CTBS
This article is about an enzyme. For Comprehensive Tests of Basic Skills, see CTB/McGraw-Hill.
| CTBS | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | CTBS, CTB, chitobiase | ||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 1921495 HomoloGene: 3231 GeneCards: CTBS | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||||||
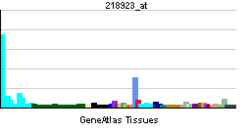 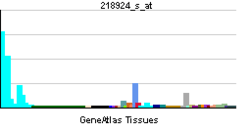 | |||||||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 1: 84.55 – 84.57 Mb | Chr 3: 146.45 – 146.47 Mb | |||||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [1] | [2] | |||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
Di-N-acetylchitobiase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CTBS gene.[3][4][5]
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Fisher KJ, Aronson NN Jr (Apr 1992). "Characterization of the cDNA and genomic sequence of a G protein gamma subunit (gamma 5)". Mol Cell Biol. 12 (4): 1585–91. PMC 369601
 . PMID 1549114.
. PMID 1549114. - ↑ Ahmad W, Li S, Chen H, Tuck-Muller CM, Pittler SJ, Aronson NN Jr (Aug 1995). "Lysosomal chitobiase (CTB) and the G-protein gamma 5 subunit (GNG5) genes co-localize to human chromosome 1p22". Cytogenet Cell Genet. 71 (1): 44–6. doi:10.1159/000134059. PMID 7606925.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: CTBS chitobiase, di-N-acetyl-".
Further reading
- Aronson NN, Halloran BA (2006). "Optimum substrate size and specific anomer requirements for the reducing-end glycoside hydrolase di-N-acetylchitobiase.". Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 70 (6): 1537–41. doi:10.1271/bbb.60183. PMID 16794344.
- Kamioka Y, Fukuhara S, Sawa H, et al. (2004). "A novel dynamin-associating molecule, formin-binding protein 17, induces tubular membrane invaginations and participates in endocytosis.". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (38): 40091–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M404899200. PMID 15252009.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932.
. PMID 12477932. - Hutchinson T, Dwivedi K, Rastogi A, et al. (2002). "N-acetyl beta-D-glucosaminidase is not attached to human sperm membranes through the glycosylphosphatidyl inositol (GPI)-anchor.". Asian J. Androl. 4 (1): 27–33. PMID 11907625.
- Liu B, Ahmad W, Aronson NN (1999). "Structure of the human gene for lysosomal di-N-acetylchitobiase.". Glycobiology. 9 (6): 589–93. doi:10.1093/glycob/9.6.589. PMID 10336991.
- Aronson NN, Backes M, Kuranda MJ (1989). "Rat liver chitobiase: purification, properties, and role in the lysosomal degradation of Asn-linked glycoproteins.". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 272 (2): 290–300. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(89)90222-1. PMID 2751306.
- Fisher KJ, Aronson NN (1992). "Cloning and expression of the cDNA sequence encoding the lysosomal glycosidase di-N-acetylchitobiase.". J. Biol. Chem. 267 (27): 19607–16. PMID 1527079.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/6/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.