Butyl acrylate
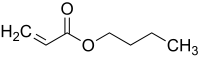 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Butyl prop-2-enoate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| 141-32-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:3245 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1546388 |
| ChemSpider | 8514 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.983 |
| EC Number | 205-480-7 |
| KEGG | C10921 |
| PubChem | 8846 |
| RTECS number | UD3150000 |
| UNII | 705NM8U35V |
| UN number | 2348 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 128.17 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid[1] |
| Odor | Strong, fruity[1] |
| Density | 0.89 g/mL (20°C)[1] |
| Melting point | −64 °C; −83 °F; 209 K [1] |
| Boiling point | 145 °C; 293 °F; 418 K [1] |
| 0.1% (20°C)[1] | |
| Solubility | ethanol, ethyl ether, acetone, carbon tetrachloride (slight) |
| Vapor pressure | 4 mmHg (20°C)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R10-R36/37/38-R43 |
| S-phrases | (S2)-S9 |
| Flash point | 39 °C; 103 °F; 313 K [1] |
| 267 °C[2] | |
| Explosive limits | 1.5% - 9.9%[1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
1800 mg/kg (dermal, rabbit)[3] |
| LC50 (median concentration) |
1000 ppm (4 hr)[3] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 10 ppm (55 mg/m3)[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Butyl acrylate is a chemical used in manufacturing.
Applications
Butyl acrylate is used in paints, sealants, coatings, adhesives, fuel, textiles, plastics, and caulk.[4]
Biochemistry
In rodent models, butyl acrylate is metabolized by carboxylesterase or reactions with glutathione; this detoxification produces acrylic acid, butanol, and mercapturic acid waste, which is excreted in the urine, feces, and as carbon dioxide.[5][6][7]
Production
Butyl acrylate can be produced in several reactions. Acetylene, 1-butyl alcohol, carbon monoxide, nickel carbonyl, and hydrochloric acid can react to make butyl acrylate. Another synthesis of butyl acrylate involves the reaction of butanol with methyl acrylate or acrylic acid.[4]
Safety
It is highly reactive and polymerizes easily when exposed to heat or peroxides; therefore, commercial preparations may contain a polymerization inhibitor. It reacts easily with strong acids and bases, amines, halogens, hydrogen compounds, and oxidizers. Butyl acrylate is designated a Class II Combustible Liquid.[1] It can be stabilized with hydroquinone or hydroquinone ethyl ether.[2]
People can be exposed to butyl acrylate via breathing it in, skin absorption, swallowing it, or eye contact. Symptoms of exposure include irritation of the eyes, skin, and upper respiratory tract; sensitization dermatitis; corneal necrosis; nausea; vomiting; diarrhea; abdominal pain; cough; sore throat; pulmonary edema; and difficulty breathing (dyspnea).[1][3][4]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0075". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- 1 2 "Butyl Acrylate". International Chemical Safety Cards. NIOSH. July 1, 2014.
- 1 2 3 "N-Butyl Acrylate". OSHA/NIOSH. September 28, 2011.
- 1 2 3 "Butyl Acrylate". PubChem. November 28, 2015.
- ↑ "Screening Information Data Set for n-Butyl acrylate, CAS #141-32-2". Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. October 2002. Archived from the original on 2015-11-07.
- ↑ Zondlo Fiume M (2002). "Final report on the safety assessment of Acrylates Copolymer and 33 related cosmetic ingredients". Int. J. Toxicol. 21 Suppl 3: 1–50. doi:10.1080/10915810290169800. PMID 12537929.
- ↑ "Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans". Geneva: World Health Organization: IARC. 1999.