Microhedylidae
| Microhedylidae | |
|---|---|
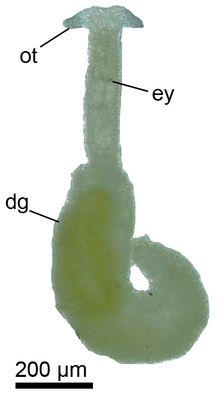 | |
| live Pontohedyle milaschewitchii ot = oral tentacles, ey = eyes, dg = digestive gland. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| (unranked): | clade Heterobranchia clade Euthyneura clade Panpulmonata clade Acochlidiacea clade Microhedylacea |
| Family: | Microhedylidae Odhner, 1937 |
| Diversity[1] | |
Microhedylidae s.s.:
Microhedylidae s.l. (including Ganitidae):
| |
| Synonyms | |
Microhedylidae are a taxonomic family of sea slugs, marine gastropod mollusks within the clade Acochlidiacea.
2005 taxonomy
Microhedylidae has been listed as a synonym of Parhedylidae in the taxonomy of Bouchet & Rocroi (2005).[2] Ganitidae Rankin, 1979 has been listed as a sole family within Hedylopsoidea.[2] The type genus of Livorniellidae was Livorniella Rankin, 1979.[2]
2010 taxonomy
Sensu Schrödl & Neusser (2010)[1] is Microhedylidae within the clade Microhedylacea.[1] Parhedylidae is a synonym of Microhedylidae.[1] Microhedylidae s.l. may informally include Ganitidae, but inclusion of Ganitidae within Microhedylidae requires further research and higher statistical support.[1]
Genera
Genera within the Microhedylidae include:
Microhedyle Hertling, 1930
- Microhedyle glandulifera (Kowalevsky, 1901)[1]
- Microhedyle nahantensis (Doe, 1974)[1]
- Microhedyle odhneri (Ev. Marcus & Er. Marcus, 1955)[1]
- Microhedyle remanei (Er. Marcus, 1953)[1]
- Ganitus Marcus, 1953 - with the only species Ganitus evelinae Marcus, 1953 - it belongs to Microhedylidae s.l. / Ganitidae[1]
- Paraganitus Challis, 1968 - with the only species Paraganitus ellynnae Challis, 1968 - it belongs to Microhedylidae s.l. / Ganitidae[1]
Parhedyle Thiele, 1931
- Parhedyle cryptophthalma (Westheide & Wawra, 1974)[1]
- Parhedyle tyrtowii (Kowalevsky, 1900)[1]
- Parhedyle gerlachi (Ev. Marcus & Er. Marcus, 1959)[1]
Pontohedyle Golikov & Starobogatov, 1972
Cladogram
A cladogram based on sequences of mitochondrial 28S ribosomal RNA, 16S ribosomal RNA and cytochrome-c oxidase I (COI) genes showing phylogenic relations within the family Microhedylidae:[5]
| Microhedylidae |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Schrödl M. & Neusser T. P. (2010). "Towards a phylogeny and evolution of Acochlidia (Mollusca: Gastropoda: Opisthobranchia)". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 158: 124-154. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2009.00544.x.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Bouchet P.; Rocroi J.-P.; Frýda J.; Hausdorf B.; Ponder W.; Valdés Á. & Warén A. (2005). "Classification and nomenclator of gastropod families". Malacologia: International Journal of Malacology. Hackenheim, Germany: ConchBooks. 47 (1-2): 1–397. ISBN 3-925919-72-4. ISSN 0076-2997.
- ↑ Rankin J. J. (1979). "A freshwater shell-less mollusc from the Caribbean: structure, biotics, and contribution to a new understanding of the Acochlidioidea". Royal Ontario Museum, Life Sciences Contributions 116: 123 pp.
- ↑ Marine Species Identification Portal : Genus Microhedyle. accessed 3 December 2010.
- ↑ Jörger K. M., Norenburg J. L., Wilson N. G. & Schrödl M. (2012). "Barcoding against a paradox? Combined molecular species delineations reveal multiple cryptic lineages in elusive meiofaunal sea slugs". BMC Evolutionary Biology 12: 245. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-12-245.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Microhedylidae. |