
malathion (organophosphorus compound)
-
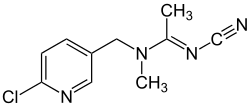
acetamiprid (neonicotinoid)
-

thiacloprid (neonicotinoid)
-

Great spotted woodpecker
In Japan, some nematocides use to prevent the disease. For example, morantel, mesulfenfos, levamisole, emamectin, milbemectin, thionazin. Some biopesticides are studying, but they remain expelimental stage. Inoculte nematode and nematophagous fungus same pine timber, the nematode decrease.[18]
-
.jpg)
Nematocide to trees
-

Levamisole
-

Emamectin
-

Milbemectin
-
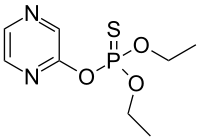
Thionazin
Gallery
-
Pointed tail end of the male
-

Austrian pine with pine wilt
-

A cross-section of an affected Austrian pine
-

Affected Scots pines on a Christmas tree farm
References
| Wikispecies has information related to: Bursaphelenchus xylophilus |
- ↑ Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, Pine Wilt Nematode. Nematology. University of Nebraska, Lincoln.
- 1 2 3 Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Archived January 4, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. Nemaplex. UC Davis.
- ↑ Yano, M. (1905) 長崎県下松樹枯死原因調査. 山林公報4
- ↑ Steiner, G.; Burher, E.M. (1934) Aphelenchoides xylophilus, n. sp, a nematode associated with blue stain and other fungi in timber. Journal of Agriculture Research 48944951.
- ↑ Tokushige, Y. and Kiyohara, T. (1969)Bursaphelenchus sp. in the wood of dead pine trees. 日本林学会誌51(7): 193-195.
- ↑ Kiyohara, T. and Tokushige, Y. (1971) Inoculation experiment of a nematode, Bursaphelenchus sp., onto pine trees. 日本林学会誌53(7): 193-195.
- ↑ Mamiya, Y.; Kiyohara, T. (1972) Description of Bursaphelenchus lignicolous n. sp. (Nematode: Aphelenchoidae) from pine wood and histopahology of nematode infected trees. Nematology 18(1): 120-124.
- ↑ Nickle, W.R.; Golden, A.M.; Mamiya, Y.; Wergin, W.P. (1981) On the taxonomy and morphology of the pine wood nematode.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dwinell, L. D. and W. R. Nickle. (1989). An Overview of the Pine Wood Nematode Ban in North America. Gen. Tech. Rep. SE-55. Asheville, North Carolina: USDA, Forest Service, Southeastern Forest Experiment Station.
- 1 2 Mota, M. M. and P. C. Vieira. 2008. Pine wilt disease in portugal. In: Pine Wilt Disease. Springer Japan. pp 33-38.
- 1 2 Mota, M. M. and P. C. Vieira (eds.) Pine Wilt Disease: A Worldwide Threat to Forest Ecosystems. Springer. 2008. ISBN 978-1-4020-8454-6
- 1 2 Suzuki, K. 2002. Pine Wilt Disease: a threat to pine forest in Europe. Dendrobiology 48, 71-74.
- 1 2 3 4 Cram, M. and J. Hanson. How to Identify and Manage Pine Wilt Disease and Treat Wood Products Infested by the Pinewood Nematodes. NA-FR-01-04. USDA, Forest Service
- ↑ Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (nematode). Global Invasive Species Database.
- 1 2 3 Morimoto, K. and Iwasaki(1972)Role of Monochamus alternatus as a vector of Bursaphelenchus lignicolous. 日本林学会誌54(6): 177-183.
- ↑ Kuroda, K.; Yamada, T.; Mineo, K.; Tamura, H. (1989)Effect of cavitation on the development of pine wilt disease caused by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. 日本植物病理学会報54(5) : 606-615.
- 1 2 Furuno, T. (1982) Studies on the Insect Damage upon the Pine-species imported in Japan : (No.7) On the Withering of the pines by the Pine Wilt. Bulletin of Kyoto University Forests 54, 16-30.
- ↑ Mamiya, Y.; Hiratsuka, M.; Murata, M. (2005) Ability of wood-decay fungi to prey on the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner et Buhrer) Nickle. 日本線虫学会誌35(1): 21-30.
External links
- Pine wilt disease. American Phytopathological Society.
- Forest living things 00154 Pine wilt nematode (Japanese)
- Forest living things 00155 Monochamus alternatus (Japanese)
- Forest living things 00253 Monochamus satuluarius (Japanese)
- Forest living things 00264 Trogossita japonica prey beetle, hope to decrease sawyers
- Forest living things 00284 Dastarcus helophoroides Parasitoid beetle, hope to decrease sawyers