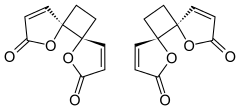
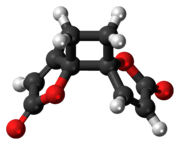
Anemonin
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
trans-4,7-Dioxadispiro[4.0.46.25]dodeca-1,9-diene-3,8-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
| 508-44-1 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 10064 |
| PubChem | 10496 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H8O4 | |
| Molar mass | 192.17 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless, odourless solid |
| Density | 1.45g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 158 °C (316 °F; 431 K) |
| Boiling point | 535.7 °C (996.3 °F; 808.9 K) @ 760mmHg |
| low | |
| Solubility in chloroform | soluble |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 300.7 °C (573.3 °F; 573.8 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
150 mg·kg−1 (mouse, i. p.) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Anemonin is a compound found in plants of the buttercup family (Ranunculaceae). It is the dimerization product of the toxin protoanemonin[1] and is easily hydrolysed to a dicarboxylic acid.[2]
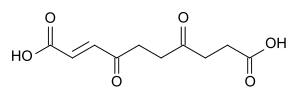
The hydrolysation product of anemonin
The substance is named for the plant genus Anemone, where it was first identified.[3] Antispasmodic and analgetic properties have been described.[4]
References
- ↑ List, PH; Hörhammer, L, eds. (1979). Hagers Handbuch der pharmazeutischen Praxis (in German) (4 ed.). Springer Verlag. ISBN 3-540-07738-3.
- ↑ "Aktuelles aus der Natur" (PDF) (in German). TU Graz. 2 April 2009. p. 4. Retrieved 27 November 2010.
- ↑ Chemie der organischen Verbindungen, Carl Löwig (German)
- ↑ Anemonin, Wissenschaft online (German)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/19/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.