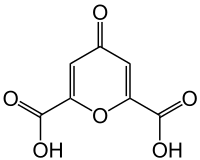
Chelidonic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
4-Oxo-4H-pyran-2,6-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Jerva acid; Jervaic acid; Jervasic acid; γ-Pyrone-2,6-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 99-32-1 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 7153 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.499 |
| PubChem | 7431 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H4O6 | |
| Molar mass | 184.10 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 257 °C (495 °F; 530 K)[1] (decomposes) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Chelidonic acid is a heterocyclic organic acid with a pyran skeleton.
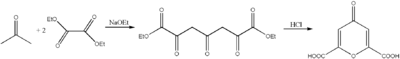
Chelidonic acid can be prepared in two steps from diethyl oxalate and acetone:[1][2]
It occurs naturally in plants of the Asparagales order.
References
- 1 2 E. Raymond Riegel and F. Zwilgmeyer (1937). "Chelidonic acid". Org. Synth. 17: 40.; Coll. Vol., 2, p. 126
- ↑ G. Horvath; C. Russa; Z. Koentoes; J. Gerencser (1999). "A new Efficient Method for the Preparation of 2,6-Pyridinedihiethyl Ditosylates from Dimethyl 2,60-Pyridinedicarboxylates". Synth. Comm. 29 (21): 3719–3732. doi:10.1080/00397919908086011.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/28/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.