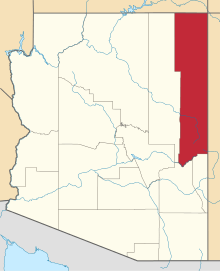
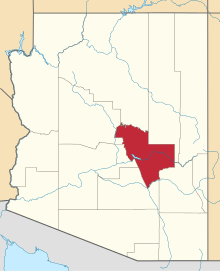
Fort Apache Indian Reservation
 Seal of the White Mountain Apache tribe | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 12,429 | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
|
| |
| Languages | |
| Western Apache, English | |
| Religion | |
| Christianity, Native American Church, traditional tribal religion | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Western Apache, San Carlos Apache, Navajo |
The Fort Apache Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation in Arizona, United States, encompassing parts of Navajo, Gila, and Apache counties. It is home to the federally recognized White Mountain Apache Tribe of the Fort Apache Reservation, a Western Apache tribe. It has a land area of 2,627 square miles (6,800 km2) and a population of 12,429 people as of the 2000 census.[1] The largest community is in Whiteriver.
History
In 1871 General George Crook enrolled 50 White Mountain Apache men to serve as scouts for his army during the Fifteen-Year Apache Wars. These wars were ended with the surrender of the Chiricahua leader Geronimo in 1886. Because of the Scouts’ service to General Cook during the Apache Wars, their tribe was able to maintain a large portion of their homeland as the White Mountain Apache reservation.
In 1922, the U.S. Army left Fort Apache and in 1923, the Bureau of Indian Affairs’ Theodore Roosevelt Indian Boarding School was established on the site.[2] The school was designated a National Historic Landmark in 2012, as a component of Fort Apache Historic Park. It is still operating as a tribal middle-school facility.[3]
The White Mountain Apaches began to progress as a community and ultimately created their own constitution and established a tribal council that oversaw all tribe owned property, local businesses and governance in 1936.
Geography
The Fort Apache Indian Reservation is covered mostly by pine forests and is habitat to a variety of forest wildlife. It is located directly south of the Mogollon Rim. The highest point in the reservation is Baldy Peak, with an elevation of 11,403 feet (3,476 m).
Economy
The tribe operates the Sunrise ski resort and the Hon Dah Resort Casino.[4] It has built the Apache Cultural Center & Museum, constructed in the traditional style of a gowa.
Other attractions within the reservation include the Fort Apache Historic Park, which has 27 buildings from the historic fort and a 288-acre (117 ha) National Historic District; and other historic sites. Kinishba Ruins, an ancient archeological site (AD 1150–1350) of the western Pueblo culture, is a National Historic Landmark and is located on nearby associated tribal trust lands. Appointments may be made to visit the site.
Demographics
According to the Arizona Census Bureau, the Fort Apache Indian Reservation, which is located in Navajo County, is populated by small communities. North Fork, Whiteriver, Fort Apache, East Fork, Rainbow City, Cibecue, Hon-Dah, Mcnary, Turkey Creek, and Seven Mile are the communities that comprise the Fort Apache Reservation which has a total population of 22,036.[5]
Communities
_on_display%2C_ca.1900_(CHS-3555).jpg)
- Carrizo
- Cibecue
- Hondah
- McNary
- Whiteriver
Gallery
-

Apache warriors near the fort, 1873
-

White Mountain Apache, photographed prior to 1903 by Edward S. Curtis
See also
- Apache
- Art of the American Southwest
- Battle of Cibecue Creek
- Battle of Fort Apache
- Sunrise Park Resort
References
- ↑ Fort Apache Reservation, Arizona, United States Census Bureau
- ↑ for a full history of the school and description as of 1970, see http://azmemory.azlibrary.gov/cdm/ref/collection/feddocs/id/1573
- ↑ http://cronkitenewsonline.com/2012/03/fort-apache-earns-historic-designation-for-role-in-tribal-assimilation/
- ↑ hon-dah.com
- ↑ http://www.census.gov/prod/cen2010/cph-2-4.pdf
- Fort Apache Reservation, Arizona United States Census Bureau
- Goddard, Pliny Earle (1920). White Mountain Apache texts. The Trustees. Retrieved 24 August 2012.
- Goodwin, Grenville. Myths and Tales of the White Mountain Apache. University of Arizona Press (March 1, 1994).
External links
- White Mountain Apache Tribe – Official website
- "Fort Apache Historic Park and Kinishba Ruins", Nohwike’ Bágowa (House of Our Footprints), White Mountain Apache Culture Center & Museum
- Fort Apache Heritage Foundation
- White Mountain Apache Tribe, Arizona Intertribal Council
Coordinates: 33°55′43″N 110°07′55″W / 33.92861°N 110.13194°W