Aortic aneurysm
| Aortic aneurysm | |
|---|---|
|
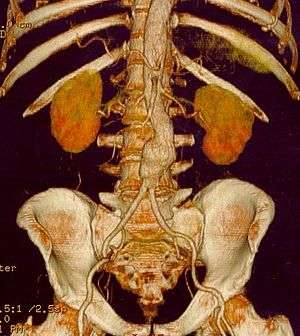
CT reconstruction image of an abdominal aortic aneurysm | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Vascular surgery |
| ICD-10 | I71 |
| ICD-9-CM | 441 |
| OMIM | 100070 |
| DiseasesDB | 792 |
| eMedicine | emerg/942 med/2783 emerg/27 radio/1 med/3443 |
| MeSH | D001014 |
An aortic aneurysm is an enlargement (dilation) of the aorta to greater than 1.5 times normal size.[1] They usually cause no symptoms except when ruptured.[2] Occasionally, there may be abdominal, back, or leg pain.[3]
They are most commonly located in the abdominal aorta, but can also be located in the thoracic aorta. Aortic aneurysms cause weakness in the wall of the aorta and increase the risk of aortic rupture. When rupture occurs, massive internal bleeding results and, unless treated immediately, shock and death can occur.
Screening with ultrasound is indicated in those at high risk. Prevention is by decreasing risk factors such as smoking. Treatment is either by open or endovascular surgery. Aortic aneurysms resulted in about 152,000 deaths in 2013, up from 100,000 in 1990.[4]
Classification
Aortic aneurysms are classified by their location on the aorta.
- An aortic root aneurysm, or aneurysm of the sinus of Valsalva.
- Thoracic aortic aneurysms are found within the chest; these are further classified as ascending, aortic arch, or descending aneurysms.
- Abdominal aortic aneurysms, "AAA" or "Triple A," the most common form of aortic aneurysm, involve that segment of the aorta within the abdominal cavity. Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms involve both the thoracic and abdominal aorta.
Signs and symptoms

Most intact aortic aneurysms do not produce symptoms. As they enlarge, symptoms such as abdominal pain and back pain may develop. Compression of nerve roots may cause leg pain or numbness. Untreated, aneurysms tend to become progressively larger, although the rate of enlargement is unpredictable for any individual. Rarely, clotted blood which lines most aortic aneurysms can break off and result in an embolus.
Aneurysms can be found on physical examination. Medical imaging is necessary to confirm the diagnosis and to determine the anatomic extent of the aneurysm. In patients presenting with aneurysm of the arch of the aorta, a common sign is a hoarse voice from stretching of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve, a branch of the vagus nerve that winds around the aortic arch to supply the muscles of the larynx.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) are more common than their thoracic counterpart. One reason for this is that elastin, the principal load-bearing protein present in the wall of the aorta, is reduced in the abdominal aorta as compared to the thoracic aorta. Another is that the abdominal aorta does not possess vasa vasorum, the nutrient-supplying blood vessels within the wall of the aorta. Most AAA are true aneurysms that involve all three layers (tunica intima, tunica media and tunica adventitia). The prevalence of AAAs increases with age, with an average age of 65–70 at the time of diagnosis. AAAs have been attributed to atherosclerosis, though other factors are involved in their formation.
The risk of rupture of an AAA is related to its diameter; once the aneurysm reaches about 5 cm, the yearly risk of rupture may exceed the risks of surgical repair for an average-risk patient. Rupture risk is also related to shape; so-called "fusiform" (long) aneurysms are considered less rupture prone than "saccular" (shorter, bulbous) aneurysms, the latter having more wall tension in a particular location in the aneurysm wall.
Before rupture, an AAA may present as a large, pulsatile mass above the umbilicus. A bruit may be heard from the turbulent flow in the aneurysm. Unfortunately, however, rupture may be the first hint of AAA. Once an aneurysm has ruptured, it presents with classic symptoms of abdominal pain which is severe, constant, and radiating to the back.
The diagnosis of an abdominal aortic aneurysm can be confirmed at the bedside by the use of ultrasound. Rupture may be indicated by the presence of free fluid in the abdomen. A contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scan is the best test to diagnose an AAA and guide treatment options.
Only 10–25% of patients survive rupture due to large pre- and post-operative mortality. Annual mortality from ruptured aneurysms in the United States is about 15,000. Most are due to abdominal aneurysms, with thoracic and thoracoabdominal aneurysms making up 1% to 4% of the total.
Aortic rupture
An aortic aneurysm can rupture from wall weakness. Aortic rupture is a surgical emergency, and has a high mortality even with prompt treatment. Weekend admission for ruptured aortic aneurysm is associated with an increased mortality compared with admission on a weekday, and this is likely due to several factors including a delay in prompt surgical intervention.[5]
Risk factors
- Coronary artery disease
- Hypertension
- Loeys-Dietz Syndrome
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Hyperhomocysteinemia
- Elevated C-reactive protein
- Tobacco use
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Marfan syndrome
- Ehlers-Danlos type IV
- Bicuspid Aortic Valve
- Syphilis
- IgG4-related disease
Pathophysiology

An aortic aneurysm can occur as a result of trauma, infection, or, most commonly, from an intrinsic abnormality in the elastin and collagen components of the aortic wall. While definite genetic abnormalities were identified in true genetic syndromes (Marfan, Elher-Danlos and others) associated with aortic aneurysms, both thoracic and abdominal aortic aneurysms demonstrate a strong genetic component in their aetiology.[6]
Prevention
The risk of aneurysm enlargement may be diminished with attention to the patient's blood pressure, smoking and cholesterol levels. There have been proposals to introduce ultrasound scans as a screening tool for those most at risk: men over the age of 65.[7][8] The tetracycline antibiotic doxycycline is currently being investigated for use as a potential drug in the prevention of aortic aneurysm due to its metalloproteinase inhibitor and collagen stabilizing properties. In contrast, fluoroquinolones antibiotics are being investigated as a potential contributor to aortic aneurysms, given their tendency to break down collagen fibrils.[9]
Anacetrapib is a cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitor that raises high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and reduces low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. Anacetrapib reduces progression of atherosclerosis, mainly by reducing non-HDL-cholesterol, improves lesion stability and adds to the beneficial effects of atorvastatin[10] Elevating the amount of HDL cholesterol in the abdominal area of the aortic artery in mice both reduced the size of aneurysms that had already grown and prevented abdominal aortic aneurysms from forming at all. In short, raising HDL cholesterol is beneficial because it induces programmed cell death. The walls of a failing aorta are replaced and strengthened. New lesions should not form at all when using this drug.[11]
Screening
Screening for an aortic aneurysm so that it may be detected and treated prior to rupture is the best way to reduce the overall mortality of the disease. The most cost-efficient screening test is an abdominal aortic ultrasound study. Noting the results of several large, population-based screening trials, the US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) now provides payment for one ultrasound study in male or female smokers aged 65 years or older ("SAAAVE Act").
Management
Surgery (open or endovascular) is the definite treatment of an aortic aneurysm. Medical therapy is typically reserved for smaller aneurysms or for elderly, frail patients where the risks of surgical repair exceed the risks of non-operative therapy (observation alone).
Medical therapy
Medical therapy of aortic aneurysms involves strict blood pressure control. This does not treat the aortic aneurysm per se, but control of hypertension within tight blood pressure parameters may decrease the rate of expansion of the aneurysm.
The medical management of patients with aortic aneurysms, reserved for smaller aneurysms or frail patients, involves cessation of smoking, blood pressure control, use of statins and occasionally beta blockers. Ultrasound studies are obtained on a regular basis (i.e. every six or 12 months) to follow the size of the aneurysm.
Surgery
Decisions about repairing an aortic aneurysm are based on the balance between the risk of aneurysm rupture without treatment versus the risks of the treatment itself. For example, a small aneurysm in an elderly patient with severe cardiovascular disease would not be repaired. The chance of the small aneurysm rupturing is overshadowed by the risk of cardiac complications from the procedure to repair the aneurysm.
The risk of the repair procedure is two-fold. First, there is consideration of the risk of problems occurring during and immediately after the procedure itself ("peri-procedural" complications). Second, the effectiveness of the procedure must be taken into account, namely whether the procedure effectively protects the patient from aneurysm rupture over the long-term, and whether the procedure is durable so that secondary procedures, with their attendant risks, are not necessary over the life of the patient. These issues attain importance and should be considered when making a choice between different treatment options. A less invasive procedure (such as endovascular aneurysm repair) may be associated with fewer short-term risks to the patient (fewer peri-procedural complications) but secondary procedures may be necessary over long-term follow-up.
The definitive treatment for an aortic aneurysm may be surgical or endovascular repair. The determination of surgical intervention is complex and determined on a per-case basis. Risk of aneurysm rupture is weighed against procedural risk. The diameter of the aneurysm, its rate of growth, the presence or absence of Marfan Syndrome, Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome or similar connective tissue disorders, and other co-morbidities are all important factors in the overall treatment.
A rapidly expanding aneurysm should under normal circumstances be operated on as soon as feasible, as it has a greater chance of rupture. Slowly expanding aortic aneurysms may be followed by routine diagnostic testing (i.e.: CT scan or ultrasound imaging).
For abdominal aneurysms, the current treatment guidelines for abdominal aortic aneurysms suggest elective surgical repair when the diameter of the aneurysm is greater than 5 cm (2 in). However, recent data on patients aged 60–76 suggest medical management for abdominal aneurysms with a diameter of less than 5.5 cm (2 in).[12]
Open surgery
Open surgery typically involves exposure of the dilated portion of the aorta and insertion of a synthetic (Dacron or Gore-Tex) graft (tube). Once the graft is sewn into the proximal (toward the patient's head) and distal (toward the patient's foot) portions of the aorta, the aneurysmal sac is closed around the graft. Alternatively, the anastomosis can be carried out with expandable devices, a simpler and quicker procedure [13][14]
The aorta and its branching arteries are cross-clamped during open surgery. This can lead to inadequate blood supply to the spinal cord, resulting in paraplegia, when repairing thoracic aneurysms. Cerebrospinal fluid drainage, when performed in experienced centers, reduces the risk of ischemic spinal cord injury by increasing the perfusion pressure to the spinal cord.[15][16]
Endovascular
Endovascular treatment of aortic aneurysms is a minimally invasive alternative to open surgery repair. It involves placement of an endo-vascular stent through small incisions at the top of each leg into the aorta.
As compared to open surgery, EVAR has a lower risk of death in the short term and a shorter hospital stay but may not always be an option.[2][17][18] There does not appear to be a difference in longer term outcomes between the two.[19] After EVAR, repeat procedures are more likely to be needed.[20]
Better results are only in uncomplicated, elective descending thoracic and infrarenal aorta. Moreover, recent USA data from 2006–2007 of isolated descending thoracic aorta aneurysms found 23% of ideal candidate (uncomplicated, elective descending aortic aneurysms) underwent to TEVAR, the remaining 77% underwent open surgical repair.[21]
Epidemiology
Aortic aneurysms resulted in about 152,000 deaths in 2013 up from 100,000 in 1990.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Johnston KW, Rutherford RB, Tilson MD, Shah DM, Hollier L, Stanley JC (March 1991). "Suggested standards for reporting on arterial aneurysms. Subcommittee on Reporting Standards for Arterial Aneurysms, Ad Hoc Committee on Reporting Standards, Society for Vascular Surgery and North American Chapter, International Society for Cardiovascular Surgery". Journal of Vascular Surgery. 13 (3): 452–8. doi:10.1067/mva.1991.26737. PMID 1999868.
- 1 2 Kent KC (27 November 2014). "Clinical practice. Abdominal aortic aneurysms.". The New England Journal of Medicine. 371 (22): 2101–8. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1401430. PMID 25427112.
- ↑ Upchurch GR, Schaub TA (2006). "Abdominal aortic aneurysm". Am Fam Physician. 73 (7): 1198–204. PMID 16623206.
- 1 2 GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators (17 December 2014). "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.". Lancet. 385: 117–71. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. PMC 4340604
 . PMID 25530442.
. PMID 25530442. - ↑ Groves EM, Khoshchehreh M, Le C, Malik S (Aug 2014). "Effects of weekend admission on the outcomes and management of ruptured aortic aneurysms". J Vasc Surg. 60 (2): 318–24. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2014.02.052.
- ↑ Saratzis A, Bown MJ (Jun 2014). "The genetic basis for aortic aneurysmal disease". Heart. 100 (12): 916–22. doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2013-305130.
- ↑ Routine screening in the management of AAA, UK Department of Health study Report
- ↑ "Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm". Bandolier. 27 (3). May 1996.
- ↑ Fluoroquinolones and Aortic Injury
- ↑ http://www.ahjonline.com/article/S0002-8703%2808%2900828-4/abstract?cc=y=
- ↑ http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2013/03/130306084157.htm
- ↑ "Mortality results for randomised controlled trial of early elective surgery or ultrasonographic surveillance for small abdominal aortic aneurysms. The UK Small Aneurysm Trial Participants". Lancet. 352 (9141): 1649–55. November 1998. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(98)10137-X. PMID 9853436.
- ↑ Aluffi A, Berti A, Buniva P, Rescigno G, Nazari S (2002). "Improved Device for Sutureless Aortic Anastomosis: Applied in a Case of Cancer". Tex Heart Inst J. 29 (1): 56–9. PMC 101273
 . PMID 11995854.
. PMID 11995854. - ↑ Nazari S, Salvi S, Visconti E, et al. (June 1999). "Descending aorta substitution with expandable ends prosthesis. Case report". J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 40 (3): 417–20. PMID 10412932.
- ↑ Cinà, C.; Abouzahr, L.; Arena, G.; Laganà, A.; Devereaux, P.; Farrokhyar, F. (2004). "Cerebrospinal fluid drainage to prevent paraplegia during thoracic and thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Journal of vascular surgery : official publication, the Society for Vascular Surgery [and] International Society for Cardiovascular Surgery, North American Chapter. 40 (1): 36–44. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2004.03.017. PMID 15218460.
- ↑ Khan, S. N.; Stansby, G. (2004). "Cerebrospinal fluid drainage for thoracic and thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm surgery". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD003635. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003635.pub2. PMID 14974026.
- ↑ Thomas DM, Hulten EA, Ellis ST, Anderson DM, Anderson N, McRae F, Malik JA, Villines TC, Slim AM (2014). "Open versus Endovascular Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in the Elective and Emergent Setting in a Pooled Population of 37,781 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.". ISRN cardiology. 2014: 149243. doi:10.1155/2014/149243. PMID 25006502.
- ↑ Biancari F, Catania A, D'Andrea V (November 2011). "Elective endovascular vs. open repair for abdominal aortic aneurysm in patients aged 80 years and older: systematic review and meta-analysis.". European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery. 42 (5): 571–6. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2011.07.011. PMID 21820922.
- ↑ Paravastu SC, Jayarajasingam R, Cottam R, Palfreyman SJ, Michaels JA, Thomas SM (23 January 2014). "Endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm.". The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 1: CD004178. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004178.pub2. PMID 24453068.
- ↑ Ilyas S, Shaida N, Thakor AS, Winterbottom A, Cousins C (February 2015). "Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) follow-up imaging: the assessment and treatment of common postoperative complications.". Clinical radiology. 70 (2): 183–196. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2014.09.010. PMID 25443774.
- ↑ Gopaldas RR, Huh J, Dao TK, et al. (November 2010). "Superior nationwide outcomes of endovascular versus open repair for isolated descending thoracic aortic aneurysm in 11,669 patients". J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 140 (5): 1001–10. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2010.08.007. PMID 20951252.
Bibliography
- Saratzis N, Melas N, Lazaridis J, et al. (June 2005). "Endovascular AAA repair with the aortomonoiliac EndoFit stent-graft: two years' experience". J Endovasc Ther. 12 (3): 280–7. doi:10.1583/04-1474.1. PMID 15943502.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Aortic aneurysms. |
- Vascular Medicine — Information for experts and laypersons regarding vascular medicine and related diseases.
- Aortic Aneurysm CT scans MedPix Medical Images