Grey problem
Grey problem (gray problem) is a term for an IT problem where the causing technology is unknown or unconfirmed. Common grey problems are:
- Intermittent errors;
- Intermittent incorrect output, or;
- Transient performance problems.
Because the causing technology is not clear IT departments often find it difficult to allocate the problem to a Technical Support Team (platform team).
Background
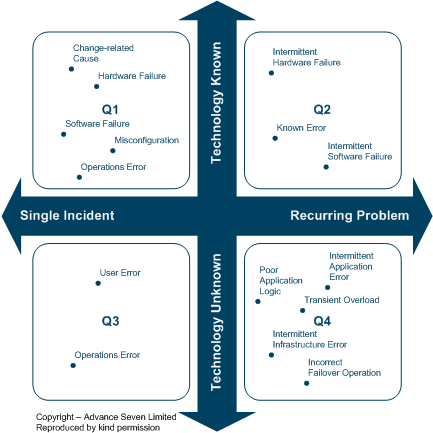
Combining frequency and causing technology information can provide a view of the complexity of a problem and so indicate how difficult it will be to investigate (see Figure 1).
The problems in each quadrant have certain characteristics:
Q1 - In a typical IT department 80 to 90% of problems are solid faults that are easily tracked down to a causing technology. The appropriate technical or platform support team efficiently deals with these problems every day.
Q2 - Some recurring problems are due to a Known Error, or are obviously being caused by a particular hardware or software component. These problems are handled by technical support people working with suppliers.
Q3 - Every so often a one-off problem occurs, and the cause of these may never be found.
Q4 – The technical ownership of these issues is unclear and so they are referred to as “grey problems” i.e. not black and white.
Impact
Grey problems have a significant impact on IT service, and:
- Form the bulk of ongoing recurring problems
- Create a disproportionately high IT support workload
- Give a pointer to more serious problems to come
- Cause the business to adjust practices around the problem
Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) perspective
Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) Service Operations implies that grey problems should be handled through a Problem Solving Group under the direction of the Problem Management function. In practice, even those IT organisations that have adopted ITIL rarely have a procedure to handle a grey problem, leaving it to bounce between Technical Support Teams as each denies that their technology is to blame.
See also
Further reading
- Offord, Paul (2011). RPR: A Problem Diagnosis Method for IT Professionals. Advance Seven Limited. ISBN 978-1-4478-4443-3.
- Grey problem case study
- Presentation to the British Computer Society