Abbotsford House
| Abbotsford House | |
|---|---|
|
Abbotsford in 1880 | |
 Location in the Scottish Borders | |
| Alternative names | Carley Hole |
| General information | |
| Type | Baronial Mansion |
| Architectural style | Gothic |
| Location | Scottish Borders |
| Town or city | Galashiels |
| Country | Scotland |
| Coordinates | 55°35′59″N 2°46′55″W / 55.59972°N 2.78194°WCoordinates: 55°35′59″N 2°46′55″W / 55.59972°N 2.78194°W |
| Renovated | 1817-1825 |
| Owner | Scott Family |
| Designations | Category A Listed Building |
Abbotsford is a historic country house in the Scottish Borders, near Melrose, on the south bank of the River Tweed. It was formerly the residence of historical novelist and poet, Sir Walter Scott.[1] It is a Category A Listed Building.[2]
Description

The nucleus of the estate was a small farm of 100 acres (0.40 km2), called Cartleyhole, nicknamed Clarty (i.e., muddy) Hole, and was bought by Scott on the lapse of his lease (1811) of the neighbouring house of Ashestiel.[1] He first built a small villa and named it Abbotsford, creating the name from a ford nearby where previously abbots of Melrose Abbey used to cross the river. Scott then built additions to the house and made it into a mansion, building into the walls many sculptured stones from ruined castles and abbeys of Scotland. In it he gathered a large library, a collection of ancient furniture, arms and armour, and other relics and curiosities, especially connected with Scottish history, notably the Celtic Torrs Pony-cap and Horns and the Woodwrae Stone, all now in the Museum of Scotland.
The last and principal acquisition was that of Toftfield (afterwards named Huntlyburn), purchased in 1817. The new house was then begun and completed in 1824.[1]
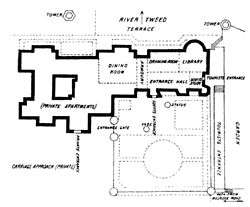
The general ground-plan is a parallelogram, with irregular outlines, one side overlooking the Tweed; and the style is mainly the Scottish Baronial. Into various parts of the fabric were built relics and curiosities from historical structures, such as the doorway of the old Tolbooth in Edinburgh.[1]
Scott had only enjoyed his residence one year when (1825) he met with that reverse of fortune which involved the estate in debt. In 1830, the library and museum were presented to him as a free gift by the creditors. The property was wholly disencumbered in 1847 by Robert Cadell, the publisher, who cancelled the bond upon it in exchange for the family's share in the copyright of Sir Walter's works. [1]
Scott's only son Walter did not live to enjoy the property, having died on his way from India in 1847. Among subsequent possessors were Scott's son-in-law, John Gibson Lockhart, J. R. Hope Scott, QC, and his daughter (Scott's great-granddaughter), the Hon. Mrs Maxwell Scott.[1]

The house was opened to the public in 1833, but continued to be occupied by Scott's descendants until 2004. The last of his direct descendants to hold the Lairdship of Abbotsford was his great-great-great-granddaughter Dame Jean Maxwell-Scott (8 June 1923 - 5 May 2004). She inherited it from her elder sister Patricia Maxwell-Scott in 1998. The sisters turned the house into one of Scotland's premier tourist attractions, after they had to rely on paying visitors to afford the upkeep of the house. It had electricity installed only in 1962. Dame Jean was at one time a lady-in-waiting to Princess Alice, Duchess of Gloucester, patron of the Dandie Dinmont Club, a breed of dog named after one of Sir Walter Scott's characters; and a horse trainer, one of whose horses, Sir Wattie, ridden by Ian Stark, won two silver medals at the 1988 Summer Olympics.[3]
Scottish Borders Council is considering an application by a property developer to build a housing estate on the opposite bank of the River Tweed from Abbotsford, to which Historic Scotland and the National Trust for Scotland object.[4][5]
Sir Walter Scott rescued the "jougs" from Threave Castle in Dumfries and Galloway and attached them to the castellated gateway he built at Abbotsford.[6]
Tweedbank railway station is located near to Abbotsford House.
Miscellaneous
Abbotsford gave its name to the Abbotsford Club, founded by William Barclay Turnbull in 1833 or 1834 in Scott's honour, and a successor to the Bannatyne and Maitland Clubs. It was a text publication society, which existed to print and publish historical works connected with Scott's writings. Its publications extended from 1835 to 1864.[1]
In 2012, a new Visitor Centre opened at Abbotsford which houses a small exhibition, gift shop and Ochiltree's Dining, a cafe/restaurant with views over the house and grounds.
In 2014 it won the European Union Prize for Cultural Heritage / Europa Nostra Award for its recent conservation project.[7][8]

See also
Notes
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chisholm 1911.
- ↑ Historic Scotland staff 2010.
- ↑ Sydney Morning Herald staff 2004, p. 32.
- ↑ "After 200 years Scott house leaves family". The Times. London. 19 May 2005. Retrieved 23 April 2010.
- ↑ Housing plan put on hold, Scotsman.com, 6 December 2005
- ↑ Napier 1897, p. 153.
- ↑ "Europa Nostra". Europa Nostra. Retrieved 2016-02-03.
- ↑ "European Commission - PRESS RELEASES - Press release - Winners of 2014 EU Prize for Cultural Heritage / Europa Nostra Awards announced". Europa.eu. Retrieved 2016-02-03.
References
- Historic Scotland staff (2010) [1971]. "Abbotsford Including House, Walled Gardens and Courtyards, Conservatory, Bothies, Game Larder, Ice H, Melrose". Historic Scotland. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
- Napier, George G. (1897), The Home and Haunts of Sir Walter Scott, Bart, Glasgow: James Maclehose, p. 153
- Sydney Morning Herald staff (13 July 2004), "Obituary of Dame Jean Maxwell-Scott", Sydney Morning Herald, p. 32
Attribution
-
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Abbotsford". Encyclopædia Britannica. 1 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Abbotsford". Encyclopædia Britannica. 1 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Abbotsford House. |
- Abbotsford - The Home of Sir Walter Scott - official site
- RCAHMS / CANMORE site record for Abbotsford House
- Edinburgh University Library
- Abbotsford (by W S Crockett - 1904 illustrated book pub. A & C Black)
- Abbotsford and Newstead Abbey by Washington Irving, from Project Gutenberg
- "Listed building details (number=15104)". Historic Scotland.
 Texts on Wikisource:
Texts on Wikisource:
- Washington Irving, "Abbotsford," in Abbotsford and Newstead Abbey
- "Abbotsford". The Nuttall Encyclopædia. 1907.
- "Abbotsford". The New Student's Reference Work. 1914.
- "Abbotsford". Collier's New Encyclopedia. 1921.
