Carleton Winslow


Carleton Monroe Winslow (1876–1946), also known as Carleton Winslow Sr., was an American architect, and key proponent of Spanish Colonial Revival architecture in Southern California in the early 20th Century.
Biography
Winslow was born in Damariscotta, Maine, studied at the Art Institute of Chicago and at the École des Beaux-Arts, and joined the office of Bertram Goodhue in time for the planning of the 1915 San Diego Panama–California Exposition. Winslow is the one "credited for choosing" Spanish Colonial style for that project, a choice with a vernacular regional precedent.[1]
He moved to Southern California in 1917, completed the Los Angeles Public Library after Goodhue's 1924 death, and also pursued his own commissions, including a number of Episcopal churches. With Clarence Stein he wrote "The architecture and the gardens of the San Diego Exposition".
His son, Carleton Winslow, Jr. (1919–1983) was also an architect, specializing in churches in Southern California, and an architectural history professor and author.
Work
- St. James Episcopal Church, South Pasadena, as associate of Cram, Goodhue & Ferguson, 1907[2]
- All Saints' Episcopal Church, San Diego, 1913, with William S. Hebbard
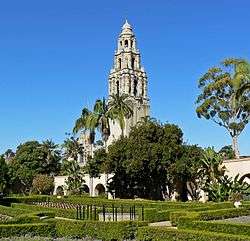
- multiple buildings at the Panama–California Exposition, 1915, in collaboration with Bertram Goodhue; solely credited for certain structures including the Botanical Building
- multiple buildings at the Bishop's School (1916 Bishops Chapel, 1930 Bishops Chapel Tower, 1930 second story and dome of Bentham Hall, 1934 Wheeler Bailey Library), some with architectural sculpture, La Jolla, California
- Casa Dorinda, private mansion for Henry W.H. Bliss and wife Anna Dorinda Blaksley, Montecito, California, 1916[3][4]
- Santa Barbara Museum of Natural History, Santa Barbara, California, 1916[5]
- studio for painter Adolfo Müller-Ury, 3400 Monterey Road, San Marino, California, 1923 (finished late 1924)
- Los Angeles Public Library, completing the project after Bertram Goodhue's death in 1924
- Santa Barbara Public Library, 1924
- Carthay Circle Theatre, with Dwight Gibbs, Mid-Wilshire district of Los Angeles, 1926[6] (razed)
- First Baptist Church, Pasadena, with Frederick Kennedy, 1926 [7]
- Bel-Air Country Club, Bel Air, Los Angeles, California, 1926[8]
- design of 18 stained glass windows for the passenger liner City of Honolulu, 1927
- Ojai Library, part of the Ventura County Library System, Ojai, California, 1928
- St Mary of the Angels Church, Hollywood, 1930
- St. Mark's Episcopal Church, Glendale, California, Winslow's last design and completed by Louis A. Thomas, 1948[9]
References
- ↑ http://www.oac.cdlib.org/data/13030/vs/kt6n39r9vs/files/kt6n39r9vs.pdf
- ↑ An architectural guidebook to Los Ángeles By David Gebhard, Robert Winter page 436
- ↑ Gebhard, Patricia (2005). George Washington Smith: architect of the Spanish colonial revival. Layton, Utah: Gibbs Smith. p. 32. ISBN 1-58685-510-7.
- ↑ Hartmann, Peter; Wright, Stacey (January 12, 2013) "Casa Dorinda - Montecito's Downton Abbey" Archived April 2, 2015, at the Wayback Machine. Santa Barbara Edhat
- ↑ https://digital.lib.washington.edu/architect/architects/789/
- ↑ https://digital.lib.washington.edu/architect/structures/1240/
- ↑ An architectural guidebook to Los Ángeles By David Gebhard, Robert Winter page 416
- ↑ Architectural Forum, March 1930
- ↑ An architectural guidebook to Los Ángeles By David Gebhard, Robert Winter page 335
External links
- Pacific Coast Architecture Database (PCAD): Carleton Winslow — biography and list of works.