Dialkylphosphinic acid
Dialkylphosphinic acids are organophosphorus compounds with the formula R2PO2H, where R is any alkyl group. They are phosphorus(V) compounds with tetrahedral molecular geometry. Under the brand names Aerophine and Cyanex, they are used in extraction and separation, i.e., hydrometallurgy, of metal salts from ore extracts.[1] Characteristically the organic substituents are branched to confer solubility and preclude crystallization.[2][3]
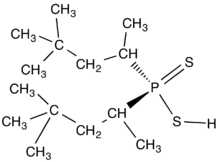
Chemical structure of the dithiophosphinic acid called Cyanex 301.
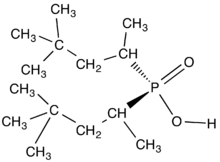
chemical structure of a dialkylphosphinic acid called Cyanex 272.
The dithiodialkyphosphinic acids (R2PS2H) are related to the diorganodithiophosphates with the formula (RO)2PS2H, which are also used as complexing agents in the purification of metals. The phosphates are more prone to hydrolysis owing to the greater lability of the RO-P linkage vs the direct C-P bond.
References
- ↑ J. Svara, N. Weferling, T. Hofmann "Phosphorus Compounds, Organic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2006. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_545.pub2
- ↑ Ayanda, Olushola S.; Adekola, Folahan A.; Baba, Alafara A.; Ximba, Bhekumusa J.; Fatoki, Olalekan S. "Application of Cyanex extractant in Cobalt/Nickel separation process by solvent extraction" International Journal of Physical Sciences 2013, vol. 8, pp. 89-97. doi:10.5897/IJPS12.135
- ↑ I.Yu. Fleitlikh, N.A. Grigorieva, , V.I. Kuz'min, G.L. Pashkov "Redox processes during cobalt extraction with bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)dithiophosphinic acid" Hydrometallurgy 2012, volumes 129–130, pp. 43–49. doi:10.1016/j.hydromet.2012.08.009
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/26/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.