Cardamomin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
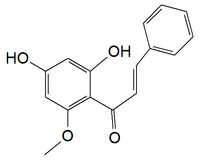
| IUPAC name
(E)-1-(2,4-dihydroxy-6-methoxyphenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one | |
| Other names
(2E)-1-(2,4-Dihydroxy-6-methoxyphenyl)-3-phenyl-2-propen-1-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| 19309-14-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL378104 |
| ChemSpider | 557026 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.189.861 |
| PubChem | 641785 |
| UNII | H8KP1OJ8JX |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H14O4 | |
| Molar mass | 270.27 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Cardamomin (also known as cardamonin) is a chalconoid that has been isolated from several plants including Alpinia katsumadai[1] and Alpinia conchigera.[2] It has received growing attention from the scientific community due to the expectations toward its benefits to human health.[3]
References
- ↑ Kimura, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Yoshida, I. (1968). "Studies on the constituents of Alpinia. XII. On the constituents of the seeds of Alpinia katsumadai hayata. I. The structure of cardamomin". Yakugaku Zasshi. 88 (2): 239–241. PMID 5692492.
- ↑ Lee, J. -H.; Jung, H. S.; Giang, P. M.; Jin, X.; Lee, S.; Son, P. T.; Lee, D.; Hong, Y. S.; Lee, K.; Lee, J. J. (2005). "Blockade of Nuclear Factor- B Signaling Pathway and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Cardamomin, a Chalcone Analog from Alpinia conchigera". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 316 (1): 271–278. doi:10.1124/jpet.105.092486. PMID 16183703.
- ↑ Gonçalves, Luís Moreira (2014). "An Overview on Cardamonin". Journal of Medicinal Food. 17 (6): 633–640. doi:10.1089/jmf.2013.0061.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/22/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.