Daphoeninae
| Daphoeninae Temporal range: 42–16.3 Ma | |
|---|---|
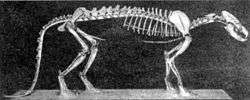 | |
| Daphoenodon skeleton. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | †Amphicyonidae |
| Subfamily: | Daphoeninae |
| Type species | |
| †Daphoenus vetus | |
| Genera | |
The Daphoeninae are an extinct subfamily of dog-like, terrestrial carnivores, which belonged to the family Amphicyonidae of the suborder Caniformia. The group inhabited North America from the Early Eocene subepoch to the Early Miocene subepoch 42—16.3 million years ago (Mya), existing for about 25.7 million years.[1]
Fossil distribution
Daphoenus fossils found in late Oligocene rocks in the Great Plains are dated about 28 million years old. Daphoenus survived to 27 Mya in the Pacific Northwest in the John Day beds of Oregon.[2] Other sites include: Alachua County, Florida (Whitneyan) estimated at 31.1—24.3 Ma., Tecuya Canyon, California (Arikareean age) 30.8—20.6 Ma., Haystack Member Formation, Wheeler County, Oregon (Hemingfordian) 20.6—16.3 Mya, Lac Pelletier, Alberta, Canada (Duchesnean) around 42 Mya.
References
- ↑ Paleobiology Database: Daphoenus, age range and collections
- ↑ Hunt, Robert M., Jr. (2004). "Global Climate and the Evolution of Large Mammalian Carnivores during the Later Cenozoic in North America" (PDF). Cenozoic Carnivores and Global Climate.