LRRC4
Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LRRC4 gene.[3][4]
This gene is significantly downregulated in primary brain tumors. The exact function of the protein encoded by this gene is unknown.[4]
References
Further reading
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery.". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Nakashiba T, Ikeda T, Nishimura S, et al. (2000). "Netrin-G1: a novel glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-linked mammalian netrin that is functionally divergent from classical netrins.". J. Neurosci. 20 (17): 6540–50. PMID 10964959.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932.
. PMID 12477932.
- Scherer SW, Cheung J, MacDonald JR, et al. (2003). "Human chromosome 7: DNA sequence and biology.". Science. 300 (5620): 767–72. doi:10.1126/science.1083423. PMC 2882961
 . PMID 12690205.
. PMID 12690205.
- Clark HF, Gurney AL, Abaya E, et al. (2003). "The secreted protein discovery initiative (SPDI), a large-scale effort to identify novel human secreted and transmembrane proteins: a bioinformatics assessment.". Genome Res. 13 (10): 2265–70. doi:10.1101/gr.1293003. PMC 403697
 . PMID 12975309.
. PMID 12975309.
- Lin JC, Ho WH, Gurney A, Rosenthal A (2004). "The netrin-G1 ligand NGL-1 promotes the outgrowth of thalamocortical axons.". Nat. Neurosci. 6 (12): 1270–6. doi:10.1038/nn1148. PMID 14595443.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs.". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928
 . PMID 15489334.
. PMID 15489334.
- Zhang Q, Wang J, Fan S, et al. (2005). "Expression and functional characterization of LRRC4, a novel brain-specific member of the LRR superfamily.". FEBS Lett. 579 (17): 3674–82. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2005.05.058. PMID 15967442.
- Zhang QH, Wang LL, Cao L, et al. (2005). "Study of a novel brain relatively specific gene LRRC4 involved in glioma tumorigenesis suppression using the Tet-on system.". Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai). 37 (8): 532–40. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7270.2005.00079.x. PMID 16077900.
- Fan SQ, Wang JR, Huang H, et al. (2007). "[Function of a novel brain-specific gene LRRC4]". Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 27 (7): 393–6. PMID 16188120.
- Zhang QH, Wu MH, Wang LL, et al. (2005). "Profiling of differentially expressed genes in LRRC4 overexpressed glioblastoma cells by cDNA array.". Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai). 37 (10): 680–7. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7270.2005.00100.x. PMID 16215635.
- Wu M, Huang C, Gan K, et al. (2006). "LRRC4, a putative tumor suppressor gene, requires a functional leucine-rich repeat cassette domain to inhibit proliferation of glioma cells in vitro by modulating the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/protein kinase B/nuclear factor-kappaB pathway.". Mol. Biol. Cell. 17 (8): 3534–42. doi:10.1091/mbc.E05-11-1082. PMC 1525233
 . PMID 16723503.
. PMID 16723503.
- Wu M, Gan K, Huang C, et al. (2007). "LRRC4 controls in vitro invasion of glioblastoma cells through inhibiting RPTP-zeta expression.". J. Neurooncol. 80 (2): 133–42. doi:10.1007/s11060-006-9173-6. PMID 16941076.
- Wu M, Huang C, Li X, et al. (2007). "LRRC4 inhibits glioblastoma cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis by downregulating pleiotropic cytokine expression and responses.". J. Cell. Physiol. 214 (1): 65–74. doi:10.1002/jcp.21163. PMID 17541939.
PDB gallery |
|---|
|
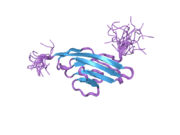
| 2dl9: Solution structure of the Ig-like domain of human Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 4 |
|
|

 . PMID 12477932.
. PMID 12477932. . PMID 12690205.
. PMID 12690205. . PMID 12975309.
. PMID 12975309. . PMID 15489334.
. PMID 15489334. . PMID 16723503.
. PMID 16723503.