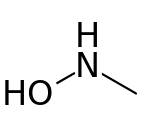
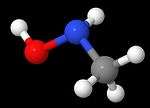
N-Methylhydroxylamine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-Methylhydroxylamine | |
| Other names
Methylhydroxylamine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 593-77-1 (Free material) 4229-44-1 (hydrochloride) | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 11157 |
| PubChem | 11647 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH5NO | |
| Molar mass | 47.06 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 38.5 °C (101.3 °F; 311.6 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 115.0 °C (239.0 °F; 388.1 K)[1] |
| Basicity (pKb) | 8.04[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
N-Methylhydroxylamine or methylhydroxylamine is a hydroxylamine derivative with a methyl group replacing one of the hydrogens of the amino group. It is an isomer of methoxyamine and aminomethanol. It decomposes in an exothermic reaction (-63 kJ/mol) into methane and azanone unless stored as a hydrochloride salt.
The compound is commercially available as its hydrochloride salt. This can be produced by electrochemical reduction of nitromethane in hydrochloric acid using a copper anode and a graphite cathode.[2]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Bissot, T. C.; Parry, R. W.; Campbell, D. H. (1957). "The Physical and Chemical Properties of the Methylhydroxylamines". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 79 (4): 796–800. doi:10.1021/ja01561a005.
- ↑ Gan, Yongping; Zhang, Wenkui; Huang, Hui; Xia, Xinhui; Cheng, Yongsheng (2006). "Industrial Synthesis of N-Methylhydroxylamine Hydrochloride by Electrochemical Reduction of Nitromethane". Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering. 14 (5): 649. doi:10.1016/S1004-9541(06)60129-8.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/2/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.