Albian
| System/ Period |
Series/ Epoch |
Stage/ Age |
Age (Ma) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paleogene | Paleocene | Danian | younger | |
| Cretaceous | Upper/ Late |
Maastrichtian | 66.0–72.1 | |
| Campanian | 72.1–83.6 | |||
| Santonian | 83.6–86.3 | |||
| Coniacian | 86.3–89.8 | |||
| Turonian | 89.8–93.9 | |||
| Cenomanian | 93.9–100.5 | |||
| Lower/ Early |
Albian | 100.5–~113.0 | ||
| Aptian | ~113.0–~125.0 | |||
| Barremian | ~125.0–~129.4 | |||
| Hauterivian | ~129.4–~132.9 | |||
| Valanginian | ~132.9–~139.8 | |||
| Berriasian | ~139.8–~145.0 | |||
| Jurassic | Upper/ Late |
Tithonian | older | |
| Subdivision of the Cretaceous system according to the IUGS, as of July 2012. | ||||
The Albian is both an age of the geologic timescale and a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is the youngest or uppermost subdivision of the Early/Lower Cretaceous epoch/series. Its approximate time range is 113.0 ± 1.0 Ma to 100.5 ± 0.9 Ma (million years ago). The Albian is preceded by the Aptian and followed by the Cenomanian.[1]
Stratigraphic definitions
The Albian stage (French Albien, from Alba = the River Aube in France) was first proposed in 1842 by Alcide d'Orbigny.
The base of the Albian is defined as the place in the stratigraphic column where the coccolithophore species Praediscosphaera columnata first appears. A reference profile for the base of the Albian stage (its GSSP) had in 2009 not yet been established.
The top of the Albian stage (the base of the Cenomanian stage and Upper Cretaceous series) is defined as the place where the foram species Rotalipora globotruncanoides first appears in the stratigraphic column.[2]
The Albian is sometimes subdivided in Early/Lower, Middle and Late/Upper subages or substages. In western Europe, especially in the UK, a subdivision in two substages (Vraconian and Gaultian) is more often used.
Lithofacies
The following representatives of the Albian stage are worthy of notice: the phosphorite beds of the Argonne and Bray areas in France; the Flammenmergel of northern Germany; the lignites of Utrillas in Spain; the Upper sandstones of Nubia, and the Fredericksburg beds of North America.
Palaeontology
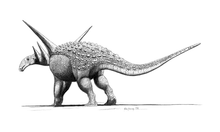
†Ankylosaurs
| Ankylosaurs of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
|
| ||||
| Cedar Mountain Formation, Utah, USA | ||||
| Aptian to ?Albian | Ulansuhai Formation, Inner Mongolia, China | |||
| Aptian to Albian | Cloverly Formation, Wyoming, Montana, Utah, USA | A medium-sized nodosaurid, measuring about 5 meters (16.5 ft) long, Sauropelta had a distinctively long tail which made up about half of its body length. Its neck and back were protected by an extensive bony body armor including characteristically large spines | ||
| Mongolia | ||||
| Dakota Formation, Kansas, USA | A nodosaurid estimated to have been approximately four meters in length (13 ft). Besides the usual rounded and polygonal osteoderms, Silvisaurus may have also sported bony spines on its shoulders and tail | |||
| Late Albian to early Cenomanian | Frontier Formation, Wyoming, USA | A poorly known genus of nodosaurid | ||
| Paw Paw Formation, Texas, USA | Poorly known, probably a nodosaurid | |||
Birds (avian theropods)
| Birds of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
| | ||||
Bony fish
| Bony Fish of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
|
| ||||
| Alabama, Georgia and Kansas, USA; Czech Republic; Canada; Australia | ||||
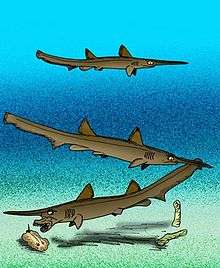
Cartilaginous fish
| Cartilaginous fish of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
| Western Interior Seaway, North America |
| |||
| Europe, Russia, North America and New Zealand | ||||
†Ceratopsia
| Ceratopsia of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
| Gobi Desert, Mongolia | Had an intermediate phylogenetic position between Liaoceratops and Archaeoceratops within Neoceratopia | | ||
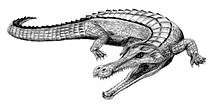
Crocodylomorphs
| Crocodylomorphs of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
| Africa | | |||
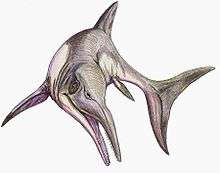
†Ichthyosaurs
| Ichthyosaurs of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
|
| ||||
Mammalia
| Mammals of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
| several species from Hauterivian to Albian | Spain, Mongolia | | ||
| Lightning Ridge, New South Wales, Australia | ||||
| Lightning Ridge, New South Wales, Australia | ||||
†Ornithopods
| Ornithopods of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
| Khukhtek Formation, Dornogovi Province, Mongolia | An advanced iguanodontian, just basal to the family Hadrosauridae |
| ||
| Aptian/Albian | Dinosaur Cove, Victoria, Australia | 2–3 meters long hypsilophodont | ||
| Albian-Cenomanian | Utah, USA | An iguanodont | ||
| China | ||||
| Mongolia | ||||
| China | An early hadrosauroid iguanodont, about 17 – 20 feet (5 – 6 metres) in length. It had a narrow snout, an elongated lower jaw and double rows of flattened cheek teeth. It was a possible ancestor of the duck-billed dinosaurs. | |||
| Barremian to Albian | ||||
| Aptian to Albian | Purgatoire Formation, Colorado, USA | An iguanodont described as intermediate in derivation between Camptosaurus and Iguanodon | ||
| Aptian to Albian | Cloverly Formation, Montana, USA | Hypsilophodont | ||
†Plesiosaurs
| †Plesiosauria of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
|
Aptian to Albian | Hughenden district, Queensland, Australia | Among the largest pliosaurs, body-length estimates put the total length of Kronosaurus at 9–10 meters |
|
†Pterosauria
| Pterosaurs of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
| Cambridge Greensand, United Kingdom |
| |||
| Morocco; Santana Formation, Brazil; Paw Paw Formation, Texas, USA | ||||
| Lianmuxin Formation, Xinjiang, China | ||||
| Valanginian to Albian | Lagarcito Formation, Argentina | |||
| Aptian or Albian | Santana Formation, Brazil | |||
| Aptian to early Albian | Santan do Cariri, Brazil; St Gallen, Switzerland | |||
| Albian or Cenomanian | Santana Formation, Brazil | |||
| ? | Zhejiang, China | |||
†Sauropods
| Sauropods of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
| Mid to Late Albian | Utah, USA |
| ||
| Egypt | The only known bones of this sauropod were destroyed in World War II. | |||
| Early Cretaceous | Brazil | |||
| Algeria | The bones referred to "B." nougaredi probably belong to more than one different species. | |||
| Atian-Albian | Utah | |||
| South America | ||||
| Aptian or Albian | Montana | |||
| Aptian-early Albian | Oklahoma | This sauropod weighed up to 60 tonnes, making it one of the largest known dinosaurs. | ||
| early Albian | Tunisia | Tataouinea had highly pneumatic pelvic bones, suggesting that sauropods had abdominal air sacs. | ||
†Theropods (non-avian)
| Theropods of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
| North America |
| |||
| Asia | ||||
| Niger | ||||
| North America | ||||
| France | ||||
| Japan | ||||
| France | ||||
| South America | ||||
| Africa | ||||
| Africa | ||||
| Australia | ||||
| North America | The largest known dromaeosaurid | |||
†Ammonites
†Ammonitida
- Moffitites
Originating in Lower Albian strata
The following is a list of Ammonite genera whose fossils are geochronologically found first in lower Albian strata. These genera may survive into later portions of the Albian stage, or even into later geological stages. This list should not be thought of in terms of the lifespan of the genera included.
- Aioloceras
- Anacleoniceras
- Anadesmoceras
- Anisoceras
- Arcthoplites
- Brancoceras
- Brewericeras
- Cleoniceras
- Cymahoplites
- Douvilleiceras
- Epileymeriella
- Eubranoceras
- Farnhamia
- Hoplites
- Kossmatella
- Labeceras
- Leconteites
- Lemuroceras
- Leymeriella
- Lyelliceras
- Neobibolites
- Otohoplites
- Oxytropidoceras
- Paracanthoplites
- Parasilesites
- Parengonoceras
- Plictetia
- Prohelicoceras
- Proleymeriella
- Prolyelliceras
- Protohoplites
- Pseudoleymeriella
- Pseudosonneratia
- Puzosia
- Puzosigella
- Rhytidohoplites
- Rossalites
- Silesitoides
- Sokolovites
- Sonneratia
- Tegoceras
- Tetrahoplites
- Tetrahoplitoides
- Zealandites
Originating in Middle Albian strata
The following is a list of Ammonite genera whose fossils are geochronologically found first in middle Albian strata. These genera may survive into later portions of the Albian stage, or even into later geological stages. This list should not be thought of in terms of the lifespan of the genera included.
- Anagaudryceras
- Anahoplites
- Astiericeras
- Dimorphoplites
- Dipoloceras
- Dipoloceroides
- Engonoceras
- Epihoplites
- Euhoplites
- Falciferella
- Falloticeras
- Gastroplites
- Hamitoides
- Hysteroceras
- Isohoplites
- Manuaniceras
- Mojsisoviczia
- Mortoniceras
- Ostlingoceras
- Protengonoceras
- Proturrilitoides
- Pseudhelicoceras
- Scaphamites
- Subarcthoplites
- Sulcohoplites
- Turrilitoides
- Venezoliceras
- Zuluscaphites
Originating in Upper Albian strata
The following is a list of Ammonite genera whose fossils are geochronologically found first in upper Albian strata. These genera may survive into later portions of the Albian stage, or even into later geological stages. This list should not be thought of in terms of the lifespan of the genera included.


- Adkinsites
- Arestoceras
- Beudantiella
- Bhimaites
- Borissiakoceras
- Cainoceras
- Callihoplites
- Cantabrigites
- Cenisella
- Cottreauites
- Cyrtochilus
- Deiradoceras
- Diplasioceras
- Discohoplites
- Ellipsoceras
- Elobiceras
- Eogunnarites
- Eopachydiscus
- Eoscaphites
- Erioliceras
- Ficheuria
- Flickia
- Gaudryceras
- Gazdaganites
- Goodhallites
- Hemiptychoceras
- Hengestites
- Hypengonoceras
- Hyphoplites
- Idiohamites
- Karamaiceras
- Karamaites
- Koloceras
- Lechites
- Lepthoplites
- Lytodiscoides
- Mantelliceras
- Mariella
- Metengonoceras
- Myloceras
- Neogastroplites
- Neoharpoceras
- Neokentoceras
- Neophlycticeras
- Pachydesmoceras
- Paradolphia
- Paraturrilites
- Pervinquieria
- Plesiohamites
- Plesioturrilites
- Pleurohoplites
- Prohysteroceras
- Psilohamites
- Rusoceras
- Salaziceras
- Saltericeras
- Scaphites
- Schloenbachia
- Sciponoceras
- Semenovites
- Spathiceras
- Stoliczkaia
- Stomohamites
- Worthoceras
†Belemnites
| Belemnites of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
 Belemnites | ||||
Nautiloids
| Nautiloids of the Albian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taxa | Presence | Location | Description | Images |
|
 An illustration of a variety of fossil nautiloids. | |||
†Phylloceratida
- Carinophylloceras
References
Notes
- ↑ For a detailed geologic timescale, see Gradstein et al. (2004)
- ↑ See Kennedy et al. (2004) for a description of the GSSP for the Cenomanian
- ↑ Mortimer, Mickey. "List of Dromaeosaurids". Archived from the original on October 3, 2011. Retrieved July 8, 2011.
Literature
- Gradstein, F.M.; Ogg, J.G. & Smith, A.G.; 2004: A Geologic Time Scale 2004, Cambridge University Press.
- Kennedy, W.J.; Gale, A.S.; Lees, J.A. & Caron, M.; 2004: The Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) for the base of the Cenomanian Stage, Mont Risou, Hautes-Alpes, France, Episodes 27, pp. 21–32.
- d'Orbigny, A.C.V.M.; 1842: Paléontologie française: Terrains crétacés, vol. ii. (French)
External links
- GeoWhen Database - Albian
- Mid-Cretaceous timescale, at the website of the subcommission for stratigraphic information of the ICS (The top of the Albian stage is also still visible on their Late Cretaceous timescale)
- Stratigraphic chart of the Lower Cretaceous, at the website of Norges Network of offshore records of geology and stratigraphy
- Albian Stage, Cretaceous Period in Hampshire
| Cretaceous Period | |
|---|---|
| Lower/Early Cretaceous | Upper/Late Cretaceous |
| Berriasian | Valanginian | Hauterivian Barremian| Aptian | Albian |
Cenomanian | Turonian | Coniacian Santonian |Campanian | Maastrichtian |