Nitrobenzoic acid
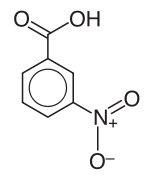
3-Nitrobenzoic acid
Nitrobenzoic acids are derivatives of benzoic acid. Two are commercially important. They are about ten times more acidic than the parent benzoic acid .[1] Nitrobenzoic acid can be prepared through the oxidation of styrene in boiling nitric acid.[2]
- 2-Nitrobenzoic acid (CAS Registry Number 552-16-9, m.p. 148 °C) is prepared by oxidation of 2-nitrotoluene.
- 3-Nitrobenzoic acid (m.p. 142 °C) is a precursor to 3-aminobenzoic acid, which in turn is used to prepare some dyes. It can be prepared by nitration of benzoic acid. It also can be prepared by treating benzaldehyde under nitration conditions, a process that initially converts the aldehyde to the acid.
- 4-Nitrobenzoic acid (m.p. 240 °C) is a precursor to 4-aminobenzoic acid, a precursor to the anestheic Procaine. It is prepared by oxidation of 4-nitrotoluene.
References
- ↑ Takao Maki, Kazuo Takeda "Benzoic Acid and Derivatives" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_555.
- ↑ Everson, William (October 1949). "The Reactions of Monomeric Styrenes". Chemical Reviews. 45 (2): 183–345. doi:10.1021/cr60141a001.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/21/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.