Vanaspati (raga)
| Carnatic music |
|---|
Tanjavur-style Tambura |
| Concepts |
| Compositions |
| Instruments |
|
Vanaspati (meaning the lord of the forest) is a rāgam in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). It is the 4th melakarta rāgam in the 72 melakarta rāgams of Carnatic music, following the Katapayadi sankhya system. In the Muthuswami Dikshitar school of music, this raga is called Bhānumati.[1][2][3]
Structure and Lakshana
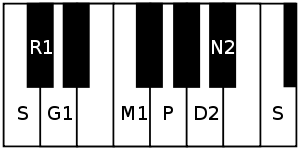
Vanaspati is the 4th rāgam in the 1st chakra Indu of the melakarta system. Its mnemonic name is Indu-Bhu. Its mnemonic phrase is sa ra ga ma pa dhi ni.[2] Its ārohaṇa-avarohaṇa structure is as follows (see swaras in Carnatic music for details on this notation):
- ārohaṇa S R1 G1 M1 P D2 N2 S
- avarohaṇa S N2 D2 P M1 G1 R1 S
Shuddha rishabham, shuddha gandharam, shuddha madhyamam, chathusruthi dhaivatham and kaisiki nishadham are the swaras used in this scale. As it is a melakarta rāgam, by definition it is a sampoorna rāgam (has all seven notes in ascending and descending scale). It is the shuddha madhyamam equivalent of Navaneetam, which is the 40th melakarta rāgam.
Asampurna Melakarta
Bhānumati is the 4th Melakarta in the original list compiled by Venkatamakhin. The notes used in the scale are the same, but the ascending scale is different. It is a shadava-sampurna raga (6 notes in ascending scale, while full 7 are used in descending scale).[4]
Janya rāgams
Rasāli is one of the better known of few janya ragams (derived scales) associated with Vanaspati. See List of janya rāgams for full list of rāgams associated with Vanaspati.
Compositions
- Pariyachakama composed by Tyagaraja in raga Vanaspati.
- ĒswarĪ JagadĪswari composed by Dr. M. Balamuralikrishna
- Brihadamba madamba, Matsyavatara and Guruguha swamini composed by Muthuswamy Dikshitar in raga Bhanumati.
Related rāgams
This section covers the theoretical and scientific aspect of this rāgam.
Vanaspati's notes when shifted using Graha bhedam, yields a minor melakarta rāgam Mararanjani. Graha bhedam is the step taken in keeping the relative note frequencies same, while shifting the shadjam to the next note in the rāgam. For further details and an illustration refer Graha bhedam on Vanaspati.
References
- ↑ Sri Muthuswami Dikshitar Keertanaigal by Vidwan A Sundaram Iyer, Pub. 1989, Music Book Publishers, Mylapore, Chennai
- 1 2 Ragas in Carnatic music by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications
- ↑ Raganidhi by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras
- ↑ Shree Muthuswami Dikshitar Keerthanaigal, by A Sundaram Iyer, Music Book Publishers, Mylapore, Chennai