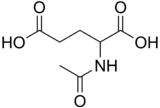
N-Acetylglutamic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Acetamidopentanedioic acid[1] | |
| Other names
Acetylglutamic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 5817-08-3 19146-55-5 R 1188-37-0 S | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| 3DMet | B00147 |
| Abbreviations |
|
| 1727473 S | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:17533 |
| ChemSpider | 180 1272049 R 64077 S |
| DrugBank | DB04075 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.024.899 |
| EC Number | 227-388-6 |
| KEGG | C00624 |
| MeSH | N-acetylglutamate |
| PubChem | 185 1560015 R 70914 S |
| RTECS number | LZ9725000 S |
| UNII | MA61H539YZ |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H11NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 189.17 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Density | 1 g mL−1 |
| Melting point | 191 to 194 °C (376 to 381 °F; 464 to 467 K) |
| 36 g L−1 | |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
>7 g kg−1 (oral, rat) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkanoic acids |
|
| Related compounds |
|
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
N-Acetylglutamic acid (abbreviated NAcGlu) is biosynthesized from glutamic acid and acetyl-CoA by the enzyme N-acetylglutamate synthase. Arginine is the activator for this reaction.
The reverse reaction, hydrolysis of the acetyl group, is catalyzed by a specific hydrolase.
NAcGlu activates carbamoyl phosphate synthetase in the urea cycle.
See also
References
- ↑ "N-Acetyl-DL-glutamic acid - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 25 March 2005. Identification. Retrieved 25 June 2012.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/6/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.