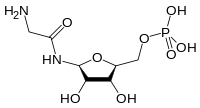
Glycineamide ribonucleotide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-[(2-aminoacetyl)amino]-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyldihydrogen phosphate | |
| Other names
Glycineamide ribotide, GAR | |
| Identifiers | |
| 10074-18-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 141370 |
| MeSH | Glycineamide+ribonucleotide |
| PubChem | 160913 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H15N2O8P | |
| Molar mass | 286.18 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Glycineamide ribonucleotide (or GAR) is an intermediate in de novo purine biosynthesis.
It is formed from phosphoribosylamine by the enzyme phosphoribosylamine—glycine ligase. In the next step of purine biosynthesis the enzyme phosphoribosylglycinamide formyltransferase acts on GAR to form FGAR.
GAR formation is stimulated by Luteinizing hormone (LH) and Chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) via activation of Glc-6-P-dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.49)[1][2]
Synonyms
Several names are associated with GAR:
- 5'-p-Ribosylglycinamide
- 5'-p-Ribosylglycineamide
- 5'-Phosphoribosyl-glycineamide
- 5'-Phosphoribosylglycinamide
- 5'-Phosphoribosylglycineamide
- Glycineamide ribotide
- Glycinamide ribonucleotide
- Glycineamide ribonucleotide
- N(1)-(5-Phospho-D-ribosyl)glycinamide
- N-Glycyl-5-O-phosphono-D-ribofuranosylamine
- N1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)glycinamide
References
- ↑ "SMPDB: Glycineamideribotide". August 24, 2015.
- ↑ "Human Metabolome Database: Glycineamideribotide". August 24, 2015.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 12/1/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.