Nu2 Canis Majoris
- For other star systems with this Bayer designation, see Nu Canis Majoris.
| |
| |
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Canis Major |
| Right ascension | 06h 36m 41.038s[1] |
| Declination | −19° 15′ 21.17″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 3.95 |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K1 III |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 5.39 km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 62.57 ± 0.15[1] mas/yr Dec.: −69.97 ± 0.16[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 50.63 ± 0.23[1] mas |
| Distance | 64.4 ± 0.3 ly (19.75 ± 0.09 pc) |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.3 ± 0.1[2] M☉ |
| Radius | 4.9 ± 0.1[2] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 11.3 ± 0.1[2] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.18 ± 0.03[2] cgs |
| Temperature | 4790 ± 27[2] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | 0.21 ± 0.10 dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 1.15 km/s |
| Age | 4.6 ± 0.7[2] Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
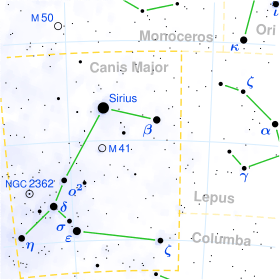
Nu2 Canis Majoris (ν2 CMa, ν2 Canis Majoris) is a star in the constellation Canis Major. It is an evolved K-type giant approximately 65 light years away, seen below Sirius. Around 1.5 times as massive as the Sun, it has expanded to around 2.3 times the Sun's diameter and 11 times its luminosity. In 2011, it was discovered to have a planet.[3]
Chinese name
In Chinese astronomy, ν2 Canis Majoris is called 野雞, Pinyin: Yějī, meaning Wild Cockerel, because this star is marking itself and stand alone in Wild Cockerel asterism, Well mansion (see : Chinese constellation).[4] 野雞 (Yějī), westernized into Ya Ke. According to R.H. Allen opinion, the name Ya Ke is asterism consisting ο1 Canis Majoris and π Canis Majoris, with other small stars in the body of the Dog[5]
Planetary system
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | ≥2.6 ± 0.6 MJ | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 763 ± 17 | 0.14 ± 0.06 | — | — |
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752
 . Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Vizier catalog entry
. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Vizier catalog entry - 1 2 3 4 5 6 Bonfanti, A.; et al. (2015). "Revising the ages of planet-hosting stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 575. A18. arXiv:1411.4302
 . Bibcode:2015A&A...575A..18B. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201424951.
. Bibcode:2015A&A...575A..18B. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201424951. - 1 2 Wittenmyer; et al. (2011). "The Pan-Pacific Planet Search. I. A Giant Planet Orbiting 7 CMa". The Astrophysical Journal. 743 (2). arXiv:1111.1007
 . Bibcode:2011ApJ...743..184W. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/743/2/184.
. Bibcode:2011ApJ...743..184W. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/743/2/184. - ↑ (Chinese) AEEA (Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy) 天文教育資訊網 2006 年 7 月 16 日
- ↑ Richard Hinckley Allen: Star Names — Their Lore and Meaning: Canis Major