Epolactaene
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
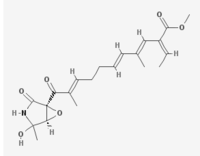
| IUPAC name
Methyl (2E,3E,5E,9E)-2-ethylidene-11-[(1R,5R)-4-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-oxo-6-oxa-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexan-1-yl]-4,10-dimethyl-11-oxoundeca-3,5,9-trienoate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| PubChem | 6442272 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H27NO6 | |
| Molar mass | 389.45 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Epolactaene is a neuritogenic fungal isolate.[1][2][3]
References
- ↑ Kakeya, H; Takahashi, I; Okada, G; Isono, K; Osada, H (1995). "Epolactaene, a novel neuritogenic compound in human neuroblastoma cells, produced by a marine fungus". The Journal of antibiotics. 48 (7): 733–5. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.48.733. PMID 7649877.
- ↑ Nagumo Y, Kakeya H, Shoji M, Hayashi Y, Dohmae N, Osada H (2005). "Epolactaene binds human Hsp60 Cys442 resulting in the inhibition of chaperone activity.". Biochem J. 387 (Pt 3): 835–40. doi:10.1042/BJ20041355. PMC 1135015
 . PMID 15603555.
. PMID 15603555. - ↑ Mizushina Y, Kuramochi K, Ikawa H, Kuriyama I, Shimazaki N, Takemura M, et al. (2005). "Structural analysis of epolactaene derivatives as DNA polymerase inhibitors and anti-inflammatory compounds.". Int J Mol Med. 15 (5): 785–93. doi:10.3892/ijmm.15.5.785. PMID 15806299.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/30/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.