Nitrolysis
Nitrolysis is a chemical reaction involving cleavage ("lysis") of a chemical bond concomitant with installation of a nitro group (NO2). Typical reagents for effecting this conversion are nitric acid and acetyl nitrate. A commercially important nitrolysis reaction is the conversion of hexamethylenetetramine to the nitramide (O2NNCH2)3. Callled RDX, this trinitramide is a widely used explosive.[1]
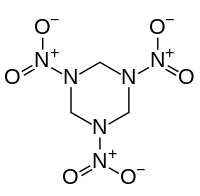
RDX is a widely used explosive material thst is produced by nitrolysis reactions.
Reference
- ↑ Jacques Boileau, Claude Fauquignon, Bernard Hueber and Hans H. Meyer "Explosives" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2009, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a10_143.pub2
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/29/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.