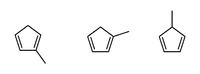
Methylcyclopentadiene
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 60141 |
| PubChem | 66775 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H8 | |
| Molar mass | 80.13 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Methylcyclopentadiene describes three isomeric cyclic dialkenes with the formula C5MeH5 (Me = CH3). These isomers are the organic precursor to the methylcyclopentadienyl ligand (C5H4Me, often denoted as Cp′), commonly found in organometallic chemistry. C5MeH5 is prepared by thermal cracking its Diels–Alder dimer, followed by distillation to remove cyclopentadiene C5H6, a common impurity.[1]
I.png)
Relative to the corresponding Cp complexes, complexes of Cp′ exhibit enhanced solubility in organic solvents. Furthermore, Cp′ is often employed to probe the structure of organometallic complexes. For example, exhibits four MeC5H4 resonances in its 1H NMR spectrum and five MeC5H4 resonances in the 13C NMR spectrum. Free rotation of the Cp′ ligand does not equivalence the diastereopic protons and carbon centers. The achiral precursor complex exhibits only two MeC5H4 resonances in the 1H NMR spectrum and three MeC5H4 resonances in the 13C NMR spectrum.[2]
References
- ↑ Darkwa, James; Giolando, Dean M.; Murphy, Catherine Jones; Rauchfuss, Thomas B.; Müller, A. (1990). "Bis(η5-Methylcyclopentadienyl)Titanium Pentasulfide, Bis(μ-Methylcyclopentadienyl)-Divanadium Pentasulfide, and Bis(μ5-Methylcyclopentadienyl)Divanadium Tetrasulfide". Inorg. Synth. 27: 51. doi:10.1002/9780470132586.ch10.
- ↑ Carlton, L.; Johnston, P.; Coville, N. J. (1988). "Substituted cyclopentadienyl complexes. II. Carbon-13 NMR spectra of some complexes". J. Organomet. Chem. 339 (3): 339–43. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)99395-1. ce stripmarker in
|title=at position 77 (help)