Bothriechis rowleyi
| Bothriechis rowleyi | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Subphylum: | Vertebrata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Viperidae |
| Subfamily: | Crotalinae |
| Genus: | Bothriechis |
| Species: | B. rowleyi |
| Binomial name | |
| Bothriechis rowleyi (Bogert, 1968) | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
- Common names: Mexican palm-pitviper.[2]
Bothriechis rowleyi is a venomous pit viper species found in Mexico. No subspecies are currently recognized.[3]
Etymology
The specific name, rowleyi, is in honor of American ornithologist John Stuart Rowley, who was one of the collectors of the holotype.[4]
Description
B. rowleyi is slender and green with a prehensile tail. Adults grow to a total length (including tail) of at least 97.3 centimetres (38.3 in)[2]
Geographic range
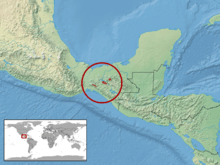
B. rowleyi is found in Mexico in southeastern Oaxaca and northern Chiapas. Occurs in cloud forests at 1,500–1,830 metres (4,920–6,000 ft) altitude. The type locality given is "a ridge that extends northward from Rancho Vicente, Colonia Rodolfo Figueroa, approximately 5 miles west of Cerro Baúl. The site is at an elevation of approximately 1,520 metres (4,990 ft), on the headwaters of the Río Grijalva, roughly 30 kilometres (19 mi) to the north and slightly to the east of San Pedero Tapánatepec, in the Distrito de Juchitán, Oaxaca, Mexico."[1]
Conservation status
The species B. rowleyi is classified as Vulnerable (VU) on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species with the following criteria: B1ab(iii)+2ab(iii) (v3.1, 2001).[5] A species is listed as such when the best available evidence indicates that the extent of occurrence is estimated to be less than 20,000 square kilometres (7,700 sq mi), that estimates indicate the population to be severely fragmented or known to exist at no more than 10 locations, and that a continuing decline has been observed, inferred or projected, in the area, extent and/or quality of habitat. In addition, the area of occupancy is estimated to be less than 2,000 square kilometres (770 sq mi). It is therefore considered to be facing a high risk of extinction in the wild. The population trend is down. Year assessed: 2007.[6]
See also
- List of crotaline species and subspecies
- Crotalinae by common name
- Crotalinae by taxonomic synonyms
- Snakebite
References
- 1 2 McDiarmid RW, Campbell JA, Touré TA (1999). Snake Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, Volume 1. Washington, District of Columbia: Herpetologists' League. 511 pp. ISBN 1-893777-00-6 (series). ISBN 1-893777-01-4 (volume).
- 1 2 Campbell JA, Lamar WW (2004). The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere. 2 volumes. Ithaca and London: Comstock Publishing Associates. 870 pp. 1,500 plates. ISBN 0-8014-4141-2.
- ↑ "Bothriechis rowleyi". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 14 September 2007.
- ↑ Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. ISBN 978-1-4214-0135-5. (Bothriechis rowleyi, p. 228).
- ↑ Bothriechis rowleyi at the IUCN Red List. Accessed 14 September 2007.
- ↑ 2001 Categories & Criteria (version 3.1) at the IUCN Red List. Accessed 14 September 2007.
Further reading
- Bogert CM (1968). "A New Arboreal Pit Viper of the Genus Bothrops from the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, Mexico". American Museum Novitates (2341): 1-14. (Bothrops rowleyi, new species).
External links
- Bothriechis rowleyi at the Reptarium.cz Reptile Database. Accessed 14 September 2007.
