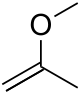
2-Methoxypropene
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Methoxy-1-propene | |||
| Other names
2-Methoxyprop-1-ene; Methyl isopropenyl ether; Isopropenyl methyl ether | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 116-11-0 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChemSpider | 7999 | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.751 | ||
| PubChem | 8300 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H8O | |||
| Molar mass | 72.11 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] | ||
| Density | 0.753 g/mL[2] | ||
| Boiling point | 34 to 36 °C (93 to 97 °F; 307 to 309 K)[2] | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
2-Methoxypropene is an ether with the chemical formula C4H8O. It is a reagent used in organic synthesis as a protecting group for alcohols,[1] and the converstion diols to the acetonide group.[3]
2-Methoxypropene can be prepared by the elimination of methanol from dimethoxypropane,[4] or by the addition of methanol to propyne or allene.[5]
References
- 1 2 Whitaker, K. Sinclair; Whitaker, D. Todd (2001). "2-Methoxypropene". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rm124. ISBN 0471936235.
- 1 2 2-Methoxypropene at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Theodora W. Greene; Peter G. M. Wuts. Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis (3rd ed.). pp. 207–215.
- ↑ Newman, Melvin S.; Vander Zwan, Michael C. (1973). "Improved synthesis of 2-methoxypropene". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 38 (16): 2910. doi:10.1021/jo00956a040.
- ↑ Agré, B. A.; Taber, A. M.; Beregovykh, V. V.; Klebanova, F. D.; Nekrasov, N. V.; Sobolev, O. B.; Kalechits, I. V. (1983). "Kinetics of the catalytic synthesis of 2-methoxypropene". Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal. 17 (3): 221. doi:10.1007/BF00765172.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/2/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.