Forth and Bargy dialect
| Forth and Bargy dialect | |
|---|---|
| Yola | |
| Native to | Ireland |
| Region | County Wexford |
| Extinct | Mid-19th century |
|
Indo-European
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 |
yol |
| Glottolog |
(insufficiently attested or not a distinct language)yola1237[1] |
| Linguasphere |
52-ABA-bd |
The Forth and Bargy dialect, also known as Yola, is an extinct variety of English once spoken in the baronies of Forth and Bargy in County Wexford, Ireland. It is thought to have evolved from Middle English, which was brought to Ireland during the Norman invasion, beginning in 1169. As such, it was similar to the Fingallian dialect of the Fingal area. Both became extinct in the 19th century, when they were replaced by modern Hiberno-English. The name "Yola" means "old" in the dialect.[2]
History
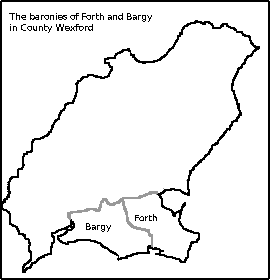
The dialect was spoken in County Wexford, particularly in the baronies of Forth and Bargy. This was the first area English-speakers came to in the Norman invasion of Ireland, supporting the theory that the dialect evolved from the Middle English introduced in that period. As such it is thought to have been similar to Fingallian, which was spoken in the Fingal region north of Dublin. Middle English, the mother tongue of the "Old English" community, was widespread throughout southeastern Ireland until the 14th century; as the Old English were increasingly assimilated into Irish culture, their original language was gradually displaced through Gaelicisation. After this point, the Forth and Bargy dialect and Fingallian were the only attested relicts of this original form of English.[3][4]
Modern English was widely introduced by British colonists during and after the 17th century, forming the basis for the modern Hiberno-English of Ireland. The new varieties were notably distinct from the surviving relict dialects.[3][4] As English continued to spread, both the Forth and Bargy dialect and the Fingal dialect died out in the 19th century.
Phonology
As in the Dutch language, in southwestern varieties of English and (to a lesser extent) in German, most voiceless fricatives in Forth and Bargy became voiced. The Middle English vowels are well-preserved, having only partially and sporadically undergone the changes associated with the Great Vowel Shift.[5]
One striking characteristic of Forth and Bargy was the fact that stress shifted to the second syllable of words in many instances: morsaale "morsel", hatcheat "hatchet", dineare "dinner", readeare "reader", weddeen "wedding", etc.[6]
Grammar
Pronouns
Forth and Bargy pronouns were similar to Middle English pronouns.[7]
| First Person | Second Person | Third Person | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| singular | plural | singular | plural | singular | plural | |
| nom. | Ich | wough/wee | thou | ye | hea, shoo, ? | thye |
| acc. | me | ouse | thee | ye | him, her, it | aam |
| gen. | mee | oure | yer | yer | aar | |
Articles
The definite article was at first a, which was later replaced by the.
Verb
Forth and Bargy verbs had some conservative characteristics. The second and third person plural endings were sometimes -eth as in Chaucerian English. The past participle retained the Middle English "y" prefix as "ee".[7]
Nouns
Some nouns retained the -en plural of ME children, such as been 'bees' and tren 'trees'.
Vocabulary
The glossary compiled by Jacob Poole provides most of what is known about Forth and Bargy vocabulary. Poole was a farmer and member of the Religious Society of Friends from Growtown in the Parish of Taghmon on the border between the baronies of Bargy and Shelmalier.[8] He collected words and phrases from his tenants and farm labourers between 1800 and his death in 1827.
Although most of its vocabulary is Anglo-Saxon in origin, Forth and Bargy contains many borrowings from Irish and French.
Interrogative words
| English | Forth and Bargy | Scots | Frisian | Low Saxon | Dutch | German | Gothic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| who | fho | wha fa in Doric Scots |
wa | wel/wokeen | wie | wer | ƕas |
| what | fade | whit fit in Doric Scots |
wat | wat | wat | was | ƕat |
| when | fan | whan fan in Doric Scots |
wannear | wanneer | wanneer | wann | ƕan |
| where | fidi | whaur faur in Doric Scots |
wêr | wo/woneem | waar | wo | ƕar |
| why | farthoo | why fy in Doric Scots |
wêrom | worüm | waarom | warum | |
| which | wich | whilk | hokker | welk | welk | welche | ƕileiks |
| how | fowe | hou | hoe | wo/woans | hoe | wie | ƕai |
Prepositions
| English | Forth and Bargy | Scots | Frisian | Low Saxon | Dutch | German |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| about | abut | aboot | om/rûn | üm/rund | om/rond | um/rund |
| above | aboo | abuin | boppe | baven | boven | über |
| against | ayenst | agin | tsjin | gegen | tegen | gegen |
| among | amang | amang | ûnder/tusken | mang/twüschen | onder/tussen | unter/zwischen |
| around | arent | aroond | om | üm | om/rond | um |
| at/by | adh/bee | at/bi | by | bi | om/bij | bei |
| before | avar | afore | foar | vöör | voor | vor |
| below/beneath/under | aloghe | ablo/anaith/unner | ûnder | (to)neddern/nedder, ünnen/ünner | beneden/onder | unten/unter |
| beside/next to | besithe/neeshte | asyd/neist | nêst/njonken | blangen/neven | bezijden/naast/neven | neben |
| between/betwixt/'twixt | betweesk/beteesh | atwein/atweish | tusken | twüschen | tussen | zwischen |
| for | vor | for | foar | för | voor | für |
| from | vrom/vrem/vreem | frae | fan | vun | van | von |
| in | i/ing | in/i' | yn | in | in | in |
| out | ut/udh | oot | út | uut | uit | aus |
| over | ower/oer | ower | oer | över | over | über |
| through | trugh | throu | troch | döör | door | durch |
| upon | apan/pa | upon/upo' | op | op | op | auf |
| with | wee | wi | mei | mit | met | mit |
Pronouns
| English | Forth and Bargy | Scots | Frisian | Low Saxon | Dutch | German |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| all | aul | aw/aa | al | all | al | alle |
| any | aany/aught | onie | elts | enig | enig, eender | einige |
| each, every | earchee, earch/erich/everich | ilk, ilka/iverie | eltse | elk, jeed/jeedeen | elk, ieder | jeder |
| few | vew | few/a whein | min | wenig | weining | wenig |
| neither | nother | naither | noch | noch | noch | weder |
| none, nothing | noucht, nodhing | nane, nocht | nimmen, neat | nüms, nix | niemand, niets/niks | niemand, nichts |
| other | ooree/oree | ither | oar | anner | ander, andere | andere |
| some | zim | sum | guon | welke | sommige | einige |
| this, that | dhicke, dhicka | this, that | dizze, dat | dit, düsse, dat | dit, deze, dat | dieser, das |
Other words
| English | Forth and Bargy | Scots | Frisian | Low Saxon | Dutch | German | Irish |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wexford | Weisforthe | Wexford | "Wexford" | "Wexford" | "Wexford" (lit. "West-voorde") |
"Wexford" (lit. "Westfurt") |
Loch Garman |
| sun | zin | sun | sinne | Sünn | zon | Sonne [zɔnə] | Grian |
| land | loan, lhoan | land | lân | Land | land | Land | Talamh |
| day | dei, die | day | dei | Dag | dag | Tag | Iá |
| yourself | theezil | yersel | dysels | du sülvst/sülven | jezelf | du selbst [du zɛlpst], du selber | tú féin |
| friend | vriene | fere | freon | Fründ | vriend | Freund | Cara |
| the | a, ee | the | de, it | de, den, dat | de, het | der, die, das, des, dem, den | an, na |
| thing | dhing | thing | ting | Ding | ding | Ding | rud, ní |
| go | ee-go | gae/gang/gan | gean | gaan | gaan | gehen | dul (go), imeacht (go away) |
| fear | vear | fear | frees | Forcht, Bang, Angst | vrees, angst | Furcht, Angst | eagla |
| old | yola, yole | auld | âld | oold, oll- | oud | alt | sean, seanda, aosta |
Cardinal numbers
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| oan | twye/twyne | dhree | voure | veeve | zeese | zeven | ayght | neen | dhen |
Compare Dorset dialect: one, two, dree, vower, vive, zix, zeven, aïght, nine, ten.
Modern South Wexford English

Diarmaid Ó Muirithe travelled to South Wexford in 1978 to study the English spoken there.[9] His informants ranged in age between 40 and 90. Among the long list of words still known or in use at that time are the following:
- Amain: ‘Going on amain’ = getting on well
- Bolsker: an unfriendly person
- Chy: a little
- Drazed: threadbare
- Fash: confusion, in a fash
- Keek: to peep
- Saak: to sunbathe, to relax in front of the fire
- Quare: 'Very' or 'Extremely'
Amain is a Norman word which means 'of easy use'
Example
A Forth and Bargy song
The following is a Forth and Bargy song, with a rough translation into English.
Yola Zong Well, gosp, c'hull be zeid; mot thee fartoo, an fade; Yerstey w'had a baree, gist ing oor hoane, Joud an moud vrem earchee ete was ee Lough. Mot w'all aar boust, hi soon was ee-teight (There are nine more verses). |
An Old Song Well, gossip, it shall be said; you ask what ails me, & for what; Yesterday we had a goal, just in our hand. Throngs and crowds from each quarter were at the Lough; But with all their bravado, they soon were taught |
Address to Lord Lieutenant in 1836
Congratulatory address in the dialect of Forth and Bargy, presented to the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland the Earl of Mulgrave Constantine Henry Phipps on his visit to Wexford in 1836 taken from the Wexford Independent newspaper of 15 February 1860. The paper's editor Mr Edmund Hore writes:
The most remarkable fact, in reality, in connexion with the address is this. In all probability it was the first time regal or vice-regal ears were required to listen to word of such a dialect; an it is even still more probable that a like event will never happen again; for if the use of this old tongue dies out as fast for the next five-and-twenty years as it has for the same bygone period, it will be utterly extinct and forgotten before the present century shall have closed.
In order for a person not acquainted with the pronunciation of the dialect to form anything like an idea of it, it is first necessary to speak slowly, and remember that the letter a has invariably the same sound, like a in “father”. Double ee sounds like e in “me”, and most words of two syllables the long accent is placed on the last. To follow the English pronunciation completely deprives the dialect of its peculiarities.
To’s Excellencie Constantine Harrie Phipps, y’ Earle Mulgrave, Lord Lieutenant-General and General Governor of Ireland. Ye soumissive Spakeen o’ouz Dwelleres o’ Baronie Forthe, Weisforthe.
MAI’T BE PLESANT TO TH’ECCELLENCIE, – Wee, Vassalès o’ ‘His Most Gracious majesty’, Wilyame ee Vourthe, an, az wee verilie chote, na coshe and loyale dwellerès na Baronie Forthe, crave na dicke luckie acte t’uck neicher th’ Eccellencie, an na plaine grabe o’ oure yola talke, wi vengem o’ core t’gie ours zense o’ y gradès whilke be ee-dighte wi yer name; and whilke we canna zei, albeit o’ ‘Governere’, ‘Statesman’, an alike. Yn ercha and aul o’ while yt beeth wi gleezom o’ core th’ oure eyen dwytheth apan ye Vigere o’dicke Zouvereine, Wilyame ee Vourthe, unnere fose fatherlie zwae oure diaez be ee-spant, az avare ye trad dicke londe yer name waz ee-kent var ee vriene o’ livertie, an He fo brake ye neckares o’ zlaves. Mang ourzels – var wee dwytheth an Irelonde az ure genreale haim – y’ast, bie ractzom o’honde, ee-delt t’ouz ye laas ee-mate var ercha vassale, ne’er dwythen na dicke waie nar dicka. Wee dwyth ye ane fose dais be gien var ee guidevare o’ye londe ye zwae, – t’avance pace an livertie, an, wi’oute vlynch, ee garde o’ generale reights an poplare vartue. Ye pace – yea, we mai zei, ye vast pace whilke bee ee-stent owr ye londe zince th’ast ee-cam, proo’th, y’at wee alane needeth ye giftes o’generale rights, az be displayth bie ee factes o’thie goveremente. Ye state na dicke daie o’ye londe, na whilke be nar fash nar moile, albeit ‘constitutional agitation’, ye wake o’hopes ee-blighte, stampe na yer zwae be rare an lightzom. Yer name var zetch avancet avare ye, e’en a dicke var hye, arent whilke ye brine o’zea an dye craggès o’noghanes cazed nae balke. Na oure gladès ana whilke we dellt wi’ mattoke, an zing t’oure caulès wi plou, wee hert ee zough o’ye colure o’ pace na name o’ Mulgrave. Wi Irishmen ower generale houpes be ee-boud – az Irishmen, an az dwellerès na cosh an loyale o’ Baronie Forthe, w’oul daie an ercha daie, our meines an oure gurles, praie var long an happie zins, shorne o’lournagh an ee-vilt wi benisons, an yersel and oure gude Zovereine, till ee zin o’oure daies be var aye be ee-go to’glade.Standard English Translation
To his Excellency, Constantine Henry Phipps, the Earl of Mulgrave, Lord Lieutenant-General, and General Governor of Ireland. The humble Address of the Inhabitants of the Barony of Forth, Wexford.
MAY IT PLEASE YOUR EXCELLENCY – We, the subjects of his Most Gracious Majesty, William IV, and, as we verily believe, both faithful and loyal inhabitants of the Barony of Forth, beg leave at this favourable opportunity to approach your Excellency, and in the simple dress of our old dialect to pour forth from the strength (or fulness) of our hearts, our sense (or admiration) of the qualities which characterise your name, and for which we have no words but of ‘Governor’, ‘Statesman’, etc. In each and every condition it is with joy of heart that our eyes rest upon the representative of the Sovereign, William IV, under whose paternal rule our days are spent; for before your foot pressed the soil, your name was known to us as the friend of liberty, and he who broke the fetters of the slave. Unto ourselves – for we look on Ireland to be our common country – you have with impartial hand ministered the laws made for every subject, without regard to this party or that. We behold in you one whose days are devoted to the welfare of the land you govern, to promote peace and liberty – the uncompromising guardian of the common right and public virtue. The peace – yes, we may say the profound peace – which overspreads the land since your arrival, proves that we alone stood in need of the enjoyment of common privileges, as is demonstrated by the results of your government. The condition, this day, of the country, in which is neither tumult nor disorder, but that constitutional agitation, the consequence of disappointed hopes, confirms your rule to be rare and enlightened. Your fame for such came before you even into this retired spot, to which neither the waters of the sea below nor the mountains above caused any impediment. In our valleys, where we were digging with the spade, or as we whistled to our horses in the plough, we heard the distant sound of the wings of the dove of peace, in the word Mulgrave. With Irishmen our common hopes are inseparably bound up – as Irishmen, and as inhabitants, faithful and loyal, of the Barony Forth, we will daily and every day, our wives and our children, implore long and happy days, free from melancholy and full of blessings, for yourself and our good Sovereign, until the sun of our lives be gone down the dark valley (of death).
"The maiden of Rosslare"
This following is a Yola poem containing correct spelling and accents from an original document;
Ee mýdhe ov Rosslaarè |
The maiden of Rosslare |
A guide for pronunciation
ch and ck are pronounced as tch, example ich (pronounced itch) dhicke pronounced dhitch-eh) ([tʃ]) gh - a guttural sound the same as the gh in lough ([ɣ])
eou (jow/yow) oo (o as in boot) ([uː]) ee (e as in bee) ([iː]) aa (as in man but longer) ([aː])
a is in "cat" ([æ]), á as in "father" ([a]) e as in "let" ([ɛ]), é as in "may" ([e]), i as in "bit" ([ɪ]), í (ee) as in "bee" ([i]), o as in "spot" ([ɔ]), ó as in "boat" ([o]), u as in "but" ([ʌ]), ú as in "boot" ([u]), y as a mix between the in spin and the ee in bee (possibly [ʏ]), ý an oiy sound not in English (possibly [y]). speak slowly to find correct pronunciation, e's after words are pronounced (examples :ross-laar-ay(rosslaaré), moidh-eh(mýdhe))
See also
Notes
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2016). "Yola". Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Hickey, Raymond (2005). Dublin English: Evolution and Change. John Benjamins Publishing. p. 238. ISBN 90-272-4895-8.
- 1 2 Hickey, Raymond (2005). Dublin English: Evolution and Change. John Benjamins Publishing. pp. 196–198. ISBN 90-272-4895-8.
- 1 2 Hickey, Raymond (2002). A Source Book for Irish English. John Benjamins Publishing. pp. 28–29. ISBN 9027237530.
- ↑ Hickey, R. (1988). A lost Middle English dialect. Historical Dialectology: Regional and Social, 37, 235.
- ↑ O'Rahilly, T. F (1932). "The Accent in the English of South-east Wexford". Irish Dialects Past and Present. Dublin: Browne and Nolan. pp. 94–98. Reprinted 1972 by the Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, ISBN 0-901282-55-3.
- 1 2 Poole 1867, p.133.
- ↑ Jacob Poole of Growtown.
- ↑ Dolan, T. P.; D. Ó Muirithe (1996). The Dialect of Forth and Bargy Co. Wexford, Ireland. Four Courts Press. ISBN 1-85182-200-3.
References
- Dolan, T. P.; D. Ó Muirithe (1996). The Dialect of Forth and Bargy Co. Wexford, Ireland. Four Courts Press. ISBN 1-85182-200-3.
- Hickey, Raymond (2005). Dublin English: Evolution and Change. John Benjamins Publishing. ISBN 90-272-4895-8.
- Hickey, Raymond (2002). A Source Book for Irish English (PDF). Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing. pp. 28–29. ISBN 90-272-3753-0.
ISBN 1-58811-209-8 (US)
- Ó Muirithe, Diarmaid (1977). "The Anglo-Norman and their English Dialect of South-East Wexford". The English Language in Ireland. Mercier Press. ISBN 0853424527.
- O'Rahilly, T. F (1932). "The Accent in the English of South-east Wexford". Irish Dialects Past and Present. Dublin: Browne and Nolan. pp. 94–98.
- Poole's Glossary (1867) – Ed. Rev. William Barnes (Editorial 'Observations')
- Poole's Glossary (1979) – Ed. Dr. D. O'Muirithe & T.P. Dolan (Corrected Etymologies)
External links
- Jacob Poole of Growtown — And the Yola Dialect
- A Glossary of Yola
- Songs sung in the Yola language on RTE,i.e. archives (under Kilmore Christmas carols)